
What is the angle between the radius vector and the centripetal acceleration?
(A) $ \dfrac{\pi }{2} $
(B) $ 2\pi $
(C) $ \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} $
(D) $ \pi $
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint
Centripetal acceleration acts on a body moving in a circular path. It acts towards the centre of the body. The angle between this acceleration and the radius vector can be found by understanding their directions.
Complete step by step answer
Centripetal is similar to ‘central-seeking’. A force that is responsible for generating circular motion in a body is called centripetal force. As we know that force is calculated as the product of mass and acceleration that a body is going through, the acceleration produced by centripetal force is consequently, termed as centripetal acceleration. Since mass is directionless but force is a vector quantity, the direction of the centripetal acceleration is the same as the direction of the force i.e. towards the centre.
In a circular motion, the radius vector points towards the circumference of the motion. It starts from the centre and ends outwards on the surface of the circle.
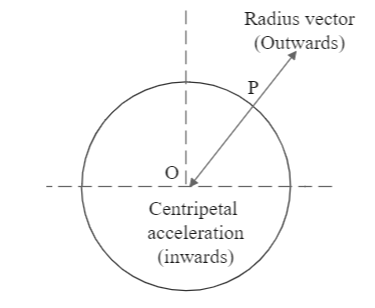
We can see that the centripetal acceleration acts towards the centre O, while the radius vector acts outwards from the centre towards point P. This implies that these two quantities have exactly opposite directions of operation. Hence, the angle between them is equal to $ \pi $ .
Option (D) is the correct answer.
Note
Centripetal acceleration can be observed with a simple experiment. Take a ball and tie a long thread around it. When you start swinging it using one end of the thread above your head or in front of your body, try to make circular motion. The system constantly moves in a circular path with the help of force provided by you. But the ball does not fall off because of the centripetal acceleration that acts inwards and keeps the system stable.
Centripetal acceleration acts on a body moving in a circular path. It acts towards the centre of the body. The angle between this acceleration and the radius vector can be found by understanding their directions.
Complete step by step answer
Centripetal is similar to ‘central-seeking’. A force that is responsible for generating circular motion in a body is called centripetal force. As we know that force is calculated as the product of mass and acceleration that a body is going through, the acceleration produced by centripetal force is consequently, termed as centripetal acceleration. Since mass is directionless but force is a vector quantity, the direction of the centripetal acceleration is the same as the direction of the force i.e. towards the centre.
In a circular motion, the radius vector points towards the circumference of the motion. It starts from the centre and ends outwards on the surface of the circle.

We can see that the centripetal acceleration acts towards the centre O, while the radius vector acts outwards from the centre towards point P. This implies that these two quantities have exactly opposite directions of operation. Hence, the angle between them is equal to $ \pi $ .
Note
Centripetal acceleration can be observed with a simple experiment. Take a ball and tie a long thread around it. When you start swinging it using one end of the thread above your head or in front of your body, try to make circular motion. The system constantly moves in a circular path with the help of force provided by you. But the ball does not fall off because of the centripetal acceleration that acts inwards and keeps the system stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




