
How are s orbitals different from p orbitals?
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint:To solve this question first we have to understand the term orbitals. Orbitals are 3 dimensional space around the nucleus where the probability of finding an electron is maximum.
Complete answer:
Difference between s and p orbitals is mentioned below-
The shape of s and p orbitals is shown below:
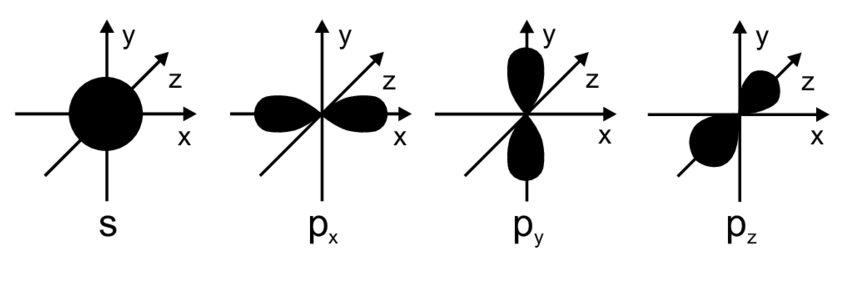
Note:
Do not get confused between the term orbit and orbitals. Both orbit and orbitals have different meanings as we know that orbitals are 3 dimensional space around the nucleus where the probability of finding an electron is maximum and orbits are the well-defined circular paths in which electrons revolve.
Complete answer:
Difference between s and p orbitals is mentioned below-
| S orbitals | P orbitals |
| The s orbitals are atomic orbitals and the shape of s orbital is spherical. | The p orbital is also an atomic orbital and the shape of p orbital is dumbbell shape. |
| S orbitals have the lowest energy levels. | The energy levels of p orbitals are higher as compared to that of p orbitals. |
| There are no angular nodes in s orbitals. | Angular nodes are present in the p orbitals. |
| The maximum number of electrons which can be present in the s orbital is 2. | The maximum number of electrons which can be present in the p orbital is 6. |
| There are no sub orbitals present in the s orbital. | P orbitals have 3 sub orbitals. |
| The value of angular momentum quantum number for s orbitals is 0. | The value of angular momentum quantum number for s orbitals is 1. |
| There are no lobed present in the s orbitals. | There are lobes present in the p orbital. |
The shape of s and p orbitals is shown below:

Note:
Do not get confused between the term orbit and orbitals. Both orbit and orbitals have different meanings as we know that orbitals are 3 dimensional space around the nucleus where the probability of finding an electron is maximum and orbits are the well-defined circular paths in which electrons revolve.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




