
What are \[SN1\] and \[SN2\] reactions?
A) Addition Reaction
B) Substitution Reaction
C) Elimination Reaction
D) Photochemical Reaction
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: It is easy to get this answer solved by looking at the questions and the given options. As the name says SN answer lies within it. $1$ and $2$ is used to define the order of the reaction and also to give the stability order for a particular reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
We are going to study about \[SN1\] and \[SN2\] reactions.
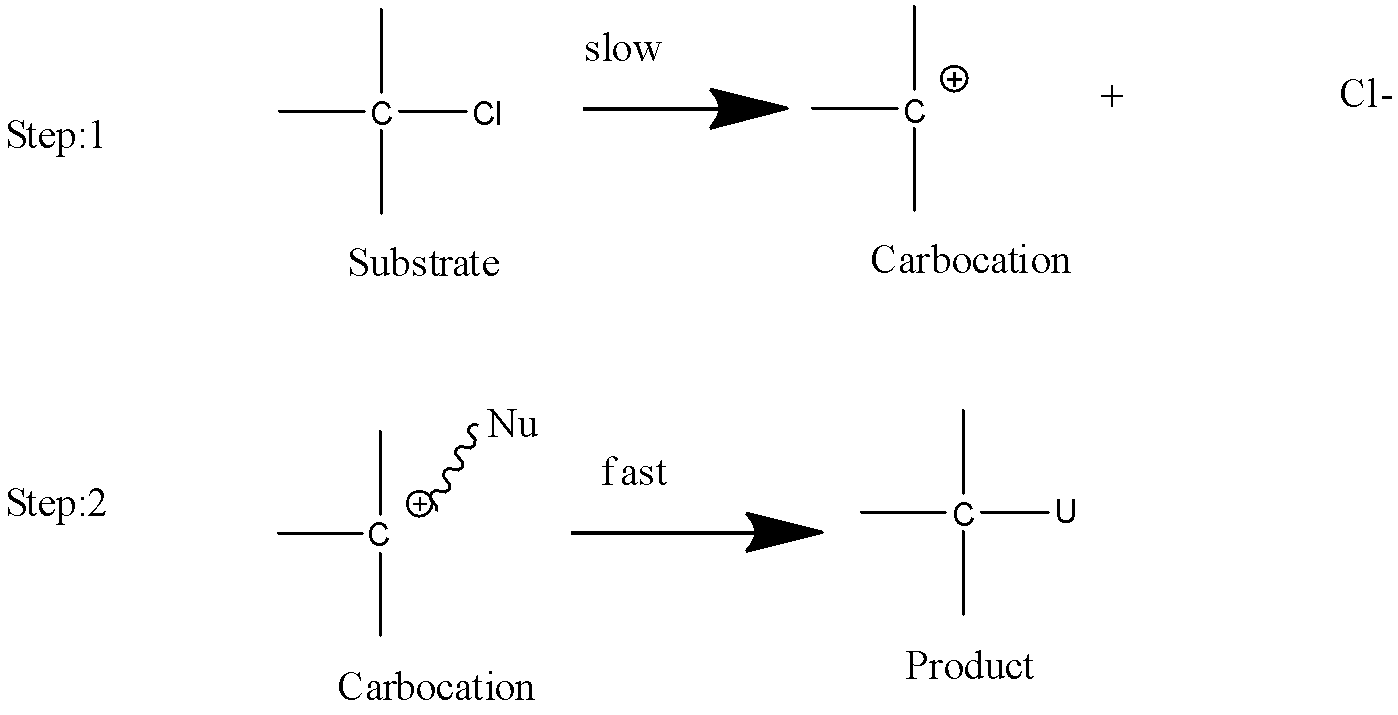
- \[SN1\] reaction:
- It is a substitution reaction as the name says SN it means nucleophilic substitution reaction and $1$ defines the rate determining step which is unimolecular in this type of reaction.
- The intermediate form in this type of reaction is carbocation due to which the stability order is \[3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ \].
- It is a first order reaction.
