
An open organ pipe of length L vibrates in a second harmonic mode. The pressure vibration is maximum
(A). At the two ends
(B). At a distance L/4 from either and inside the tube
(C). At the midpoint of the tube
(D). None of these
Answer
614.4k+ views
- Hint: In these types of questions remember the basic concepts of harmonic mode and also the formula of the length of an organ pipe .i.e.$L = \dfrac{{n\lambda }}{2}$to find the modes of vibrations putt n = 1, 2, 3 ……..then find the correct option.
Complete step-by-step solution -
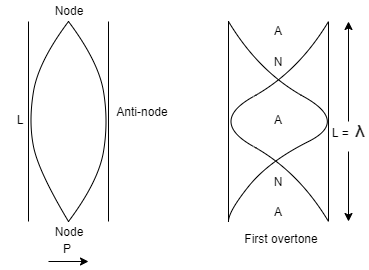
We know that for an open organ pipe, the length L is given as $L = \dfrac{{n\lambda }}{2}$
Where $\lambda $ is the wavelength of the wave and n is an integer and by putting n = 1, 2, 3 ….... we get the modes of vibration.
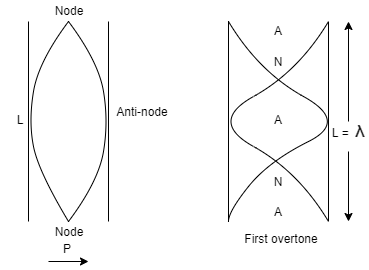
Let substituting n=1 gives for first harmonics and let n=2 gives second harmonics and so on.
Here, an open organ pipe of length L vibrates in second harmonic mode,
Hence the length of the pipe is
$L = \lambda $$L = \dfrac{{2\lambda }}{2}$
Therefore, the length of the pipe at both open ends is equal to the distance between two adjacent antinodes. The nodes are at distance $\dfrac{\lambda }{4}$ from the antinodes.
Because there is no particle displacement at nodes, there is maximal pressure vibration.
Hence, in an open organ pipe, the pressure vibration is maximum at a distance $\dfrac{L}{4}$(since, L=λ) from either end inside the tube.
Note: In the above question a term harmonic frequency is used which can be explained as; every natural frequency produced by an object or instrument has its characteristic vibrational mode or standing wave pattern. Such patterns are produced only at different vibrational frequencies within the object or instrument; such frequencies are known as harmonic frequencies, or merely harmonics. The resulting disturbance to the medium is unpredictable and non-repetitive at any frequency other than a harmonic frequency.
Complete step-by-step solution -

We know that for an open organ pipe, the length L is given as $L = \dfrac{{n\lambda }}{2}$
Where $\lambda $ is the wavelength of the wave and n is an integer and by putting n = 1, 2, 3 ….... we get the modes of vibration.

Let substituting n=1 gives for first harmonics and let n=2 gives second harmonics and so on.
Here, an open organ pipe of length L vibrates in second harmonic mode,
Hence the length of the pipe is
$L = \lambda $$L = \dfrac{{2\lambda }}{2}$
Therefore, the length of the pipe at both open ends is equal to the distance between two adjacent antinodes. The nodes are at distance $\dfrac{\lambda }{4}$ from the antinodes.
Because there is no particle displacement at nodes, there is maximal pressure vibration.
Hence, in an open organ pipe, the pressure vibration is maximum at a distance $\dfrac{L}{4}$(since, L=λ) from either end inside the tube.
Note: In the above question a term harmonic frequency is used which can be explained as; every natural frequency produced by an object or instrument has its characteristic vibrational mode or standing wave pattern. Such patterns are produced only at different vibrational frequencies within the object or instrument; such frequencies are known as harmonic frequencies, or merely harmonics. The resulting disturbance to the medium is unpredictable and non-repetitive at any frequency other than a harmonic frequency.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




