
Aldehydes other than formaldehyde react with Grignard’s reagent to give addition products which on hydrolysis give:
A. tertiary alcohols
B. secondary alcohols
C. primary alcohols
D. carboxylic acids
Answer
520.8k+ views
Hint: Aldehyde reacts with Grignard’s reagent to give organometallic compounds. Which on further hydrolysis gives alcohols. Grignard’s reagent is magnesium alkyl halide, which is formed when alkyl halide is reacted with magnesium.
Complete answer:
- We will take an aldehyde like acetaldehyde and react it with Grignard reagent then it will give additional products, which on hydrolysis will give secondary alcohol. We can see the reaction:
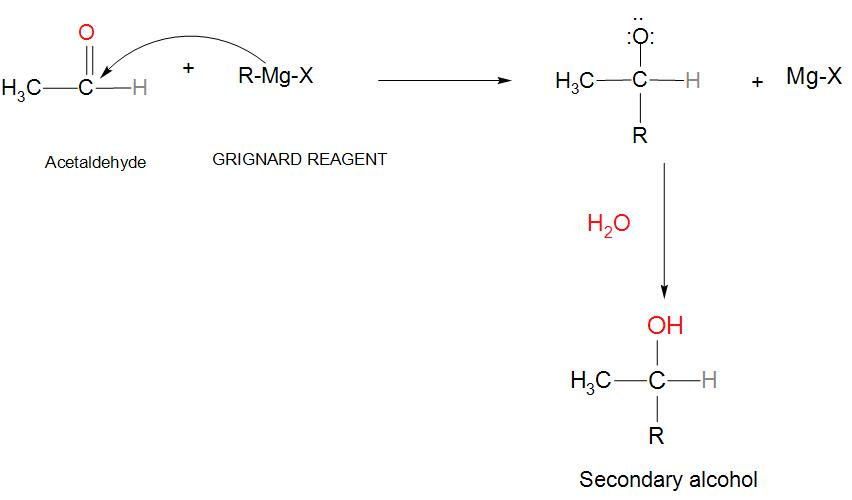
- If we take an Aldehyde like acetaldehyde and when it reacts with Grignard’s reagent (that is an alkyl halide mixed with Mg). We can see that the carbonyl carbon of acetaldehyde is having positive charge and the oxygen is having negative charge.
- When it is attacked with Grignard reagent, at that time it will push the double bond between carbon and oxygen to become a lone pair around the oxygen, and we get the product along with Mg-Halide.
- In the next step the products are mixed up with some aqueous acid and we get a secondary alcohol as our main product.
Hence, we can conclude that option (B) is correct, that aldehydes other than formaldehyde react with Grignard’s reagent to give additional products which on hydrolysis give secondary alcohols.
Note:
- All the aldehydes except formaldehyde when reacted with Grignard’s reagent will give secondary alcohol. Formaldehyde will give primary alcohol.
- Ketones also react with Grignard’s reagent to give alcohol.
Complete answer:
- We will take an aldehyde like acetaldehyde and react it with Grignard reagent then it will give additional products, which on hydrolysis will give secondary alcohol. We can see the reaction:

- If we take an Aldehyde like acetaldehyde and when it reacts with Grignard’s reagent (that is an alkyl halide mixed with Mg). We can see that the carbonyl carbon of acetaldehyde is having positive charge and the oxygen is having negative charge.
- When it is attacked with Grignard reagent, at that time it will push the double bond between carbon and oxygen to become a lone pair around the oxygen, and we get the product along with Mg-Halide.
- In the next step the products are mixed up with some aqueous acid and we get a secondary alcohol as our main product.
Hence, we can conclude that option (B) is correct, that aldehydes other than formaldehyde react with Grignard’s reagent to give additional products which on hydrolysis give secondary alcohols.
Note:
- All the aldehydes except formaldehyde when reacted with Grignard’s reagent will give secondary alcohol. Formaldehyde will give primary alcohol.
- Ketones also react with Grignard’s reagent to give alcohol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




