
Answer the following –
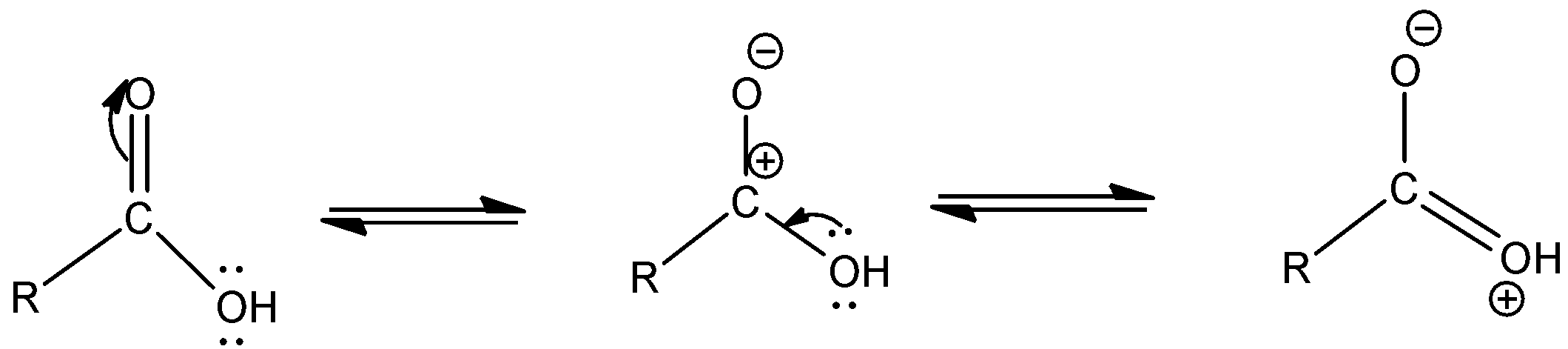
a. Give the resonating structure of a carboxylic group?
b. Give chemical reaction to obtain the following –
i. Carboxylic acid from Grignard reagent
ii. Benzoic acid from ethyl benzoate
iii. Benzamide from benzoic acid
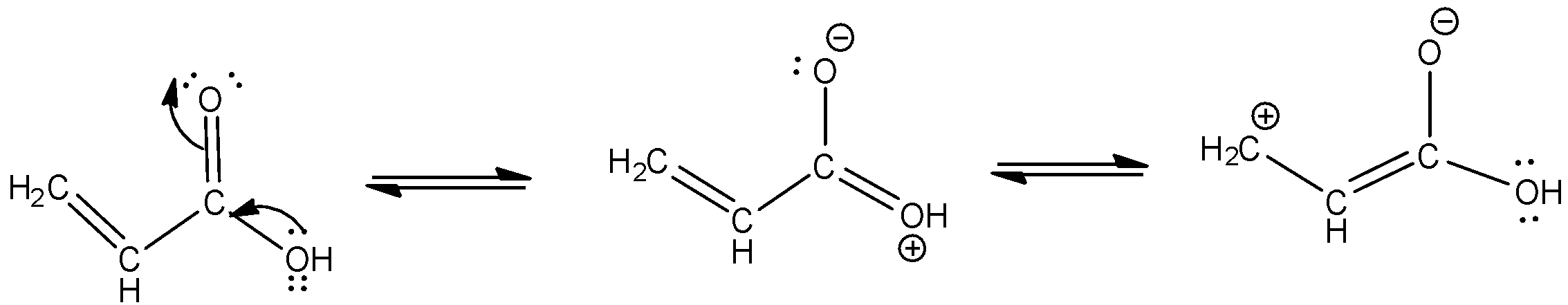
c. Give resonating structures of propenoic acid?
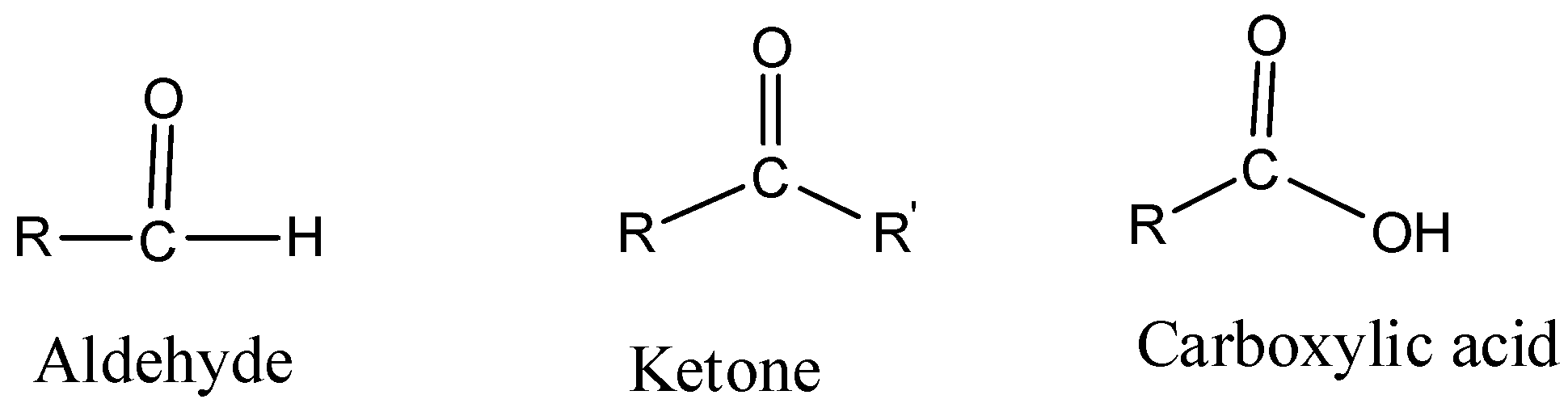
d. How will you distinguish amongst aldehyde, ketone and carboxylic acid?
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: You can solve all these questions by understanding the basic difference amongst aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids. The basic structure of an aldehyde, ketone and carboxylic acid is –
Complete step by step answer:
a.The resonating structures of carboxylic group are as given below –
- Let us begin by drawing the structure of a carboxylic acid.
- A carboxylic acid is given by a terminal carbon bonded to (-OH) group by a single bond and bonded to (-O) by a double bond.
b. The chemical reactions are given below –
i. Carboxylic acid from Grignard reagent
- The general reaction for conversion of any compound to carboxylic acid is as given below –
$R-MgX+C{{O}_{2}}\to RCOO-MgX\xrightarrow{{{H}_{2}}O}R-COOH+Mg(OH)X$
ii. Benzoic acid from ethyl benzoate
- The reaction is as given below -
$PhCOOEt\xrightarrow[-EtOH]{NaOH}PhCOONa\xrightarrow[-NaCl]{HCl}PhCOOH$
iii. Benzamide from benzoic acid
The reaction is as given below -
$PhCOOH+N{{H}_{3}}PhCO{{O}^{-}}N{{H}_{4}}^{+}\xrightarrow{\Delta }PhCON{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
c. Resonating structures of propenoic acid –
- Let us begin by drawing the structure of a propenoic acid. As the name suggests, “prop-ene-oic acid” contains 3 carbons, 1 double bond and a carboxylic acid group.
-The structure and resonating structures are as given below -
d. We distinguish amongst aldehyde, ketone and carboxylic acid
- Aldehydes and Ketones can be distinguished by Tollen’s test. Whereas, carboxylic acids can be identified with sodium bicarbonate test, which gives effervescence of carbon dioxide gas upon reaction with sodium hydrogen carbonate.
- Tollen’s reagent is prepared by mixing silver nitrate with ammonium hydroxide. Aldehydes give a positive test – forms a silver mirror. Ketones give a negative test. Tollen’s reagent oxidizes aldehydes to corresponding acids and gets reduced to Tollen’s metallic silver.
Note: Note that aldehydes gives positive test for the silver mirror test or the Tollen’s test because aldehydes on treatment with the Tollen’s reagent is able to oxidise into the carboxylic acid that forms silver mirror.

