
Addition of hydrogen bromide to propene yields $2 - bromopropane$, while in the presence of benzoyl peroxide, the same reaction yields $1 - bromopropane$. Explain and give mechanism.
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: We know that Markovnikov’s rule is employed to predict regioselectivity of electrophilic addition reactions of alkenes and alkynes. It states that, in hydrohalogenation of an unsymmetrical alkene, the atom within the hydrogen halide forms a bond with the doubly bonded atom within the alkene, bearing the greater number of hydrogen atoms.
Complete step by step answer: Let we see details about the formation of 1-bromopropane and 2-bromopropane.
Formation of 2-Bromopropane:
Addition to HBr to propene (unsymmetrical alkene) follows Markovnikov Rule according to which the negative part of the addition gets attached to that C atom which possesses a lesser number of hydrogen atoms. The reaction proceeds via an ionic mechanism and forms carbocation as intermediate. Secondary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation.
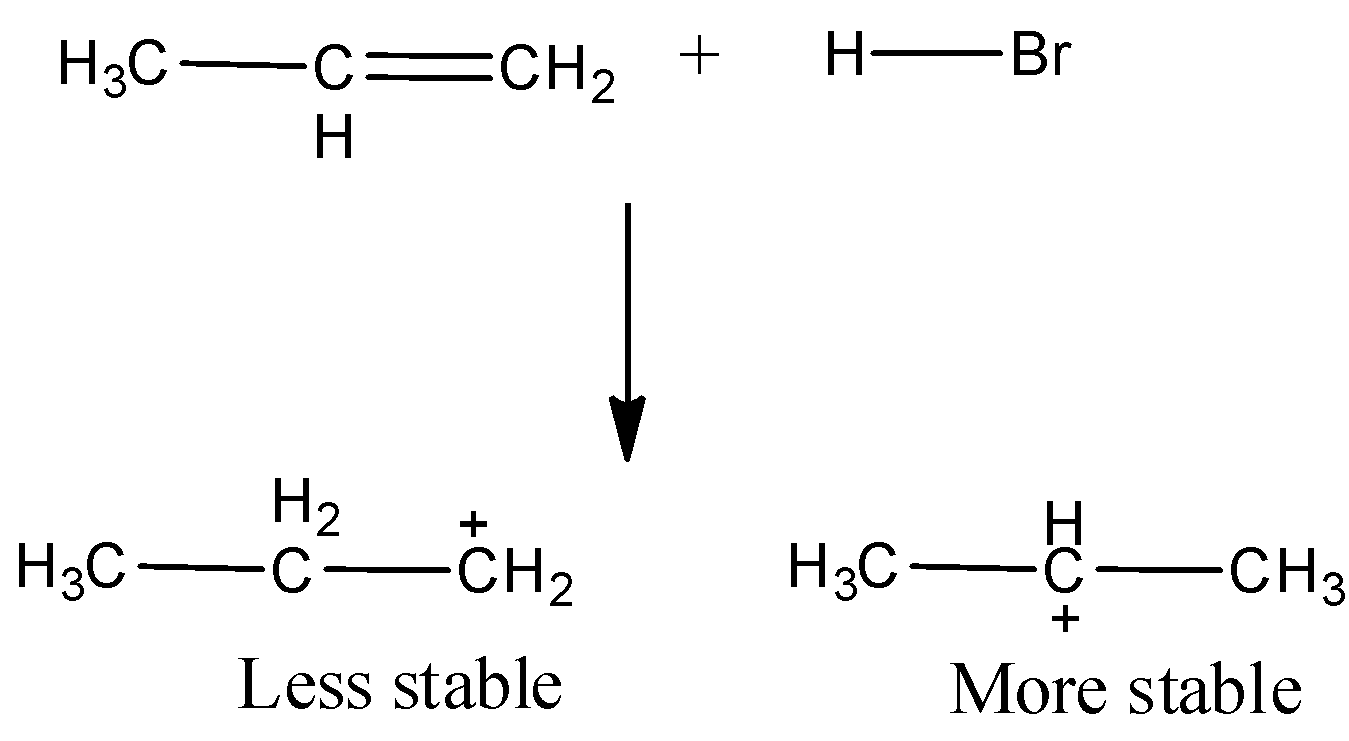
We know that the secondary carbocations are more stable than primary carbocation. Hence, in the next step, bromine attacks the secondary carbocation to form $2 - bromopropane$as the major product.

