
What are petals? Why are they generally coloured?
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: A flower is a modified shoot to carry out the reproductive activities of a plant. A typical flower is composed of four whorls or appendages- Calyx(sepals), Corolla(petals), Androecium(stamens) and Gynoecium (pistil or carpels).
Complete answer:
In a plant, the shoot apical meristem is transformed into a floral meristem and the leaves are specialised into floral appendage leading to the emergence of a flower. A typical flower is composed of 4 whorls or appendages organised successively on the thalamus or receptacle. The swollen end of the pedicel (stalk of a flower) is called the thalamus.
-The outermost whorl is calyx composed of sepals, followed by corolla which is a collection of petals. They are also referred to as accessory floral appendages The innermost whorls or essential whorls are androecium or male reproductive organ and gynoecium or female reproductive organ.
- Sepals are green and their function is to protect the inner set of whorls when a flower is still a bud.
-Petals are the most striking and noticeable part of a flower. They are brightly coloured to draw pollinators toward itself. Thus, their function is to help in pollination while also protecting the inner set of essential whorls.
-Though pollination may be carried out by wind or water, insects such as bees are also important pollinators. Insect pollinated flowers are vividly coloured, scented and produce nectar. The bees in search of nectar travel from flower to flower, helping in the dispersal of pollens.
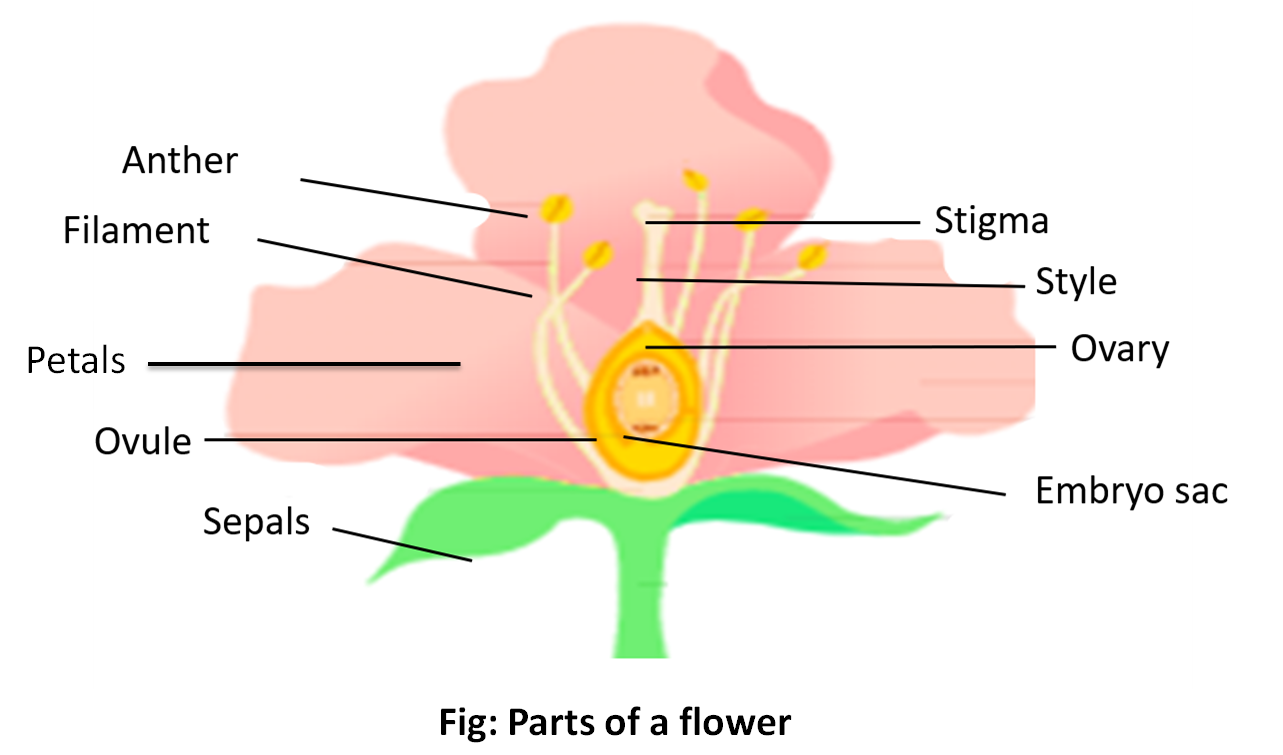
Note: - Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains -the reduced male gametophyte from stamens to the sticky stigma-the receptacle of the female reproductive organ ‘pistil’. The male gamete is then transported to the female gametophyte i.e ovary via a long, slender channel called style.
- The corolla may be polypetalous i.e they are free or gamopetalous i.e fused with each other. -Polypetalous condition is observed in Rose, mustard etc. the corolla is gamopetalous in Petunia and Larkspur. When the stamens are fused with petals, it is known as epipetalous. E.g. Solanum, Petunia.
Complete answer:
In a plant, the shoot apical meristem is transformed into a floral meristem and the leaves are specialised into floral appendage leading to the emergence of a flower. A typical flower is composed of 4 whorls or appendages organised successively on the thalamus or receptacle. The swollen end of the pedicel (stalk of a flower) is called the thalamus.
-The outermost whorl is calyx composed of sepals, followed by corolla which is a collection of petals. They are also referred to as accessory floral appendages The innermost whorls or essential whorls are androecium or male reproductive organ and gynoecium or female reproductive organ.
- Sepals are green and their function is to protect the inner set of whorls when a flower is still a bud.
-Petals are the most striking and noticeable part of a flower. They are brightly coloured to draw pollinators toward itself. Thus, their function is to help in pollination while also protecting the inner set of essential whorls.
-Though pollination may be carried out by wind or water, insects such as bees are also important pollinators. Insect pollinated flowers are vividly coloured, scented and produce nectar. The bees in search of nectar travel from flower to flower, helping in the dispersal of pollens.

Note: - Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains -the reduced male gametophyte from stamens to the sticky stigma-the receptacle of the female reproductive organ ‘pistil’. The male gamete is then transported to the female gametophyte i.e ovary via a long, slender channel called style.
- The corolla may be polypetalous i.e they are free or gamopetalous i.e fused with each other. -Polypetalous condition is observed in Rose, mustard etc. the corolla is gamopetalous in Petunia and Larkspur. When the stamens are fused with petals, it is known as epipetalous. E.g. Solanum, Petunia.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




