
Among the three isomers of the nitrophenol, the one that is least soluble in water is:
(a) m-nitrophenol
(b) o-nitrophenol
(c) p-nitrophenol
(d) none of these
Answer
604.2k+ views
Hint: Some of the organic compounds can form effective hydrogen bonds. Due to such hydrogen bonds, it can decrease the solubility of that compound.
Complete step by step solution:
Organic compounds can form intermolecular hydrogen bonds. Intra hydrogen bonding is hydrogen bond formation within the molecule. It generally leads to cyclisation of the molecule and prevents its association with other molecules as well prevents it from dissociating in water. It renders its activity.
Let us now consider each option.
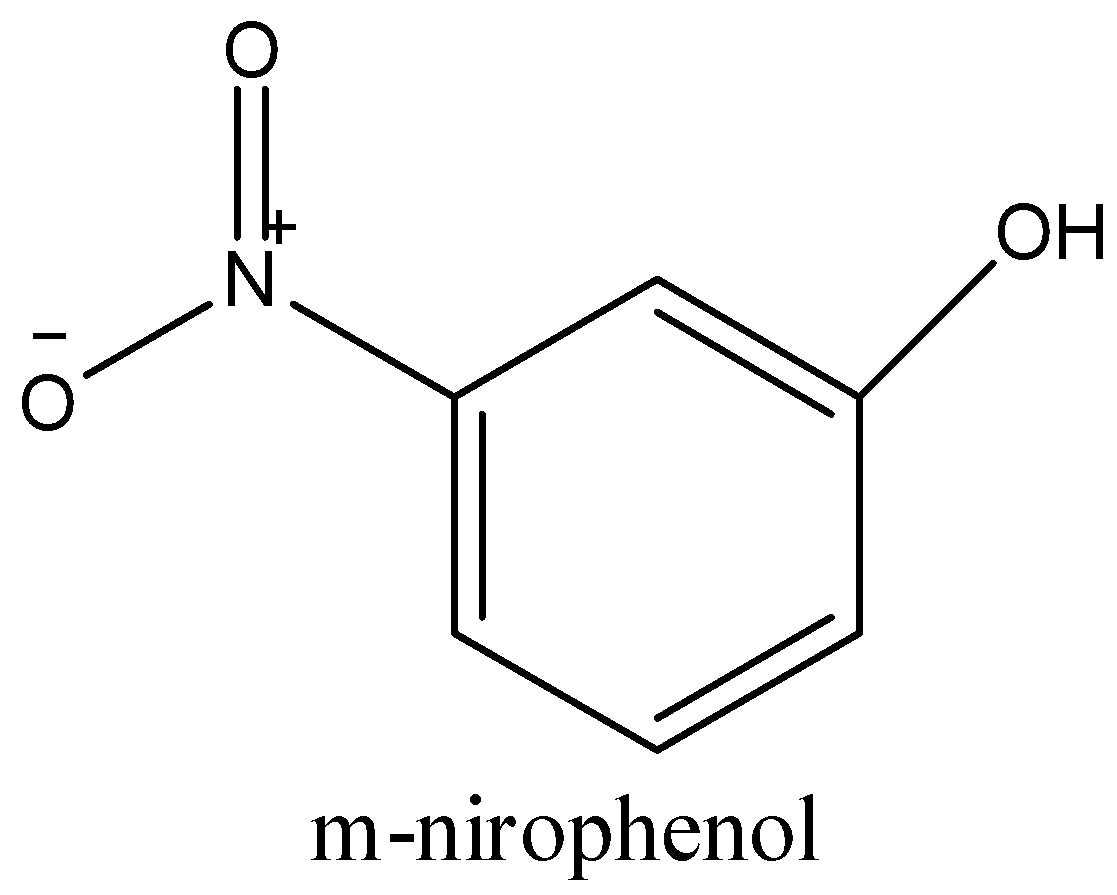
-m-nitrophenol has hydroxyl group in the meta position of the benzene ring of nitrophenol. There is distance between the OH- group and the nitro group and cannot form any intermolecular hydrogen bond. So, it is soluble in water due to the presence of free hydroxyl and nitro groups.
-In o-nitrophenol, the hydroxyl group is in the ortho position of nitrobenzene; that is; it is next to the nitro group. The hydrogen of the hydroxyl group can easily form an intermolecular hydrogen bond with the oxygen of the nitro group as shown in the figure below.
