
An enzyme absent in mitochondria ETS is
(a) FeS protease
(b) Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase
(c) NADH dehydrogenase
(d) Cytochrome C oxidase
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: An enzyme absent in the ETS mitochondria is an enzyme that is involved in a parallel glycolysis metabolic pathway. This enzyme is an enzyme that is cytosolic. They are present in the enzyme group that catalyzes the removal of atoms of hydrogen. This deficiency of the enzyme is a genetic condition that occurs in males almost exclusively.
Complete step by step answer:
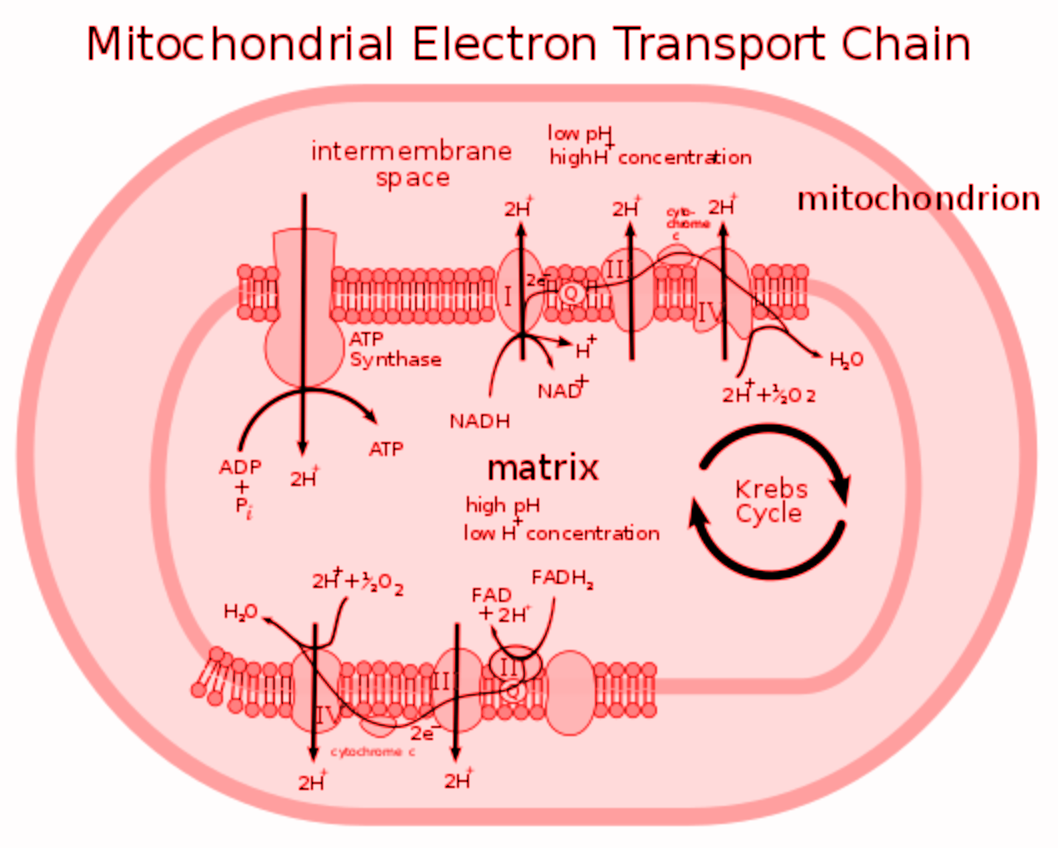
ETC in mitochondria is the final phase of cellular respiration. Here, each oxidative step releases a pair of hydrogen atoms that dissociate into $2{ H }^{ + }$ and $2{ e }^{ - }$.
Cytochromes, coenzymes, and other enzymes are composed of ETC. ETC is found in FeS protease, NADH dehydrogenase, and cytochrome c-oxidase.
There is no presence of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase in ETC. It is involved in the pentose phosphate pathway where glucose 6-phosphate is a substrate.
A cytosolic enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction is glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
This enzyme is involved in the pentose phosphate pathway, a metabolic pathway that, by maintaining the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) level, supplies cells with reduced energy (such as erythrocytes).
So, the correct answer is, ‘Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase’.
Note: Cell organelles that are involved in aerobic respiration are mitochondria. In the matrix of mitochondria, the Krebs cycle takes place and it generates decreased coenzymes that are oxidized by electron carriers of the Electron Transport System or ETC to generate Atp through oxidative phosphorylation. In eukaryotes, the ETS electron carriers are found in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Deficiency of Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase primarily affects red blood cells, which bring oxygen in the body from the lungs to tissues. It makes red blood cells break down prematurely in affected individuals. This red blood cell death is called hemolysis.
Complete step by step answer:
ETC in mitochondria is the final phase of cellular respiration. Here, each oxidative step releases a pair of hydrogen atoms that dissociate into $2{ H }^{ + }$ and $2{ e }^{ - }$.
Cytochromes, coenzymes, and other enzymes are composed of ETC. ETC is found in FeS protease, NADH dehydrogenase, and cytochrome c-oxidase.
There is no presence of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase in ETC. It is involved in the pentose phosphate pathway where glucose 6-phosphate is a substrate.

A cytosolic enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction is glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
This enzyme is involved in the pentose phosphate pathway, a metabolic pathway that, by maintaining the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) level, supplies cells with reduced energy (such as erythrocytes).
So, the correct answer is, ‘Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase’.
Note: Cell organelles that are involved in aerobic respiration are mitochondria. In the matrix of mitochondria, the Krebs cycle takes place and it generates decreased coenzymes that are oxidized by electron carriers of the Electron Transport System or ETC to generate Atp through oxidative phosphorylation. In eukaryotes, the ETS electron carriers are found in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Deficiency of Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase primarily affects red blood cells, which bring oxygen in the body from the lungs to tissues. It makes red blood cells break down prematurely in affected individuals. This red blood cell death is called hemolysis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




