
An amino acid that is not optically active is
(a) Glycine
(b) Valine
(c) Isoleucine
(d) Leucine
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: The simplest nonessential and glucogenic amino acid. This amino acid can be synthesised from serine or threonine. It is involved in the synthesis of heme, purine, creatine etc. It is highly present in the collagen.
Complete answer:
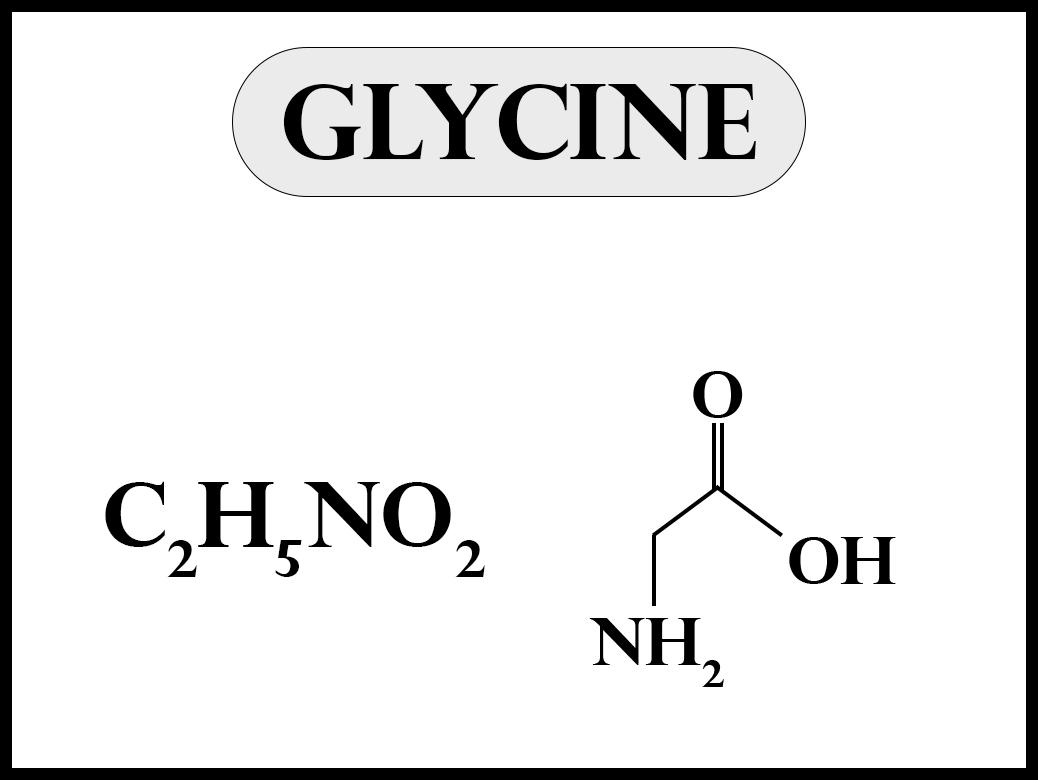
Glycine is the only chiral amino acid with a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. The absence of asymmetric carbon atoms makes glycine optically inactive that means glycine does not rotate the plane polarised light. It is the simplest stable amino acid encoded by all the codons starting with GG like, GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG.
Additional information:
- The simplest unstable amino acid is carbonic acid.
- Glycine is very important in the formation of alpha-h) helices in secondary protein structure.
- Glycine functions as glutathione, conjugating agent, neurotransmitter and as a constituent of protein.
- Glycine used as a conjugating agent in bile acid to increase its amphipathic property.
- Glycine is formed from:
Carbon dioxide, ammonia and one- carbon unit by glycine synthase multienzyme complex.
Threonine catalysed by threonine aldolase.
Serine by the enzyme hydroxymethyl transferase which is dependent on tetrahydrofolate.
Glyoxylate, glutamate or alanine by the glycine aminotransferase. Anyway is your hair is
So, the correct answer is, ‘glycine.’
Note:
- Glycosuria is a rare disease result of the high amount of glycine excreted in urine because of defective renal reabsorption. There is some
- This amino acid acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter by interfering with its release within the spinal cord like during Clostridium Petani infection which can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibition muscle contraction.
Complete answer:
Glycine is the only chiral amino acid with a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. The absence of asymmetric carbon atoms makes glycine optically inactive that means glycine does not rotate the plane polarised light. It is the simplest stable amino acid encoded by all the codons starting with GG like, GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG.

Additional information:
- The simplest unstable amino acid is carbonic acid.
- Glycine is very important in the formation of alpha-h) helices in secondary protein structure.
- Glycine functions as glutathione, conjugating agent, neurotransmitter and as a constituent of protein.
- Glycine used as a conjugating agent in bile acid to increase its amphipathic property.
- Glycine is formed from:
Carbon dioxide, ammonia and one- carbon unit by glycine synthase multienzyme complex.
Threonine catalysed by threonine aldolase.
Serine by the enzyme hydroxymethyl transferase which is dependent on tetrahydrofolate.
Glyoxylate, glutamate or alanine by the glycine aminotransferase. Anyway is your hair is
So, the correct answer is, ‘glycine.’
Note:
- Glycosuria is a rare disease result of the high amount of glycine excreted in urine because of defective renal reabsorption. There is some
- This amino acid acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter by interfering with its release within the spinal cord like during Clostridium Petani infection which can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibition muscle contraction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




