
What are electrophiles and nucleophiles? Explain with examples.
Answer
528.6k+ views
Hint: Electrophile are referred to as species which are electron-loving species and such species are positively charged species, and on the other hand, Nucleophile is referred to as species which are nucleus-loving and such species are negatively charged species.
Complete answer:
Electrophiles as we know are electron-loving. This can be referred to in other words electron-deficient species and thus can accept an electron pair from electron-rich species. Some of the examples are carbocations and carbonyl compounds. A nucleophile is nucleus-loving or in other words an electron-rich species and has a tendency to donate electron pairs to electron-deficient species. Some of the examples are carbanions, water, ammonia, cyanide ion, etc.
To understand these terms let’s explain with the help of a reaction:
When an aldehyde is allowed to react with alcohol it is a type of nucleophilic-electrophilic reaction or as an acid-base reaction as the aldehyde is an electrophile with a positive charge on carbonyl carbon and the alcohol is a nucleophile with a negative charge on the oxygen atom, the reaction is as follows:
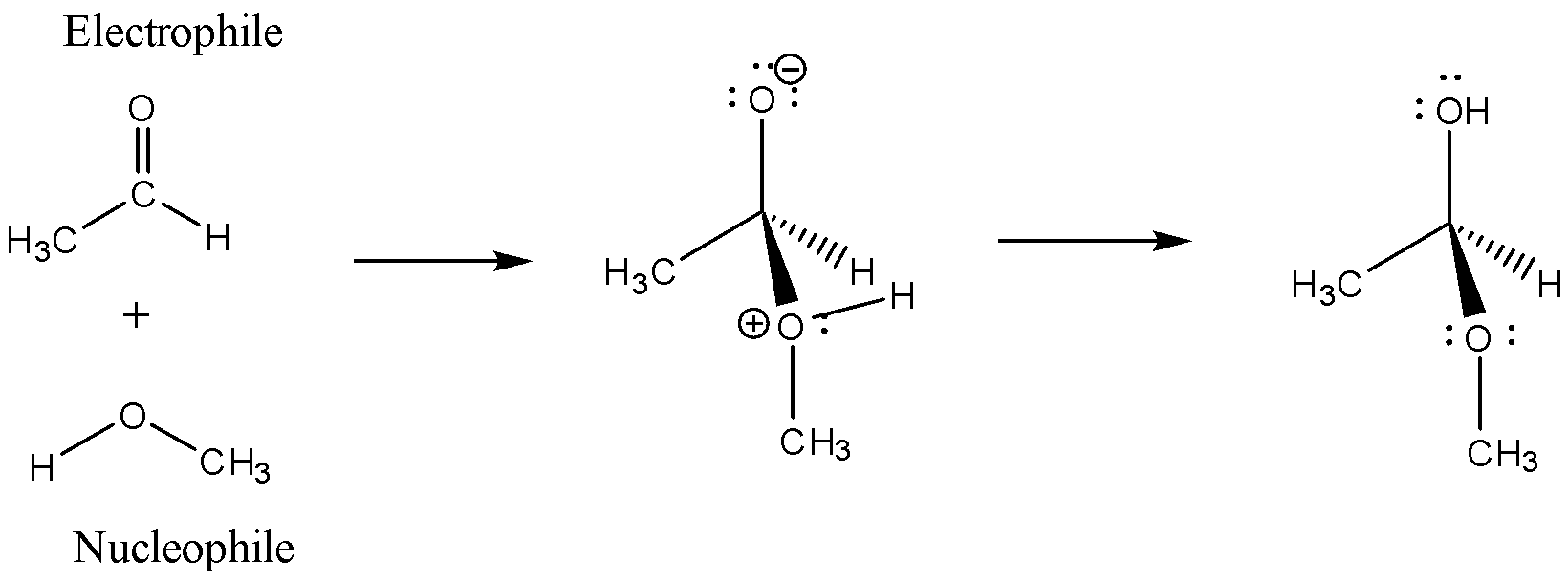
Here, Methanol and Ethanal are taken as substrates and methanol here is acting as a nucleophile as there is a negative charge formation on the oxygen atom, whereas ethanal is acting as an electrophile as there is a formation of partial positive charge on carbonyl carbon.
Note:
The molecules which are referred to as nucleophiles can be also referred to as bases as the difference is just on the attacking sites the attack of the nucleophile at the carbon atom and the base attack at the hydrogen atom.
Complete answer:
Electrophiles as we know are electron-loving. This can be referred to in other words electron-deficient species and thus can accept an electron pair from electron-rich species. Some of the examples are carbocations and carbonyl compounds. A nucleophile is nucleus-loving or in other words an electron-rich species and has a tendency to donate electron pairs to electron-deficient species. Some of the examples are carbanions, water, ammonia, cyanide ion, etc.
To understand these terms let’s explain with the help of a reaction:
When an aldehyde is allowed to react with alcohol it is a type of nucleophilic-electrophilic reaction or as an acid-base reaction as the aldehyde is an electrophile with a positive charge on carbonyl carbon and the alcohol is a nucleophile with a negative charge on the oxygen atom, the reaction is as follows:

Here, Methanol and Ethanal are taken as substrates and methanol here is acting as a nucleophile as there is a negative charge formation on the oxygen atom, whereas ethanal is acting as an electrophile as there is a formation of partial positive charge on carbonyl carbon.
Note:
The molecules which are referred to as nucleophiles can be also referred to as bases as the difference is just on the attacking sites the attack of the nucleophile at the carbon atom and the base attack at the hydrogen atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




