
What are electron deficient species compounds? Are $BC{l_3}$ and $SiC{l_4}$ electron deficient species? Explain
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint:Compounds having less number of electrons than the required amount to attain maximum stability is known as electron deficient species. Generally these compounds don’t have enough electrons to form normal covalent bonds. For making their stability generally atom have to need $8\,electrons\,$ in their outermost shell.
Complete step-by-step answer:We know that in the electron deficient compounds the central atoms do not have enough number of electron in its valence shell also it has sufficient number of electrons but they can expand its valency beyond $4$ due to presence of $d - $ orbital. These electron deficient compounds generally form bridging with other molecule or they possess back bonding.
In the given question we have to determine whether $BC{l_3}$ and $SiC{l_4}$ are electron deficient species or not. Let us discuss them one by one. In $BC{l_3}$ the central atom is Boron $(B)$ it has $6$ valence electron in its valence shell. So, it required $2$ electron to complete their octet or attain maximum stability.

In the case of $SiC{l_4}$ the central atom is silicon $(Si)$ although it has eight electrons in its valence shell but it can expand its valency beyond $4$ due to presence of vacant $d - $ orbital. Therefore it is also an electron deficient compound.
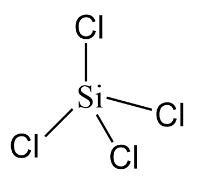
Hence, $BC{l_3}$ and $SiC{l_4}$ are electron deficient compounds.
On the basis of the number of electrons present in central atoms the compounds can be divided into three categories that are electron deficient, electron precise and electron rich compounds. Electron deficient compounds: In this type of compounds the central atoms do not have sufficient number of valence electrons to form covalent bonds. Electron precise compounds: In this type of compounds the central atoms have sufficient number of valence electrons to form covalent bonds. Electron rich compounds: In this type of compounds the central atoms have an excess number of valence electrons to form covalent bonds.
Note:It is to be noted that in an electron deficient compound, the octet of the electron is not complete, that is the central atom has an incomplete octet. Therefore, it requires electrons to complete their octet.
Complete step-by-step answer:We know that in the electron deficient compounds the central atoms do not have enough number of electron in its valence shell also it has sufficient number of electrons but they can expand its valency beyond $4$ due to presence of $d - $ orbital. These electron deficient compounds generally form bridging with other molecule or they possess back bonding.
In the given question we have to determine whether $BC{l_3}$ and $SiC{l_4}$ are electron deficient species or not. Let us discuss them one by one. In $BC{l_3}$ the central atom is Boron $(B)$ it has $6$ valence electron in its valence shell. So, it required $2$ electron to complete their octet or attain maximum stability.

In the case of $SiC{l_4}$ the central atom is silicon $(Si)$ although it has eight electrons in its valence shell but it can expand its valency beyond $4$ due to presence of vacant $d - $ orbital. Therefore it is also an electron deficient compound.

Hence, $BC{l_3}$ and $SiC{l_4}$ are electron deficient compounds.
On the basis of the number of electrons present in central atoms the compounds can be divided into three categories that are electron deficient, electron precise and electron rich compounds. Electron deficient compounds: In this type of compounds the central atoms do not have sufficient number of valence electrons to form covalent bonds. Electron precise compounds: In this type of compounds the central atoms have sufficient number of valence electrons to form covalent bonds. Electron rich compounds: In this type of compounds the central atoms have an excess number of valence electrons to form covalent bonds.
Note:It is to be noted that in an electron deficient compound, the octet of the electron is not complete, that is the central atom has an incomplete octet. Therefore, it requires electrons to complete their octet.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




