
All are examples of cranial reflexes but not
A. Salivation
B. Scratching
C. Blushing
D. Sneezing
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: Cranial reflexes involve sensory and motor nerve fibres of cranial nerves that control vital and involuntary responses of the head region.
Complete answer: Nerves that emerge from the brain and brain stem and extend throughout the body are known as cranial nerves.
They help in carrying information from the brain to the head and some other parts of the body. They facilitate smell, vision, muscle movement, and hearing.
They control the involuntary actions of the head, neck, and other facial regions of the body. They arise from the brain and exit the foramina.
They form a part of the peripheral nervous system. Cranial reflexes such as salivation, sneezing, and blushing are all involuntary actions.
While scratching is a voluntary action and is controlled by the spinal nerves of the brain.
The schematic below shows the location of different types of nerves-
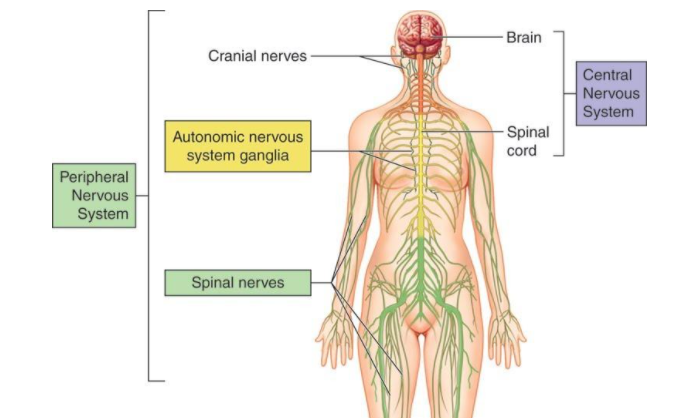
Additional information: A reflex is very fast, involuntary response to a stimulus.
A reflex arc is a passage traveled by the nerve impulses at the time of reflex.
Most reflexes are spinal reflexes with a passage that traverse only the spinal cord.
During a spinal reflex, information may be provided to the brain, but it is the spinal cord, not the brain, that is in charge of the integration of sensory information and a response transmitted to motor neurons.
Hence, the correct option is (B) Scratching.
Note: Most of the cranial nerves belong to the somatic system and are responsible for sensory and motor functions because they contain only sensory and motor fibres. Most of the cranial nerves contain both afferent and efferent fibres and are known as mixed nerves.
Complete answer: Nerves that emerge from the brain and brain stem and extend throughout the body are known as cranial nerves.
They help in carrying information from the brain to the head and some other parts of the body. They facilitate smell, vision, muscle movement, and hearing.
They control the involuntary actions of the head, neck, and other facial regions of the body. They arise from the brain and exit the foramina.
They form a part of the peripheral nervous system. Cranial reflexes such as salivation, sneezing, and blushing are all involuntary actions.
While scratching is a voluntary action and is controlled by the spinal nerves of the brain.
The schematic below shows the location of different types of nerves-

Additional information: A reflex is very fast, involuntary response to a stimulus.
A reflex arc is a passage traveled by the nerve impulses at the time of reflex.
Most reflexes are spinal reflexes with a passage that traverse only the spinal cord.
During a spinal reflex, information may be provided to the brain, but it is the spinal cord, not the brain, that is in charge of the integration of sensory information and a response transmitted to motor neurons.
Hence, the correct option is (B) Scratching.
Note: Most of the cranial nerves belong to the somatic system and are responsible for sensory and motor functions because they contain only sensory and motor fibres. Most of the cranial nerves contain both afferent and efferent fibres and are known as mixed nerves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




