
Adenine pairs with Thymine through:
A) Two hydrogen bonds
B) One hydrogen bond
C) Three hydrogen bonds
D) Four hydrogen bonds
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Adenine and Thymine are the nitrogenous bases that are found attached with the pentose sugar in Nucleic Acids. In DNA, there are four nitrogenous bases found called Adenine, Thymine, Guanine and Cytosine. However, in RNA, Thymine is replaced with another Nitrogenous base called Uracil.
Complete answer:
Nucleic acids can be considered as the polymers of Nucleotides, where each nucleotide is basically a pentose sugar (Ribose in case of RNA and Deoxyribose in case of DNA) attached with a Nitrogenous base and a Phosphate group. These nucleotides are attached to each other by means of Phophodiester bonds.
There are two types of Nitrogenous bases that are found in the nucleic acids. These are: Purines and Pyrimidines. Adenine and Guanine are Purines while Thymine, Uracil and Cytosine are Pyrimidines. There structures are best shown as:
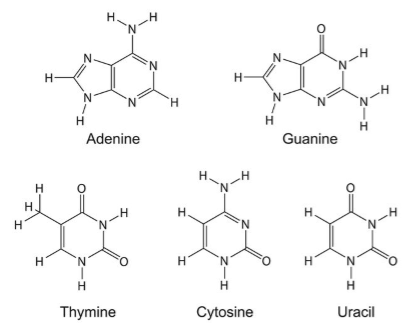
Nitrogenous bases attached to the pentose sugar alone (no phosphate group attached) are called Nucleosides.
Once the nucleotides polymerise, they form a long chain of nucleic acid. Two such long chains with complementary bases present opposite to each other get bonded with the help of hydrogen bonds between the complementary nitrogen bases to form a double stranded structure.
Adenine always forms two hydrogen bonds with Thymine (in case of DNA) and Uracil (in case of RNA) while Cytosine always forms three hydrogen bonds with Guanine.
This can be easily understood with the following diagram:
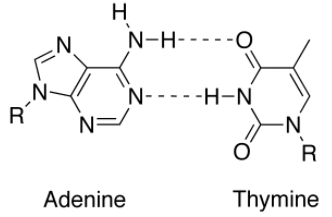
So, the correct answer would be option (A).
Note: Students generally get confused between the idea of Nucleotide and Nucleoside. Always remember, a nucleoside along with a phosphate group is called a nucleotide. Nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.
Complete answer:
Nucleic acids can be considered as the polymers of Nucleotides, where each nucleotide is basically a pentose sugar (Ribose in case of RNA and Deoxyribose in case of DNA) attached with a Nitrogenous base and a Phosphate group. These nucleotides are attached to each other by means of Phophodiester bonds.
There are two types of Nitrogenous bases that are found in the nucleic acids. These are: Purines and Pyrimidines. Adenine and Guanine are Purines while Thymine, Uracil and Cytosine are Pyrimidines. There structures are best shown as:

Nitrogenous bases attached to the pentose sugar alone (no phosphate group attached) are called Nucleosides.
Once the nucleotides polymerise, they form a long chain of nucleic acid. Two such long chains with complementary bases present opposite to each other get bonded with the help of hydrogen bonds between the complementary nitrogen bases to form a double stranded structure.
Adenine always forms two hydrogen bonds with Thymine (in case of DNA) and Uracil (in case of RNA) while Cytosine always forms three hydrogen bonds with Guanine.
This can be easily understood with the following diagram:

So, the correct answer would be option (A).
Note: Students generally get confused between the idea of Nucleotide and Nucleoside. Always remember, a nucleoside along with a phosphate group is called a nucleotide. Nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




