
What are microstates in chemistry?
Answer
509.1k+ views
Hint: The microstate is the arrangement or specific way of energy of each molecule in the system at one kind of instance. It is something like a theoretical instantaneous photo of the location of a molecule and atom in the macro-state.
Complete answer:
Let us understand the concept in detail-
Microstates, basically, are the microscopic ways to observe certain processes taking place in the system. These microstates describe the location and arrangement of micro molecules within the macro-state. The visual location is captured and thus is described as a microstate. An example is shown below-
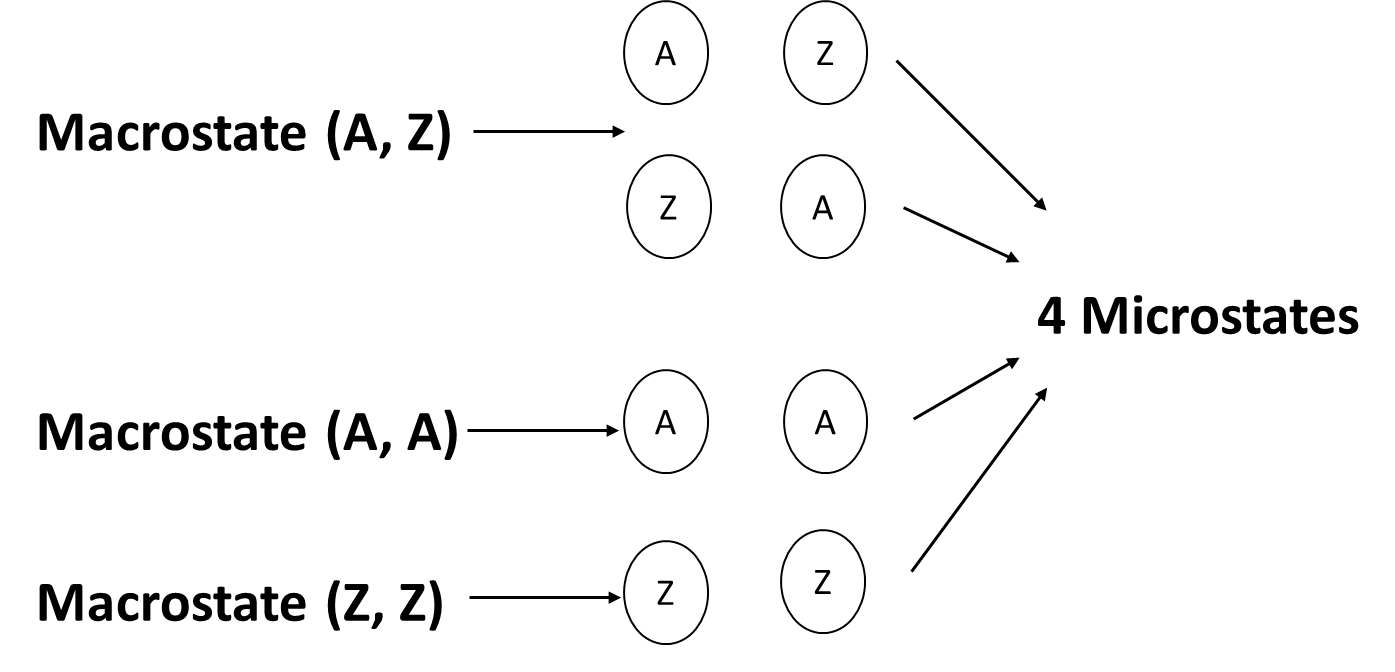
Analogous to this, there is a macro-state which is the matter which is large enough for us to measure i.e., which is present in bulk. For example, volume, pressure or temperature.
Note:
Factually, macro means something that is large whereas micro means something which is comparatively smaller. In chemical thermodynamics, these terms do not have the relatively stated English meaning. Instead, they are the two different ways of looking towards the working system.
The microstate is one of the arrangements of molecules for a particular macro-state.
Complete answer:
Let us understand the concept in detail-
Microstates, basically, are the microscopic ways to observe certain processes taking place in the system. These microstates describe the location and arrangement of micro molecules within the macro-state. The visual location is captured and thus is described as a microstate. An example is shown below-

Analogous to this, there is a macro-state which is the matter which is large enough for us to measure i.e., which is present in bulk. For example, volume, pressure or temperature.
Note:
Factually, macro means something that is large whereas micro means something which is comparatively smaller. In chemical thermodynamics, these terms do not have the relatively stated English meaning. Instead, they are the two different ways of looking towards the working system.
The microstate is one of the arrangements of molecules for a particular macro-state.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




