
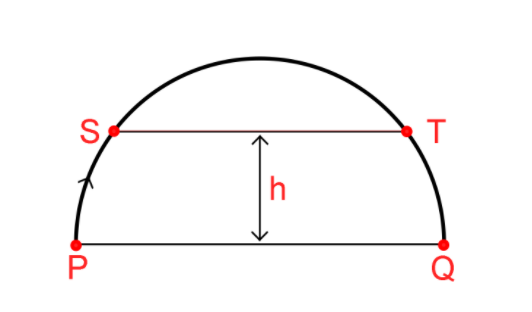
An oblique projectile projected from the ground takes time $4s$ to travel from $P$ to $Q$ while takes $2s$ to travel from $S$ to $T$. The height $h$ of level $ST$ from level $PQ$ is:
(A). $15m$
(B). $10m$
(C). $12.5m$
(D). $8.5m$

Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: You can start by explaining projectiles. Then write the equation for the time of flight of a projectile and the equation for the maximum height i.e. \[t = \dfrac{{2u\sin \theta }}{g}\] for the motion of projectile from point $P$ to $Q$ and from $S$ to $T$ and calculate the value of \[u\sin \theta \] and \[u'\sin \theta \]. Then use the equation Maximum height \[ = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta }}{{2g}}\] and calculate the maximum height for the motion of projectile from point $P$ to $Q$ and from $S$ to $T$. Then find the difference between these two to reach the solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Projectiles are bodies that are launched with some initial velocity, reach a certain maximum height while covering a certain horizontal range. An example of projectiles is a ball thrown into the sky.
Given time of flight of a projectile for motion from point \[P\] to \[Q = 4\sec \] and for the motion from point \[S\] to \[T = 2\sec \] .
Let’s assume that the velocity of the projectile at the point \[P\] is \[u\] and the velocity of the projectile at the point \[S\] is \[u'\] .
We know that the equation for the time of flight of a projectile is
\[t = \dfrac{{2u\sin \theta }}{g}\]
So, for the motion of the projectile from point \[P\] to \[Q\] , we have
\[\dfrac{{2u\sin \theta }}{g} = 4\sec \]
\[u\sin \theta = \dfrac{{4g}}{2} = 2g\]
\[u\sin \theta = 20m/s\] (Taking \[g = 10m/{s^2}\] )
And, for the motion of the projectile from point \[S\] to \[T\] , we have
\[\dfrac{{2u'\sin \theta }}{g} = 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow u'\sin \theta = g = 10m/s\]
We also know that the equation for the maximum height is
Maximum height \[ = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta }}{{2g}}\]
So, the maximum height for the motion of the projectile from point \[P\] to \[Q\] is
\[H = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta }}{{2g}} = \dfrac{{400}}{{2 \times 10}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow H = 20m\]
And, the maximum height for the motion of the projectile from point \[S\] to \[T\] is
\[H' = \dfrac{{u{'^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta }}{{2g}} = \dfrac{{100}}{{2 \times 10}} = 5m\]
\[\therefore h = H - H' = 15m\]
Hence, option A is the correct choice.
Note: In the solution above, we have used the equations for the time of flight of projectile and the maximum height of the projectile, i.e. \[t = \dfrac{{2u\sin \theta }}{g}\] and Maximum height \[ = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta }}{{2g}}\] respectively. We could also use the equations for motion, but it would be an unnecessarily long method.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Projectiles are bodies that are launched with some initial velocity, reach a certain maximum height while covering a certain horizontal range. An example of projectiles is a ball thrown into the sky.
Given time of flight of a projectile for motion from point \[P\] to \[Q = 4\sec \] and for the motion from point \[S\] to \[T = 2\sec \] .
Let’s assume that the velocity of the projectile at the point \[P\] is \[u\] and the velocity of the projectile at the point \[S\] is \[u'\] .
We know that the equation for the time of flight of a projectile is
\[t = \dfrac{{2u\sin \theta }}{g}\]
So, for the motion of the projectile from point \[P\] to \[Q\] , we have
\[\dfrac{{2u\sin \theta }}{g} = 4\sec \]
\[u\sin \theta = \dfrac{{4g}}{2} = 2g\]
\[u\sin \theta = 20m/s\] (Taking \[g = 10m/{s^2}\] )
And, for the motion of the projectile from point \[S\] to \[T\] , we have
\[\dfrac{{2u'\sin \theta }}{g} = 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow u'\sin \theta = g = 10m/s\]
We also know that the equation for the maximum height is
Maximum height \[ = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta }}{{2g}}\]
So, the maximum height for the motion of the projectile from point \[P\] to \[Q\] is
\[H = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta }}{{2g}} = \dfrac{{400}}{{2 \times 10}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow H = 20m\]
And, the maximum height for the motion of the projectile from point \[S\] to \[T\] is
\[H' = \dfrac{{u{'^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta }}{{2g}} = \dfrac{{100}}{{2 \times 10}} = 5m\]
\[\therefore h = H - H' = 15m\]
Hence, option A is the correct choice.
Note: In the solution above, we have used the equations for the time of flight of projectile and the maximum height of the projectile, i.e. \[t = \dfrac{{2u\sin \theta }}{g}\] and Maximum height \[ = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta }}{{2g}}\] respectively. We could also use the equations for motion, but it would be an unnecessarily long method.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




