
An organic compound with molecular formula ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{10}}}}{\rm{O}}$ does not react with sodium. With excess of HI it gives only one type of alkyl halide. The compound is:
A.${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}$
B.
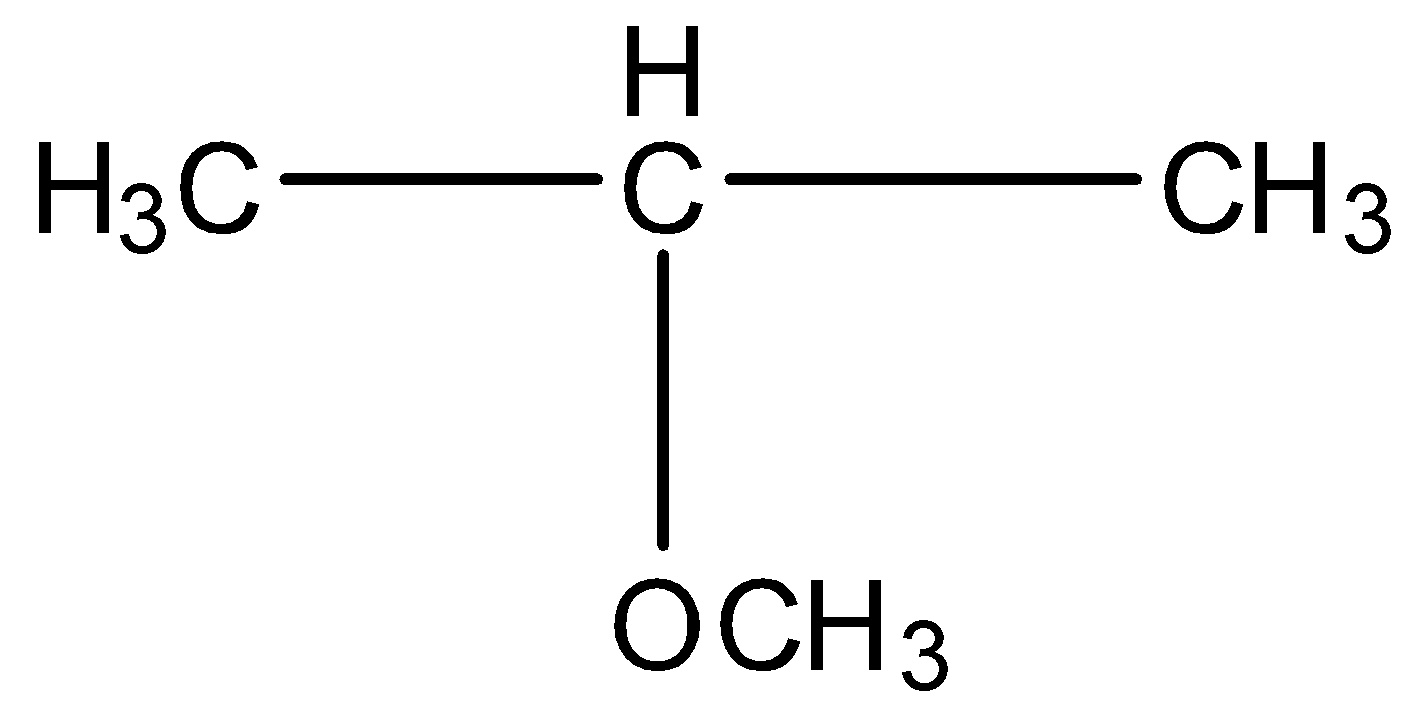
C.${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{OC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$
D.${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{OH}}$

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: know that an organic compound is the compound where there is a covalent link of carbon with other atoms like hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen etc. Although in carbonates, carbides, cyanides carbon atoms are present but they are not classified as organic compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, the molecular formula of the compound is ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{10}}}}{\rm{O}}$. The O atom in the compound indicates that there may be a presence of alcohol, carbonyl group or ether. But compounds in the options are ether and alcohol. Also, given that the compound does not react with sodium. We know that alcohol reacts with sodium to form sodium alkoxide (salt) that means the compound must be ether.
