
Why are amines soluble in nature?
Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: Derivatives of ammonia which are formed by the removal of hydrogen atoms of ammonia are known as amines $ \left( {RN{H_2}} \right) $ . Presence of nitrogen atom in the molecule imparts the electronegativity to it and therefore amines participate in hydrogen bonding.
Complete answer:
Amines are aliphatic and aromatic in nature depending upon the substituent added to the nitrogen atom. Nitrogen atom has five electrons in its outermost valence shells out of which three electrons of nitrogen are shared with other atoms during the bond formation and the rest two electrons present over the nitrogen as a lone pair. Due to higher availability of electrons into nitrogen atoms they readily react with water molecules to form the hydrogen bonding. Strength of hydrogen bonding depends on the availability of electrons over nitrogen atoms. Due to this reason, as the molecular mass of the amine increases the proportion of hydrophobic portion increases due to increase in the hydrophobic alkyl group.
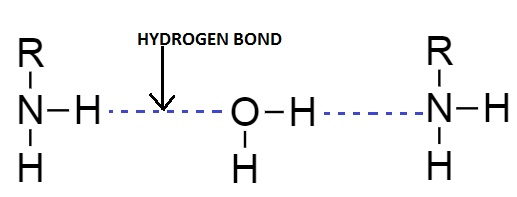
With increase in the number of carbon atoms, solubility of aliphatic amines decreases gradually. The higher member of amine, more than $ 6 $ carbon atom, is practically insoluble in water. Electronegativity of the nitrogen atom is lower than electronegativity of oxygen atom therefore with increase in size of alkyl group electronegativity of amine decreases and results in formation of very weak hydrogen bonding.
Starting members of aliphatic amines show good solubility in water as a solvent.
$ \Rightarrow $ Due to formation of hydrogen bonding amines are soluble in water.
Note:
Aromatic amines also contain the lone pair of electrons over the nitrogen atom but still they are practically insoluble in water due to presence of large hydrophobic structure of benzene ring which impart high hydrophobic character to the molecule. Aromatic amines show good solubility in the organic solvent like ether, benzene or ether.
Complete answer:
Amines are aliphatic and aromatic in nature depending upon the substituent added to the nitrogen atom. Nitrogen atom has five electrons in its outermost valence shells out of which three electrons of nitrogen are shared with other atoms during the bond formation and the rest two electrons present over the nitrogen as a lone pair. Due to higher availability of electrons into nitrogen atoms they readily react with water molecules to form the hydrogen bonding. Strength of hydrogen bonding depends on the availability of electrons over nitrogen atoms. Due to this reason, as the molecular mass of the amine increases the proportion of hydrophobic portion increases due to increase in the hydrophobic alkyl group.

With increase in the number of carbon atoms, solubility of aliphatic amines decreases gradually. The higher member of amine, more than $ 6 $ carbon atom, is practically insoluble in water. Electronegativity of the nitrogen atom is lower than electronegativity of oxygen atom therefore with increase in size of alkyl group electronegativity of amine decreases and results in formation of very weak hydrogen bonding.
Starting members of aliphatic amines show good solubility in water as a solvent.
$ \Rightarrow $ Due to formation of hydrogen bonding amines are soluble in water.
Note:
Aromatic amines also contain the lone pair of electrons over the nitrogen atom but still they are practically insoluble in water due to presence of large hydrophobic structure of benzene ring which impart high hydrophobic character to the molecule. Aromatic amines show good solubility in the organic solvent like ether, benzene or ether.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




