
What are sepals? What are their functions?
Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint: A typical flower has four main parts or whorls known as the calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium. Morphologically, both sepals and petals are modified leaves.
Complete answer: The outermost whorl of the flower has green, leafy structures known as sepals.
-Collectively the sepals are called the calyx, the outermost whorl of parts that form a flower.
-After flowering, most plants have no more use for the calyx which withers or becomes vestigial.
-Some plants retain a thorny calyx, either dried or live, as protection for the fruit or seeds.
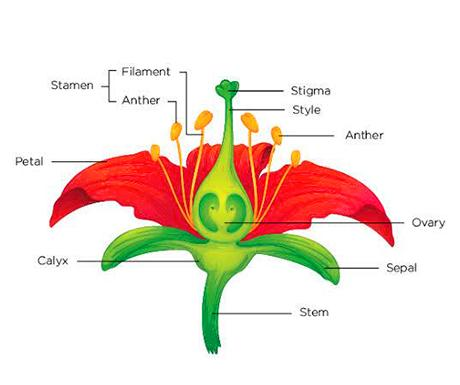
-The functions of sepals are:
1. Sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom.
2. The sepal is a defensive organ that encloses and protects the developing reproductive structures. At maturity, the sepal opens when the flower blooms.
Additional information:
a. In some species the calyx not only persists after flowering but instead of withering begins to grow until it forms a bladder-like enclosure around the fruit.
b. This is an effective protection against some kinds of birds and insects, for example in Hibiscus trionum and the cape gooseberry.
c. In other species, the calyx grows into an accessory fruit.
Note: The term sepalum was coined by Noël Martin Joseph de Necker in 1790, and derived from the Greek word which means a covering. The calyx (the sepals) and the corolla (the petals) are the outer sterile whorls of the flower, which together form what is known as the perianth.
Complete answer: The outermost whorl of the flower has green, leafy structures known as sepals.
-Collectively the sepals are called the calyx, the outermost whorl of parts that form a flower.
-After flowering, most plants have no more use for the calyx which withers or becomes vestigial.
-Some plants retain a thorny calyx, either dried or live, as protection for the fruit or seeds.

-The functions of sepals are:
1. Sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom.
2. The sepal is a defensive organ that encloses and protects the developing reproductive structures. At maturity, the sepal opens when the flower blooms.
Additional information:
a. In some species the calyx not only persists after flowering but instead of withering begins to grow until it forms a bladder-like enclosure around the fruit.
b. This is an effective protection against some kinds of birds and insects, for example in Hibiscus trionum and the cape gooseberry.
c. In other species, the calyx grows into an accessory fruit.
Note: The term sepalum was coined by Noël Martin Joseph de Necker in 1790, and derived from the Greek word which means a covering. The calyx (the sepals) and the corolla (the petals) are the outer sterile whorls of the flower, which together form what is known as the perianth.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