- \[SN2\] reaction:
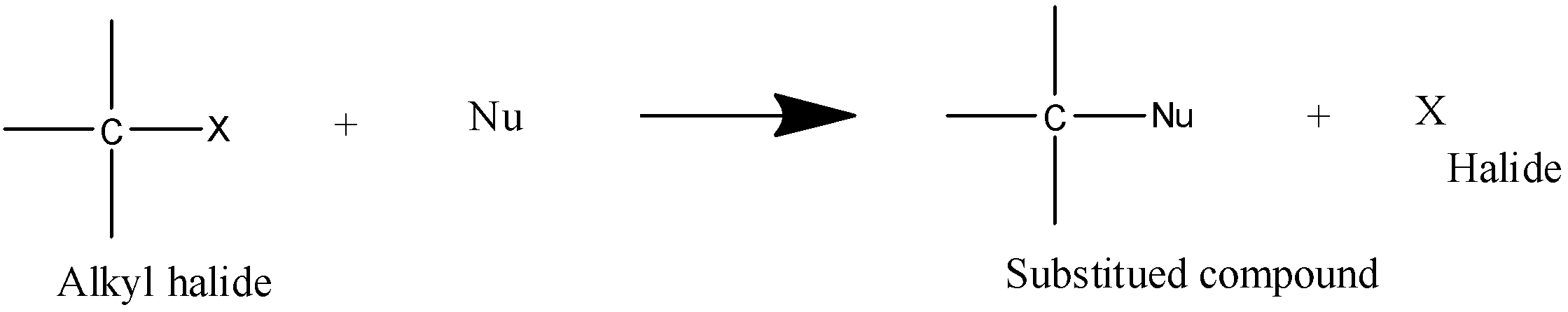
- It is a substitution reaction as the name says SN it means nucleophilic substitution reaction and $2$ defines the rate determining step which is bimolecular in this type of reaction.
- Transition state is formed in \[SN2\] reaction.
- Stability order is $1^\circ > 2^\circ > 3^\circ $.
- It is a second order reaction.
Option A) this is an incorrect option since addition reactions are the one which involves the addition of two reactants or species.
Option B) This is a correct option since \[SN1\] and \[SN2\] are substitution reactions as explained above.
Option C) this is an incorrect option since Elimination reactions are the one in which substituents are removed from the molecule, but in \[SN1\] and \[SN2\] belongs to substitution type.
Option D) this is an incorrect option as photochemical reactions involve light at different frequencies.
Hence, the correct answer is, ‘Option B’.
Note: \[SN1\] and \[SN2\] are nucleophilic substitution reactions involving intermediates and transition states in them. The stability of the reaction depends upon the respective intermediates and transition states which is further easy to define the order of the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
We are going to study about \[SN1\] and \[SN2\] reactions.
- \[SN1\] reaction:
- It is a substitution reaction as the name says SN it means nucleophilic substitution reaction and $1$ defines the rate determining step which is unimolecular in this type of reaction.
- The intermediate form in this type of reaction is carbocation due to which the stability order is \[3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ \].
- It is a first order reaction.

- \[SN2\] reaction:
- It is a substitution reaction as the name says SN it means nucleophilic substitution reaction and $2$ defines the rate determining step which is bimolecular in this type of reaction.
- Transition state is formed in \[SN2\] reaction.
- Stability order is $1^\circ > 2^\circ > 3^\circ $.
- It is a second order reaction.

Option A) this is an incorrect option since addition reactions are the one which involves the addition of two reactants or species.
Option B) This is a correct option since \[SN1\] and \[SN2\] are substitution reactions as explained above.
Option C) this is an incorrect option since Elimination reactions are the one in which substituents are removed from the molecule, but in \[SN1\] and \[SN2\] belongs to substitution type.
Option D) this is an incorrect option as photochemical reactions involve light at different frequencies.
Hence, the correct answer is, ‘Option B’.
Note: \[SN1\] and \[SN2\] are nucleophilic substitution reactions involving intermediates and transition states in them. The stability of the reaction depends upon the respective intermediates and transition states which is further easy to define the order of the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




