
Where are neurons found in the body and what is their function ?
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: Neurons are certain cells in our body that are specialized to execute special functions which help various systems of the body to coordinate easily with each other. They are found primarily in the system that performs the functions of control and coordination.
Complete answer:
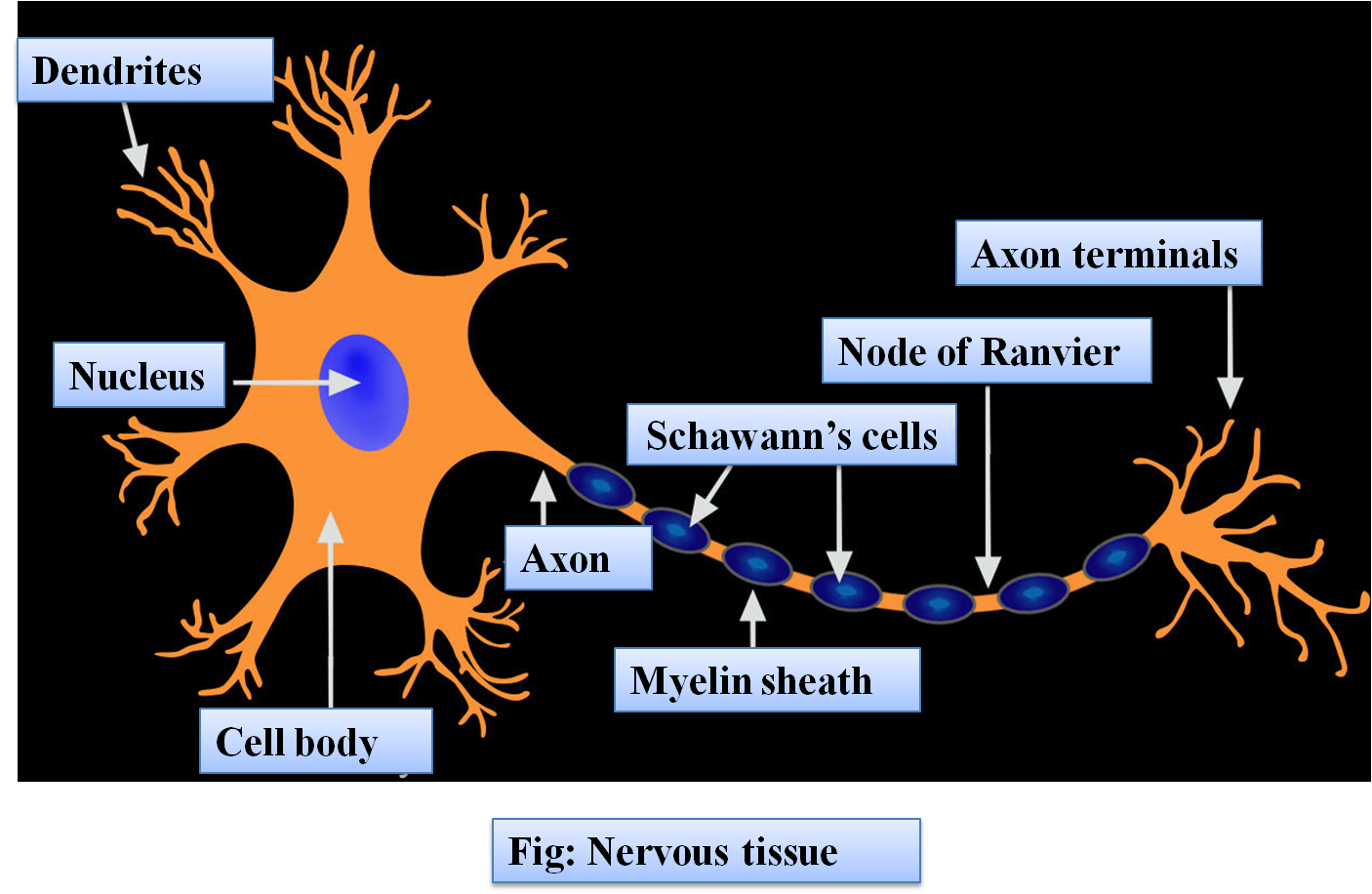
Neurons are electrically or chemically excitable cells that communicate with each other through special junctions called synapses. They form the nervous system of the body. They are present in the ganglia and nerve fibers; which comprise the central and peripheral nervous system. These cells are found in animals except sponges whereas plants and fungi lack these cells.
Neurons form the nerves or the nerve fibers, that are a part of the central and peripheral nervous system that spread out across every part of the body and help in establishing internal communication.
Neurons send signals using specific action potentials. An action potential is a shift in a neuron’s electric potential because of the flow of ions in and out of its neural membrane. Action potentials trigger both the chemical and electrical synapses causing signal and information transmission.
This transmission can of two types, a normal conduction and saltatory conduction in nerve cells with Schwann cells which results in faster transmission of information.
Note:
- Functionally neurons can be classified as motor neurons or sensory neurons. - Motor neurons get information from the other neurons and convey the messages or commands to the muscles, organs, glands, etc. - Sensory neurons get information from various organs, muscles, and glands and convey them to the brain or the spinal cord where the information can be processed and commands can be relayed to the motor neurons to carry out the task.
Complete answer:
Neurons are electrically or chemically excitable cells that communicate with each other through special junctions called synapses. They form the nervous system of the body. They are present in the ganglia and nerve fibers; which comprise the central and peripheral nervous system. These cells are found in animals except sponges whereas plants and fungi lack these cells.
Neurons form the nerves or the nerve fibers, that are a part of the central and peripheral nervous system that spread out across every part of the body and help in establishing internal communication.
Neurons send signals using specific action potentials. An action potential is a shift in a neuron’s electric potential because of the flow of ions in and out of its neural membrane. Action potentials trigger both the chemical and electrical synapses causing signal and information transmission.
This transmission can of two types, a normal conduction and saltatory conduction in nerve cells with Schwann cells which results in faster transmission of information.

Note:
- Functionally neurons can be classified as motor neurons or sensory neurons. - Motor neurons get information from the other neurons and convey the messages or commands to the muscles, organs, glands, etc. - Sensory neurons get information from various organs, muscles, and glands and convey them to the brain or the spinal cord where the information can be processed and commands can be relayed to the motor neurons to carry out the task.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




