
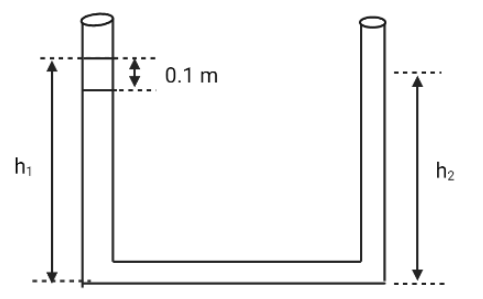
An open-ended U-tube of uniform cross-sectional area contains water (density ${\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{kg}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$). Initially the water level stands at ${\text{0}}{\text{.29}}\,{\text{m}}$ from the bottom in each arm. Kerosene oil (a water-immiscible liquid) of density ${\text{800kg}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$ is added to the left arm until its length is ${\text{0}}{\text{.1}}\,{\text{m}}$, as shown in the schematic figure below. The ratio ($1/2$) of the heights of the liquid in the two arms is
A. $\dfrac{{15}}{{14}}$
B. $\dfrac{{35}}{{33}}$
C. $\dfrac{7}{6}$
D. $\dfrac{5}{4}$

Answer
520.8k+ views
Hint:The term "density" refers to the amount of mass per unit of volume. An object's average density is equal to its total mass divided by its total volume. An object made of a relatively dense material (such as iron) would have less volume than one made of a less dense substance of equal mass (such as water).
Complete step by step answer:
Temperature and pressure affect the density of a material. For solids and liquids, this variation is usually small, but for gases, it is much greater. When you apply more pressure to an object, it shrinks in volume and thus becomes denser. With a few exceptions, increasing the temperature of a material reduces its density by increasing its volume.
Let us consider ${{\text{h}}_{{\text{1}}\,}}{\text{and}}\,{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}$ and add them
${h_1}\, + \,{h_2}\, = \,0.29 \times 2\, + \,0.1$
On further solving we get,
${{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}\,{\text{ + }}\,{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}\,{\text{ = }}\,{\text{0}}{\text{.68}}.........\left( {\text{1}} \right)$
Let ${\rho _k}$denote the density of the kerosene and ${{{\rho }}_{\text{w}}}$ denote the density of water.
${{\text{P}}_{\text{0}}}\,{\text{ + }}\,{{{\rho }}_{\text{k}}}{\text{g}}\left( {{\text{0}}{\text{.1}}} \right)\,{\text{ + }}\,{{{\rho }}_{\text{w}}}{\text{g}}\left( {{{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}\,{\text{ - }}\,{\text{0}}{\text{.1}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ - }}{{{\rho }}_{\text{w}}}{\text{g}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}\,{\text{ = }}\,{{\text{P}}_{\text{0}}} \\ $
On substituting and expanding the equations,
\[{{{\rho }}_{\text{k}}}{\text{g}}\left( {{\text{0}}{\text{.1}}} \right)\,{\text{ + }}\,{{{\rho }}_{\text{w}}}{\text{g}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}\,{\text{ - }}\,{{{\rho }}_{\text{w}}}{\text{g}}\,{{ \times }}\left( {{\text{0}}{\text{.1}}} \right){\text{ = }}\,{{{\rho }}_{\text{w}}}{\text{g}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}} \\ \]
On further substituting,
$800\, \times 10 \times 0.1 + 1000 \times 10 \times {h_1} \\
\Rightarrow \, - 1000\, \times 10 \times 0.1 = 1000 \times 10 \times {h_2} \\ $
On further solving, we get
$10000\left( {{{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}\,{\text{ - }}\,{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)\, = \,200 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{h_{\text{1}}}\,{\text{ - }}\,{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)\,\, = \,0.02.................\left( 2 \right) \\ $
Comparing equations $\left( {\text{1}} \right)\,{\text{and}}\,\left( {\text{2}} \right)\,{\text{we}}\,{\text{get,}}$
${{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}\,{\text{ = }}\,{\text{0}}{\text{.35}}\,\,{\text{;}}\,\,{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}\,{\text{ = }}\,{\text{0}}{\text{.33}}$
So, the ratio ($1/2$) of the heights of the liquid in the two arms is,
$\therefore \dfrac{{{{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}}}{{{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}}}\,{\text{ = }}\,\dfrac{{{\text{35}}}}{{{\text{33}}}}$
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:Heating the bottom of a fluid causes heat to convect from the bottom to the top of most materials due to a reduction in the density of the heated fluid. As a result, it rises in comparison to more dense unheated material.
Complete step by step answer:
Temperature and pressure affect the density of a material. For solids and liquids, this variation is usually small, but for gases, it is much greater. When you apply more pressure to an object, it shrinks in volume and thus becomes denser. With a few exceptions, increasing the temperature of a material reduces its density by increasing its volume.
Let us consider ${{\text{h}}_{{\text{1}}\,}}{\text{and}}\,{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}$ and add them
${h_1}\, + \,{h_2}\, = \,0.29 \times 2\, + \,0.1$
On further solving we get,
${{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}\,{\text{ + }}\,{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}\,{\text{ = }}\,{\text{0}}{\text{.68}}.........\left( {\text{1}} \right)$
Let ${\rho _k}$denote the density of the kerosene and ${{{\rho }}_{\text{w}}}$ denote the density of water.
${{\text{P}}_{\text{0}}}\,{\text{ + }}\,{{{\rho }}_{\text{k}}}{\text{g}}\left( {{\text{0}}{\text{.1}}} \right)\,{\text{ + }}\,{{{\rho }}_{\text{w}}}{\text{g}}\left( {{{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}\,{\text{ - }}\,{\text{0}}{\text{.1}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ - }}{{{\rho }}_{\text{w}}}{\text{g}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}\,{\text{ = }}\,{{\text{P}}_{\text{0}}} \\ $
On substituting and expanding the equations,
\[{{{\rho }}_{\text{k}}}{\text{g}}\left( {{\text{0}}{\text{.1}}} \right)\,{\text{ + }}\,{{{\rho }}_{\text{w}}}{\text{g}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}\,{\text{ - }}\,{{{\rho }}_{\text{w}}}{\text{g}}\,{{ \times }}\left( {{\text{0}}{\text{.1}}} \right){\text{ = }}\,{{{\rho }}_{\text{w}}}{\text{g}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}} \\ \]
On further substituting,
$800\, \times 10 \times 0.1 + 1000 \times 10 \times {h_1} \\
\Rightarrow \, - 1000\, \times 10 \times 0.1 = 1000 \times 10 \times {h_2} \\ $
On further solving, we get
$10000\left( {{{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}\,{\text{ - }}\,{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)\, = \,200 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{h_{\text{1}}}\,{\text{ - }}\,{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)\,\, = \,0.02.................\left( 2 \right) \\ $
Comparing equations $\left( {\text{1}} \right)\,{\text{and}}\,\left( {\text{2}} \right)\,{\text{we}}\,{\text{get,}}$
${{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}\,{\text{ = }}\,{\text{0}}{\text{.35}}\,\,{\text{;}}\,\,{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}\,{\text{ = }}\,{\text{0}}{\text{.33}}$
So, the ratio ($1/2$) of the heights of the liquid in the two arms is,
$\therefore \dfrac{{{{\text{h}}_{\text{1}}}}}{{{{\text{h}}_{\text{2}}}}}\,{\text{ = }}\,\dfrac{{{\text{35}}}}{{{\text{33}}}}$
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:Heating the bottom of a fluid causes heat to convect from the bottom to the top of most materials due to a reduction in the density of the heated fluid. As a result, it rises in comparison to more dense unheated material.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