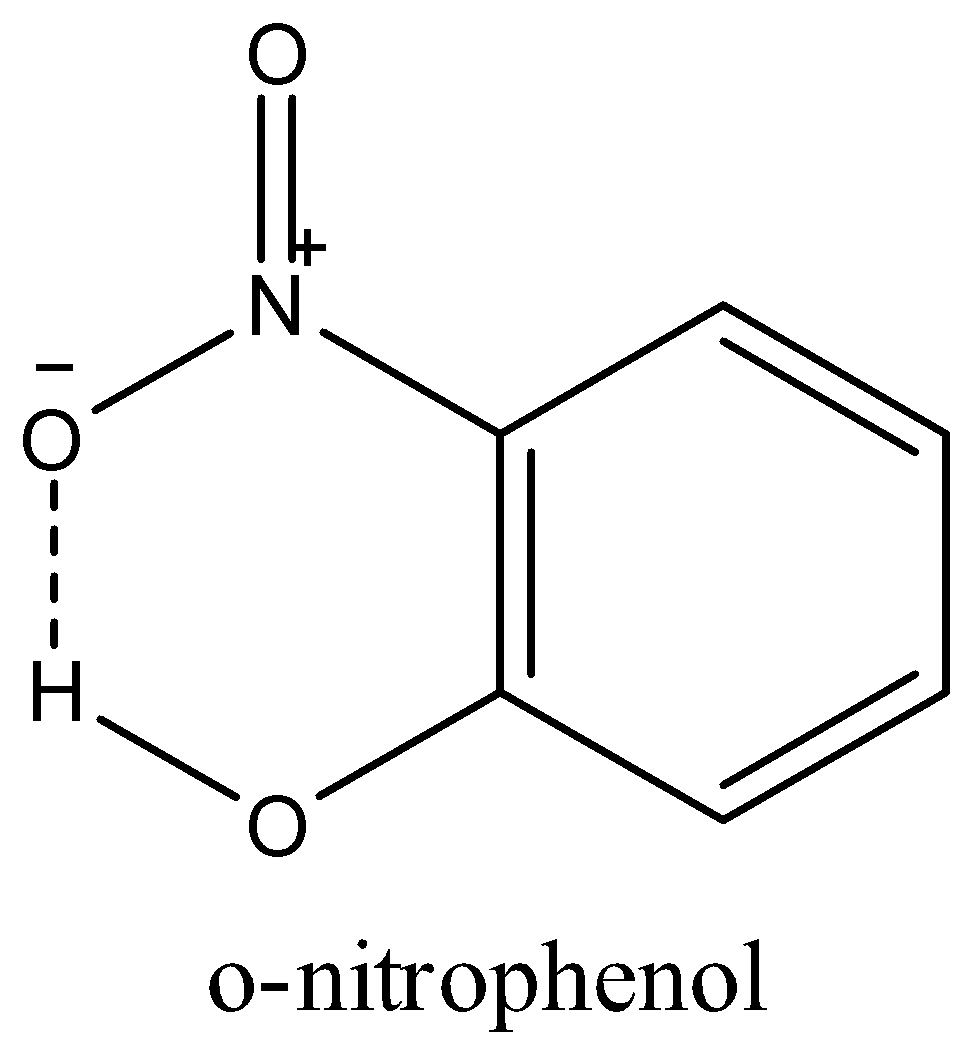
So, the nitro group and the hydroxyl groups are not free and o-nitrophenol will not get soluble in water.