Complete step by step answer:
a.The resonating structures of carboxylic group are as given below –
- Let us begin by drawing the structure of a carboxylic acid.
- A carboxylic acid is given by a terminal carbon bonded to (-OH) group by a single bond and bonded to (-O) by a double bond.

b. The chemical reactions are given below –
i. Carboxylic acid from Grignard reagent
- The general reaction for conversion of any compound to carboxylic acid is as given below –
$R-MgX+C{{O}_{2}}\to RCOO-MgX\xrightarrow{{{H}_{2}}O}R-COOH+Mg(OH)X$
ii. Benzoic acid from ethyl benzoate
- The reaction is as given below -
$PhCOOEt\xrightarrow[-EtOH]{NaOH}PhCOONa\xrightarrow[-NaCl]{HCl}PhCOOH$
iii. Benzamide from benzoic acid
The reaction is as given below -
$PhCOOH+N{{H}_{3}}PhCO{{O}^{-}}N{{H}_{4}}^{+}\xrightarrow{\Delta }PhCON{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
c. Resonating structures of propenoic acid –
- Let us begin by drawing the structure of a propenoic acid. As the name suggests, “prop-ene-oic acid” contains 3 carbons, 1 double bond and a carboxylic acid group.
-The structure and resonating structures are as given below -

d. We distinguish amongst aldehyde, ketone and carboxylic acid
- Aldehydes and Ketones can be distinguished by Tollen’s test. Whereas, carboxylic acids can be identified with sodium bicarbonate test, which gives effervescence of carbon dioxide gas upon reaction with sodium hydrogen carbonate.
- Tollen’s reagent is prepared by mixing silver nitrate with ammonium hydroxide. Aldehydes give a positive test – forms a silver mirror. Ketones give a negative test. Tollen’s reagent oxidizes aldehydes to corresponding acids and gets reduced to Tollen’s metallic silver.
Note: Note that aldehydes gives positive test for the silver mirror test or the Tollen’s test because aldehydes on treatment with the Tollen’s reagent is able to oxidise into the carboxylic acid that forms silver mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




