
Amitosis is a characteristic of -
(a)Higher plants
(b)Higher animals
(c)Bryophyta
(d)Lower organisms
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: As we know, mitosis is an important process of cell division that occurs in human beings. Amitosis is another method of cell division that is found in primitive organisms and it does not follow the same pathway as mitosis. It is also known as binary fission.
Complete answer:
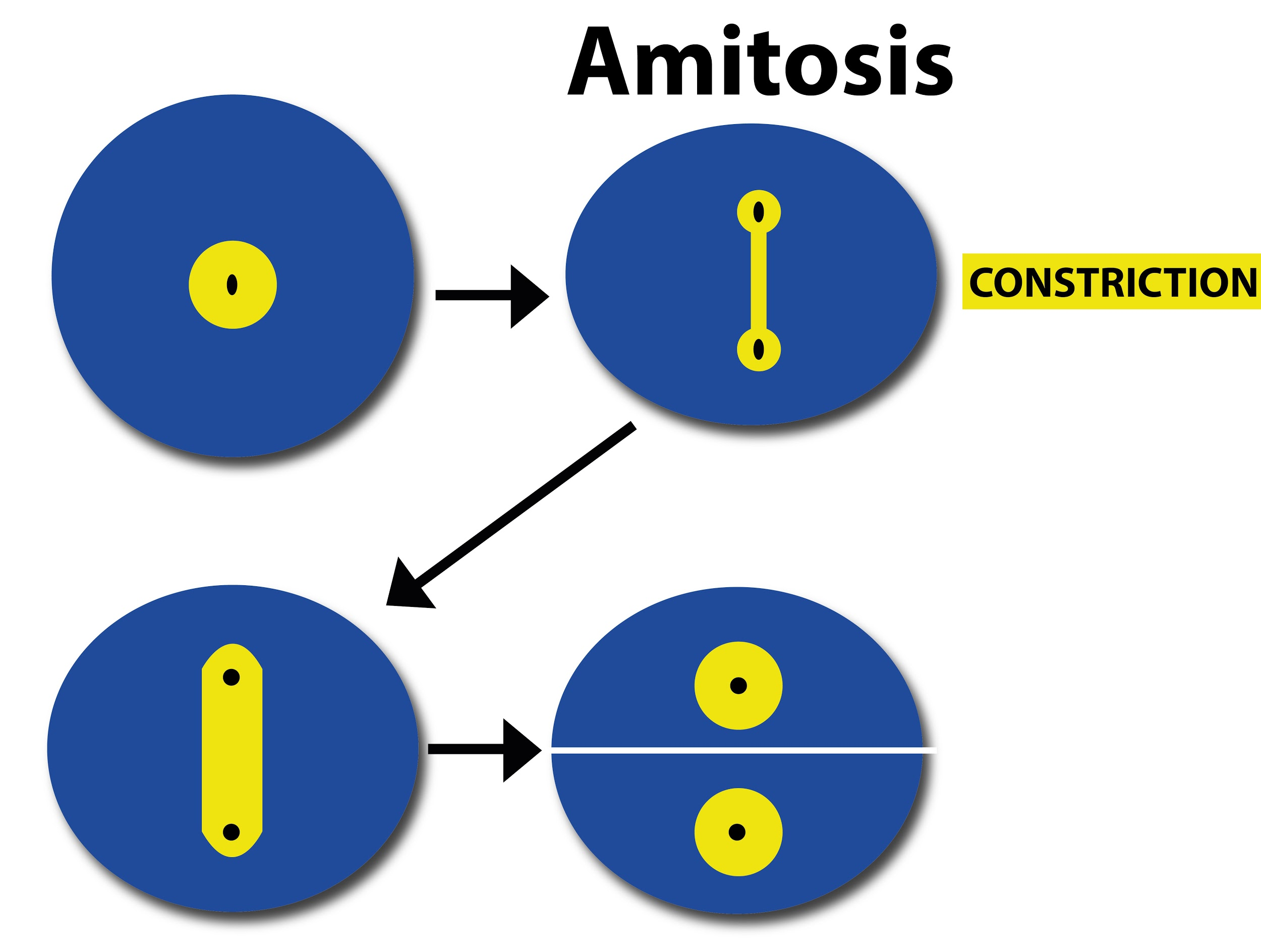
Amitosis is the process of cell division that is characteristic of lower organisms such as yeast, fungi, bacteria, and amoeba.
- It occurs mainly in prokaryotes that do not have membrane-bound organelles and nucleus. Here, karyokinesis is followed by cytokinesis.
- Here, the chromatin fibers do not condense into chromosomes and the centromeres are not distinctly seen.
- During karyokinesis, the genetic material does not get equally distributed when the nucleus splits into two nuclei. Thus, the two daughter cells do not look identical. This is followed by cytokinesis where the cytoplasm which is viscous gets divided.
Additional Information:
- Mitosis occurs through several phases while amitosis is a direct process of division.
- The mitotic spindle that is visible during mitosis is not in the case of amitosis. The latter is characterized by nuclear proliferation without the involvement of chromosomes.
- As the daughter cells of amitotic division do not have an equal number of chromosomes or equal amounts of genetic material, they do not undergo proper metabolic and reproductive processes.
So, the correct answer is ‘Lower organisms’.
Note:
- Amitosis is also known as karyostenosis, direct cell division, and closed mitosis.
- Amitosis has been observed in some eukaryotic cells of higher mammals as well, including placental and liver cells. In 1855 Robert Remak first discovered amitosis in red blood cells. The term mitosis was coined in 1882 by Flemming.
Complete answer:
Amitosis is the process of cell division that is characteristic of lower organisms such as yeast, fungi, bacteria, and amoeba.
- It occurs mainly in prokaryotes that do not have membrane-bound organelles and nucleus. Here, karyokinesis is followed by cytokinesis.
- Here, the chromatin fibers do not condense into chromosomes and the centromeres are not distinctly seen.
- During karyokinesis, the genetic material does not get equally distributed when the nucleus splits into two nuclei. Thus, the two daughter cells do not look identical. This is followed by cytokinesis where the cytoplasm which is viscous gets divided.
Additional Information:
- Mitosis occurs through several phases while amitosis is a direct process of division.
- The mitotic spindle that is visible during mitosis is not in the case of amitosis. The latter is characterized by nuclear proliferation without the involvement of chromosomes.
- As the daughter cells of amitotic division do not have an equal number of chromosomes or equal amounts of genetic material, they do not undergo proper metabolic and reproductive processes.

So, the correct answer is ‘Lower organisms’.
Note:
- Amitosis is also known as karyostenosis, direct cell division, and closed mitosis.
- Amitosis has been observed in some eukaryotic cells of higher mammals as well, including placental and liver cells. In 1855 Robert Remak first discovered amitosis in red blood cells. The term mitosis was coined in 1882 by Flemming.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