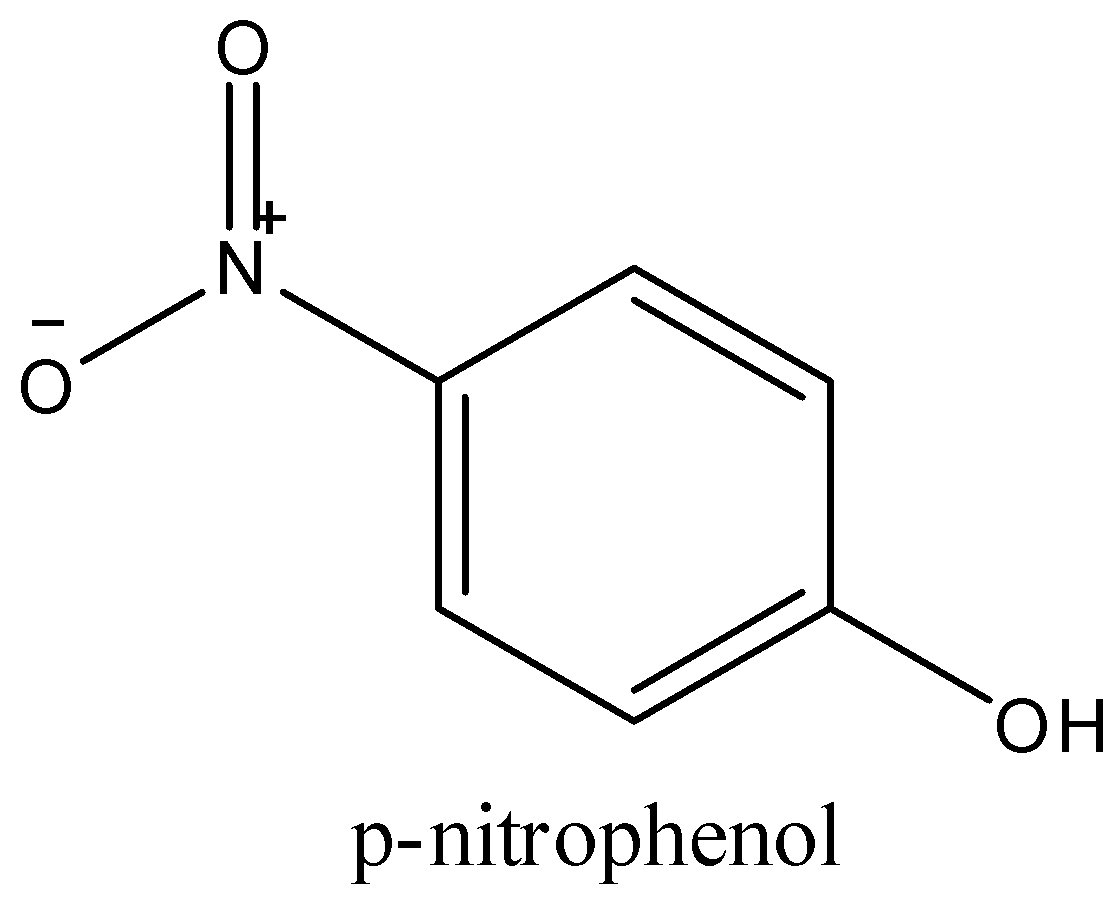
-p-nitrophenol, in this the hydroxyl group is on the para position and the nitro group and hydroxyl groups cannot form any bonds between them. They are free, and p-nitrophenol is soluble in water.
Thus, o-nitrophenol is least soluble in water and the correct option is (b).
Note: In p-nitrophenol intermolecular hydrogen bonding occurs not intramolecular. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is the hydrogen bond between two different molecules.
Complete step by step solution:
Organic compounds can form intermolecular hydrogen bonds. Intra hydrogen bonding is hydrogen bond formation within the molecule. It generally leads to cyclisation of the molecule and prevents its association with other molecules as well prevents it from dissociating in water. It renders its activity.
Let us now consider each option.
-m-nitrophenol has hydroxyl group in the meta position of the benzene ring of nitrophenol. There is distance between the OH- group and the nitro group and cannot form any intermolecular hydrogen bond. So, it is soluble in water due to the presence of free hydroxyl and nitro groups.

-In o-nitrophenol, the hydroxyl group is in the ortho position of nitrobenzene; that is; it is next to the nitro group. The hydrogen of the hydroxyl group can easily form an intermolecular hydrogen bond with the oxygen of the nitro group as shown in the figure below.

So, the nitro group and the hydroxyl groups are not free and o-nitrophenol will not get soluble in water.
-p-nitrophenol, in this the hydroxyl group is on the para position and the nitro group and hydroxyl groups cannot form any bonds between them. They are free, and p-nitrophenol is soluble in water.

Thus, o-nitrophenol is least soluble in water and the correct option is (b).
Note: In p-nitrophenol intermolecular hydrogen bonding occurs not intramolecular. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is the hydrogen bond between two different molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




