
Anabolic reactions are always endergonic reactions. Justify this statement with an example.
Answer
498.3k+ views
Hint: Anabolic reactions are the processes where small organic molecules are being used for producing bigger molecules. These reactions can be of endergonic and exogenic reactions. Endergonic reactions are nonspontaneous reactions which have positive free energy. Exergonic reactions have negative free energy. They are spontaneous reactions when the system remains closed.
Complete answer:
Anabolic reactions are mechanisms which use small organic molecules to describe bigger molecules. Anabolic reactions can always be endergonic reactions. Examples to explain anabolic reactions are- proteins and enzymes interaction. Proteins, as we know, are building blocks of the body and they are formed from chains of small monomers of amino acids or peptides.
All enzymes are derived from proteins. Proteins are macromolecules which are said to be building blocks of the body, combining with other macromolecules like- carbohydrates and fats. Enzymes have a lock-key mechanism in which they directly attach to the substrate and get activated by factors and start the reaction at a faster rate. Every enzyme does not perform with every substrate. They have specific substrates for specific enzymes.
There is a big misconception between several of us that enzymes make reactions happen. No, enzymes only make the reaction faster, enhance it so that the reaction can be completed soon. The enzyme which acts in forward reaction is the same which will catalyse for the reverse reaction. Enzymes cannot alter the reaction permanently.
Note:
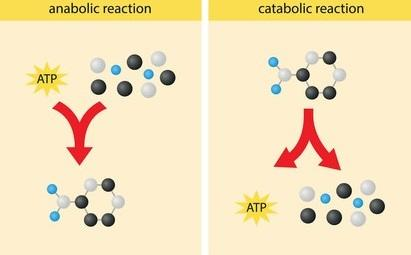
Anabolic is an energy-requiring process and catabolic reactions are energy releasing processes, where larger molecules dissociate into smaller molecules. That is known as enzyme nomenclature. nomenclature key response is to describe the terms as enzyme catalysts. The first showing the name of the substrate or in any bimolecular reaction two substrates are to be shown up.
Complete answer:
Anabolic reactions are mechanisms which use small organic molecules to describe bigger molecules. Anabolic reactions can always be endergonic reactions. Examples to explain anabolic reactions are- proteins and enzymes interaction. Proteins, as we know, are building blocks of the body and they are formed from chains of small monomers of amino acids or peptides.
All enzymes are derived from proteins. Proteins are macromolecules which are said to be building blocks of the body, combining with other macromolecules like- carbohydrates and fats. Enzymes have a lock-key mechanism in which they directly attach to the substrate and get activated by factors and start the reaction at a faster rate. Every enzyme does not perform with every substrate. They have specific substrates for specific enzymes.
There is a big misconception between several of us that enzymes make reactions happen. No, enzymes only make the reaction faster, enhance it so that the reaction can be completed soon. The enzyme which acts in forward reaction is the same which will catalyse for the reverse reaction. Enzymes cannot alter the reaction permanently.

Note:
Anabolic is an energy-requiring process and catabolic reactions are energy releasing processes, where larger molecules dissociate into smaller molecules. That is known as enzyme nomenclature. nomenclature key response is to describe the terms as enzyme catalysts. The first showing the name of the substrate or in any bimolecular reaction two substrates are to be shown up.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




