
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of $50cm$ . A plane mirror is introduced covering the lower half of the convex mirror. If the distance between the object and the plane mirror is $30cm$ it is found that there is no parallax between the images formed by the two mirrors. What is the radius of curvature of the convex mirror?
Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint:For a convex lens, real image is not obtained. The image of the object will be obtained on the same side of the mirror. No parallax between the images formed means the images coincide. Use a mirror formula.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$,
where v and u , f are the positions of the image, the object and the focus of the mirror, according to the sign convection.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first write down the given information: We have a convex mirror, the distance of the object from the convex mirror is $50cm$ . The mirror covers the lower half of the convex lens. Distance of object and plane mirror is $30cm$ . Therefore, the distance between the convex mirror and the object will be: $50cm - 30cm = 20cm$
Let’s draw the figure for the same:
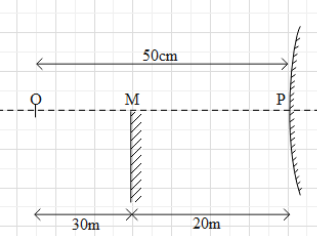
Here M denotes the plane mirror, M’ denotes the convex mirror. O is the position of the object, I is the position of the imaginary image formed.It is given that there is no parallax between the images formed by the two mirrors. Therefore, the images formed by the plane mirror and the convex mirror will be at the same position.
Also, we know that the image formed by plane mirror is at the same distance as the object.
So, the image formed by the plane mirror will be at a distance of $30cm$ from the plane mirror. Since an imaginary image is formed, the image behind the plane mirror.Therefore, we have distance $MI = 30cm$. But the distance between the convex mirror and the plane mirror is $20cm$ . Therefore, distance $PI = 10cm$.Hence, the image formed by a convex mirror will also be at a distance of $10cm$ .
To find the radius of curvature, we will use mirror formula as:
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Where the distance of object from convex mirror is $u = - 50cm$ which is in negative X-axis
$v = 10cm$ which is distance of image formed
$f$ is the focal length and we know that $R = 2f$ , substituting values, we can have
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{10}} + \dfrac{1}{{ - 50}} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
$ \Rightarrow f = 12.5cm$
$ \therefore R = 2 \times 12.5cm = 25cm$
Therefore, the radius of curvature is of $25cm$.
Note: The image formed by a plane mirror is at the same distance as the object. The distance of an object from a convex mirror is taken as negative. Be careful while calculating the distances between the object and mirror, mirror and lens.For a real object a virtual object is always formed on the other side of the mirror. Whereas if a real image is formed, it is always formed in front of the mirror.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$,
where v and u , f are the positions of the image, the object and the focus of the mirror, according to the sign convection.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first write down the given information: We have a convex mirror, the distance of the object from the convex mirror is $50cm$ . The mirror covers the lower half of the convex lens. Distance of object and plane mirror is $30cm$ . Therefore, the distance between the convex mirror and the object will be: $50cm - 30cm = 20cm$
Let’s draw the figure for the same:

Here M denotes the plane mirror, M’ denotes the convex mirror. O is the position of the object, I is the position of the imaginary image formed.It is given that there is no parallax between the images formed by the two mirrors. Therefore, the images formed by the plane mirror and the convex mirror will be at the same position.
Also, we know that the image formed by plane mirror is at the same distance as the object.
So, the image formed by the plane mirror will be at a distance of $30cm$ from the plane mirror. Since an imaginary image is formed, the image behind the plane mirror.Therefore, we have distance $MI = 30cm$. But the distance between the convex mirror and the plane mirror is $20cm$ . Therefore, distance $PI = 10cm$.Hence, the image formed by a convex mirror will also be at a distance of $10cm$ .
To find the radius of curvature, we will use mirror formula as:
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Where the distance of object from convex mirror is $u = - 50cm$ which is in negative X-axis
$v = 10cm$ which is distance of image formed
$f$ is the focal length and we know that $R = 2f$ , substituting values, we can have
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{10}} + \dfrac{1}{{ - 50}} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
$ \Rightarrow f = 12.5cm$
$ \therefore R = 2 \times 12.5cm = 25cm$
Therefore, the radius of curvature is of $25cm$.
Note: The image formed by a plane mirror is at the same distance as the object. The distance of an object from a convex mirror is taken as negative. Be careful while calculating the distances between the object and mirror, mirror and lens.For a real object a virtual object is always formed on the other side of the mirror. Whereas if a real image is formed, it is always formed in front of the mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which country won the ICC Men's ODI World Cup in 2023?

In cricket, how many legal balls are there in a standard over?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

What does "powerplay" mean in limited-overs cricket?

What is the "Powerplay" in T20 cricket?




