
Alicyclic compounds are:
A. Aromatic compounds
B. Aliphatic cyclic compounds
C. Heterocyclic compounds
D. None of the above
Answer
536.1k+ views
Hint: Non aromatic cyclic compounds are called alicyclic compounds. It may be unicyclic or multicyclic.
Complete step by step answer:
The compounds which have one or more all-carbon rings, either saturated or unsaturated but do not have aromatic character are called alicyclic compounds. In other words, alicyclic compounds are aliphatic cyclic compounds. The bonds between pairs of adjacent atoms may all be of the type designated single bonds (involving two electrons), or some of them may be double or triple bonds (with four or six electrons, respectively); six-membered rings for which a system of alternating single and double bonds may be envisioned. Alicyclic compounds may have one or more aliphatic side chains attached.
The simplest alicyclic compounds are the monocyclic cycloalkanes. Monocyclic cycloalkanes include: cyclopropane, cyclobutene, cyclopentane, cyclohexane, cycloheptane, cyclooctane, etc.
Bicyclic alkanes include: bicyclo undecane, decalin, etc.
Polycyclic alkanes include cubane, basketane and tetrahedrane.
The smallest alicyclic compound is cyclopropane. The mode of ring-closing in the formation of many alicyclic compounds can be predicted by Baldwin's rules.
Those alicyclic compounds in which the ring contains three or four carbon atoms are less stable than the compounds having larger rings, because the angles formed by adjacent covalent bonds are smaller than is necessary for maximum effectiveness. In the larger rings all the bond angles have the preferred value (about 109.5°); consequently, the atoms in the ring do not lie in one plane.
Some structures of alicyclics are:
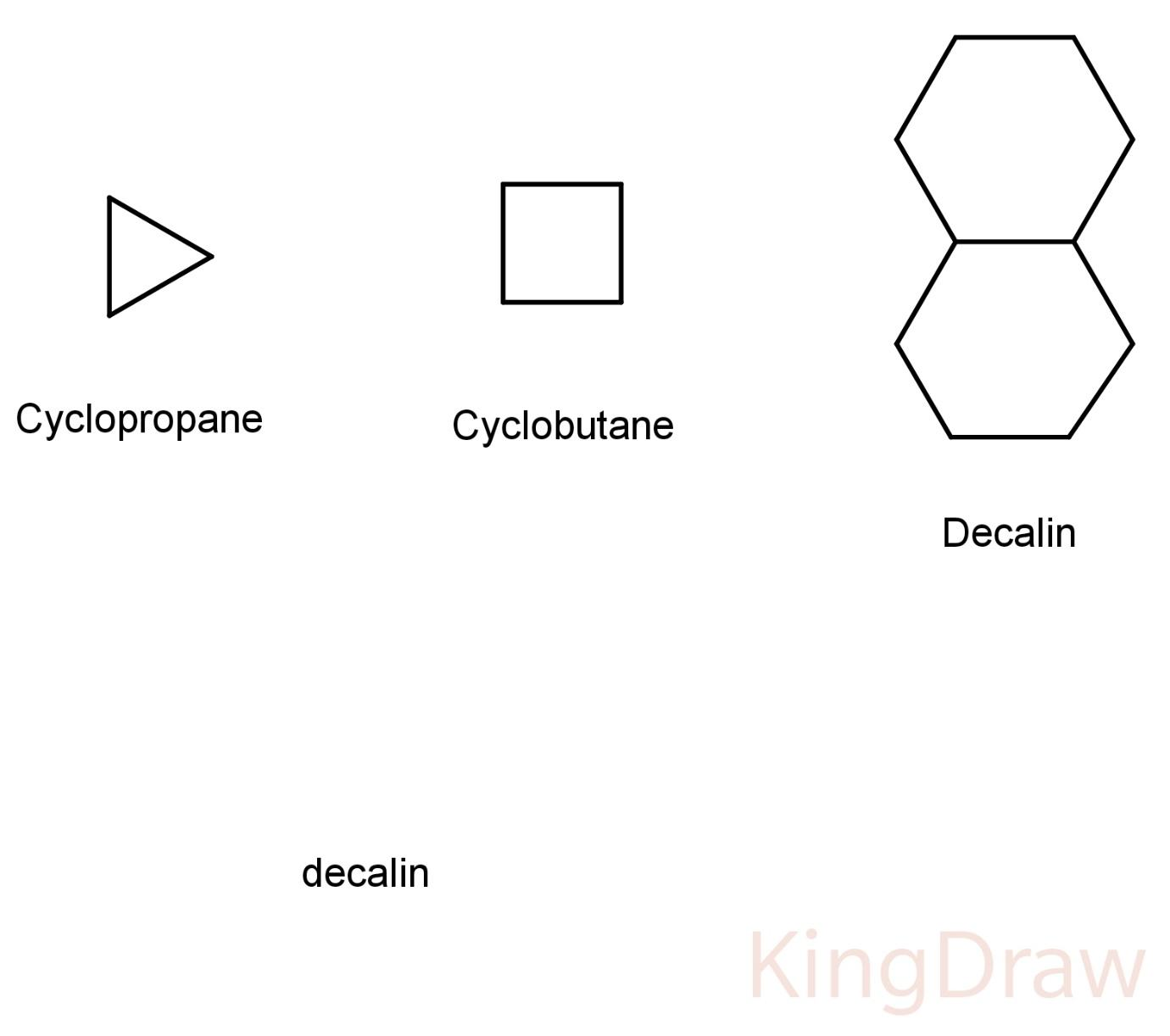
Hence, the correct answer is (B) aliphatic cyclic compounds.
Note: A student must know that homocyclic organic compounds are classified into aromatic and alicyclic compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
The compounds which have one or more all-carbon rings, either saturated or unsaturated but do not have aromatic character are called alicyclic compounds. In other words, alicyclic compounds are aliphatic cyclic compounds. The bonds between pairs of adjacent atoms may all be of the type designated single bonds (involving two electrons), or some of them may be double or triple bonds (with four or six electrons, respectively); six-membered rings for which a system of alternating single and double bonds may be envisioned. Alicyclic compounds may have one or more aliphatic side chains attached.
The simplest alicyclic compounds are the monocyclic cycloalkanes. Monocyclic cycloalkanes include: cyclopropane, cyclobutene, cyclopentane, cyclohexane, cycloheptane, cyclooctane, etc.
Bicyclic alkanes include: bicyclo undecane, decalin, etc.
Polycyclic alkanes include cubane, basketane and tetrahedrane.
The smallest alicyclic compound is cyclopropane. The mode of ring-closing in the formation of many alicyclic compounds can be predicted by Baldwin's rules.
Those alicyclic compounds in which the ring contains three or four carbon atoms are less stable than the compounds having larger rings, because the angles formed by adjacent covalent bonds are smaller than is necessary for maximum effectiveness. In the larger rings all the bond angles have the preferred value (about 109.5°); consequently, the atoms in the ring do not lie in one plane.
Some structures of alicyclics are:

Hence, the correct answer is (B) aliphatic cyclic compounds.
Note: A student must know that homocyclic organic compounds are classified into aromatic and alicyclic compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




