
What are Conjugative and non-Conjugative plasmids?
Answer
491.1k+ views
Hint: Plasmids are small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecules, which are distinct from a cell's chromosomal DNA. Usually, plasmids exist in bacterial cells and some eukaryotic cells. Plasmids have a broad range of lengths typically ranging from one thousand base pairs of DNA to hundreds of thousands of base pairs. When a bacterium divides, all plasmids inside the cell are copied, leading to each daughter cell obtaining a copy of each plasmid.
Complete answer
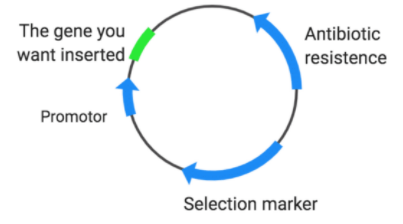
Figure: Anatomy of a Plasmid
Based on the ability of plasmids to be transferred to other bacteria, plasmids are classified into two types:
1. Conjugative plasmids
2. Non-conjugative plasmids
1. Conjugative plasmids are the plasmids that contain tra genes, which achieve the complex phenomenon of conjugation. Conjugation is the process of transfer of a plasmid from one bacterium to another bacterium. They are capable of performing horizontal transmission. They are found abundant in often naturally isolated bacteria. They can cause fitness issues to the cell, which is overshadowed by the supply of some beneficial genes to the bacterial host.
2. Non-conjugative plasmids are the plasmids, which are incapable of initiation of conjugation. Therefore, they can be transferred to another bacterium with the help of conjugative plasmids. Example of a non-conjugative plasmid is ColE\[1\]. It has relatively lower molecular mass. Further, it does not encode the essential gene needed for it to be transferred from one cell into another.
Note:
Plasmids offer bacteria with genetic advantages like antibiotic resistance. Plasmids are used as a tool in cloning, transferring and manipulating genes. Plasmids, which are utilized for above mentioned purposes, are said to be vectors. Researchers are able to insert genes or DNA fragments into a plasmid, creating a recombinant plasmid. Through the process of transformation, the plasmid is able to be introduced into a bacterium.
Complete answer

Figure: Anatomy of a Plasmid
Based on the ability of plasmids to be transferred to other bacteria, plasmids are classified into two types:
1. Conjugative plasmids
2. Non-conjugative plasmids
1. Conjugative plasmids are the plasmids that contain tra genes, which achieve the complex phenomenon of conjugation. Conjugation is the process of transfer of a plasmid from one bacterium to another bacterium. They are capable of performing horizontal transmission. They are found abundant in often naturally isolated bacteria. They can cause fitness issues to the cell, which is overshadowed by the supply of some beneficial genes to the bacterial host.
2. Non-conjugative plasmids are the plasmids, which are incapable of initiation of conjugation. Therefore, they can be transferred to another bacterium with the help of conjugative plasmids. Example of a non-conjugative plasmid is ColE\[1\]. It has relatively lower molecular mass. Further, it does not encode the essential gene needed for it to be transferred from one cell into another.
Note:
Plasmids offer bacteria with genetic advantages like antibiotic resistance. Plasmids are used as a tool in cloning, transferring and manipulating genes. Plasmids, which are utilized for above mentioned purposes, are said to be vectors. Researchers are able to insert genes or DNA fragments into a plasmid, creating a recombinant plasmid. Through the process of transformation, the plasmid is able to be introduced into a bacterium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