Now, we have to identify the correct ether whose molecular formula is ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{10}}}}{\rm{O}}$. Another information given is that the compound when undergoing reaction with excess of HI gives one type of alkyl halide. For this, both the alkyl groups bonded to the oxygen atom must be the same. So, the compound is ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}$. The chemical reaction can be shown as below:
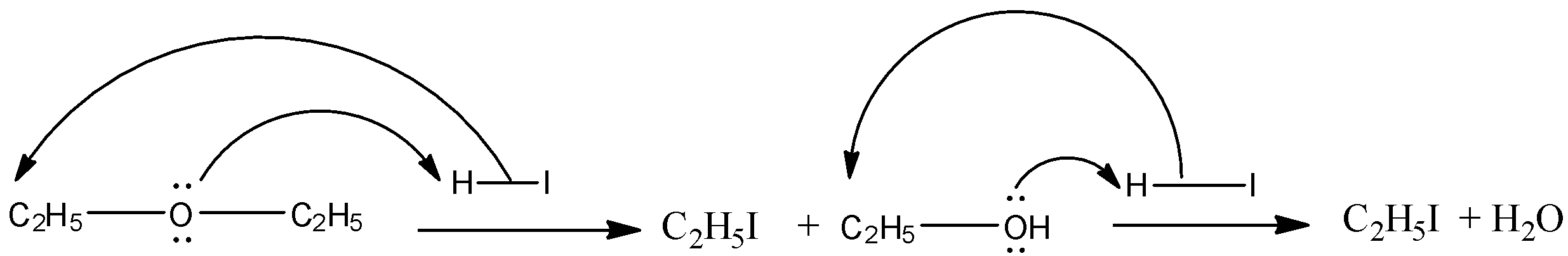
So, when ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}$ reacts with excess HI, only one type of alkyl halide$\left( {{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{I}}} \right)$produces.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Additional Information:
Functional groups are atoms or groups of atoms that decide the chemical properties of an organic compound. Some functional groups are alcohol, aldehyde, carboxylic acid, ether, amide etc. The structure of ether is R-O-R (R is alkyl group). If the two alkyl groups in ether are same, the ether is termed as symmetrical ether and if alkyl groups are different then the ether is termed as unsymmetrical ether.
Note:
There are many methods for preparation of ether, such as, Williamson synthesis, dehydration of alcohol etc. Williamson synthesis is the method used in the laboratory for preparation of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ether. In this method, an alkyl halide undergoes reaction with sodium alkoxide.
${\rm{R}} - {\rm{X}} + {\rm{R}} - {\rm{O}} - {\rm{Na}} \to {\rm{R}} - {\rm{O}} - {\rm{R}} + {\rm{NaX}}$
Here, R is an alkyl group.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, the molecular formula of the compound is ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{10}}}}{\rm{O}}$. The O atom in the compound indicates that there may be a presence of alcohol, carbonyl group or ether. But compounds in the options are ether and alcohol. Also, given that the compound does not react with sodium. We know that alcohol reacts with sodium to form sodium alkoxide (salt) that means the compound must be ether.
Now, we have to identify the correct ether whose molecular formula is ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{10}}}}{\rm{O}}$. Another information given is that the compound when undergoing reaction with excess of HI gives one type of alkyl halide. For this, both the alkyl groups bonded to the oxygen atom must be the same. So, the compound is ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}$. The chemical reaction can be shown as below:

So, when ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}$ reacts with excess HI, only one type of alkyl halide$\left( {{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{I}}} \right)$produces.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Additional Information:
Functional groups are atoms or groups of atoms that decide the chemical properties of an organic compound. Some functional groups are alcohol, aldehyde, carboxylic acid, ether, amide etc. The structure of ether is R-O-R (R is alkyl group). If the two alkyl groups in ether are same, the ether is termed as symmetrical ether and if alkyl groups are different then the ether is termed as unsymmetrical ether.
Note:
There are many methods for preparation of ether, such as, Williamson synthesis, dehydration of alcohol etc. Williamson synthesis is the method used in the laboratory for preparation of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ether. In this method, an alkyl halide undergoes reaction with sodium alkoxide.
${\rm{R}} - {\rm{X}} + {\rm{R}} - {\rm{O}} - {\rm{Na}} \to {\rm{R}} - {\rm{O}} - {\rm{R}} + {\rm{NaX}}$
Here, R is an alkyl group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




