
An electrician has to repair an electric fault on an electric pole of height 4 m. He needs to reach a point 1.3 m below the top of the pole in order to undertake the repair work. What should be the length of the ladder that he should use which, when inclined at an angle of $60{}^\circ $ to the horizontal, would enable him to reach the required position? Also, how far from the foot of the pole should he place the foot of the ladder? $\left( \sqrt{3}=1.732 \right)$.
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: The height of the pole is given as 4 m. He needs to reach a point 1.3 m below the top of the pole. A ladder is inclined at an angle of, so it is making a right-angled triangle. So, we will use the formula, $\sin \theta =\dfrac{perpendicular}{hypotenuse}$ to find the length of the ladder and $\tan \theta =\dfrac{perpendicular}{base}$ to find how far he is from the foot of the pole.
Complete step by step answer:
We will first draw the diagram according to the situation given in the question below.
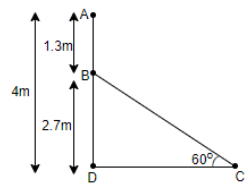
It is given that the height of the pole is 4 m, that is AD = 4 m and AB = 1.3 m. Therefore, we can say that, BD = AD - AB = 4 - 1.3 = 2.7 m. So, we get the value of BD as 2.7 m.
Now, let us assume the length of the ladder as x m, that is BC = x m and the length from the foot of the pole to where the ladder is inclined as y m, so DC = y m. Now, we can see that triangle BDC is a right angled triangle, so we will use the formula, $\sin \theta =\dfrac{perpendicular}{hypotenuse}$ to find the length of the ladder. So, we get,
$\sin 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{BD}{BC}$
Now, we have the values of BD = 2.7 m and BC = x and $\sin 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$. So, we will substitute these values in the above equality. So, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{2.7}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}x=2.7\times 2 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2.7\times 2}{\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we have been given the value of $\sqrt{3}=1.732$, so using that we get,
$\begin{align}
& x=\dfrac{5.4}{1.73} \\
& \Rightarrow x=3.12m \\
\end{align}$
So, we get the height of the ladder as 3.12 m. Now to find the length of CD, we will use the formula, $\tan \theta =\dfrac{perpendicular}{base}$. So, we get,
$\tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{BD}{CD}$
We will now put the values of BD = 2.7 m, CD = y m and $\tan 60{}^\circ =\sqrt{3}$. So, we have,
$\begin{align}
& \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{2.7}{y} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}y=2.7 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2.7}{\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}$
We know the value of $\sqrt{3}=1.732$ is given to us, so we get,
$\begin{align}
& y=\dfrac{2.7}{1.73} \\
& \Rightarrow y=1.56m \\
\end{align}$
So, we get the length from the foot of the pole to the foot of the ladder as 1.56 m and the length of the ladder as 3.12 m.
Note: There is a possibility that the students may not deduct the 1.3 m from 4 m and may directly use the length of AD instead of BD and get the height of the ladder as 4.62 m ( They will get the equation as, $\sin 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{AD}{BC}$, which will be simplified as, $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{4}{x}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8}{\sqrt{3}}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8}{1.73}\Rightarrow x=4.62m$) and similarly they will get the length from the foot of the pole to the foot of the ladder as 2.31 m.
Complete step by step answer:
We will first draw the diagram according to the situation given in the question below.

It is given that the height of the pole is 4 m, that is AD = 4 m and AB = 1.3 m. Therefore, we can say that, BD = AD - AB = 4 - 1.3 = 2.7 m. So, we get the value of BD as 2.7 m.
Now, let us assume the length of the ladder as x m, that is BC = x m and the length from the foot of the pole to where the ladder is inclined as y m, so DC = y m. Now, we can see that triangle BDC is a right angled triangle, so we will use the formula, $\sin \theta =\dfrac{perpendicular}{hypotenuse}$ to find the length of the ladder. So, we get,
$\sin 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{BD}{BC}$
Now, we have the values of BD = 2.7 m and BC = x and $\sin 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$. So, we will substitute these values in the above equality. So, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{2.7}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}x=2.7\times 2 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2.7\times 2}{\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we have been given the value of $\sqrt{3}=1.732$, so using that we get,
$\begin{align}
& x=\dfrac{5.4}{1.73} \\
& \Rightarrow x=3.12m \\
\end{align}$
So, we get the height of the ladder as 3.12 m. Now to find the length of CD, we will use the formula, $\tan \theta =\dfrac{perpendicular}{base}$. So, we get,
$\tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{BD}{CD}$
We will now put the values of BD = 2.7 m, CD = y m and $\tan 60{}^\circ =\sqrt{3}$. So, we have,
$\begin{align}
& \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{2.7}{y} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}y=2.7 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2.7}{\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}$
We know the value of $\sqrt{3}=1.732$ is given to us, so we get,
$\begin{align}
& y=\dfrac{2.7}{1.73} \\
& \Rightarrow y=1.56m \\
\end{align}$
So, we get the length from the foot of the pole to the foot of the ladder as 1.56 m and the length of the ladder as 3.12 m.
Note: There is a possibility that the students may not deduct the 1.3 m from 4 m and may directly use the length of AD instead of BD and get the height of the ladder as 4.62 m ( They will get the equation as, $\sin 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{AD}{BC}$, which will be simplified as, $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{4}{x}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8}{\sqrt{3}}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8}{1.73}\Rightarrow x=4.62m$) and similarly they will get the length from the foot of the pole to the foot of the ladder as 2.31 m.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