Formation of 1-Bromopropane:
In the presence of benzoyl peroxide, addition to\[\;HBr\] to propene gives\[1{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}bromopropane\] via anti Markovnikov’s rule. This happens in the presence of peroxide and with \[\;HBr\] only. The reaction proceeds through a free radical mechanism.
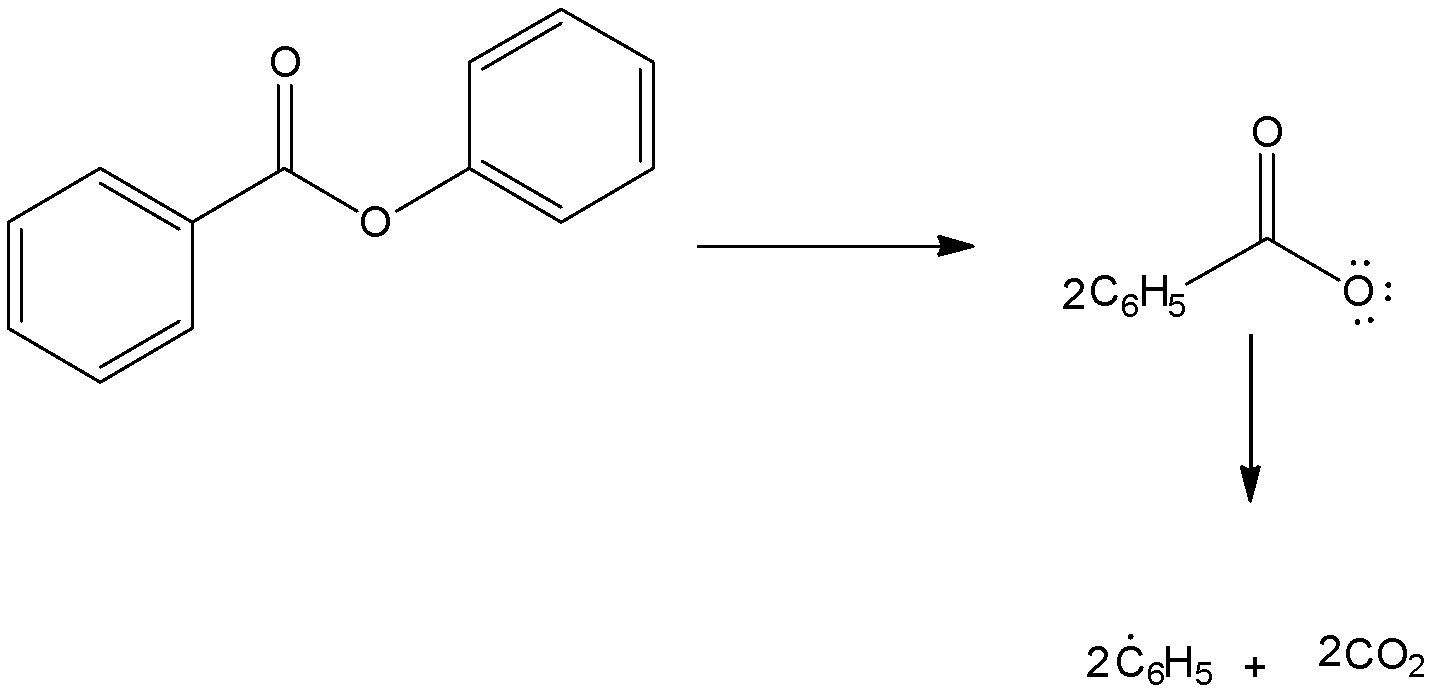
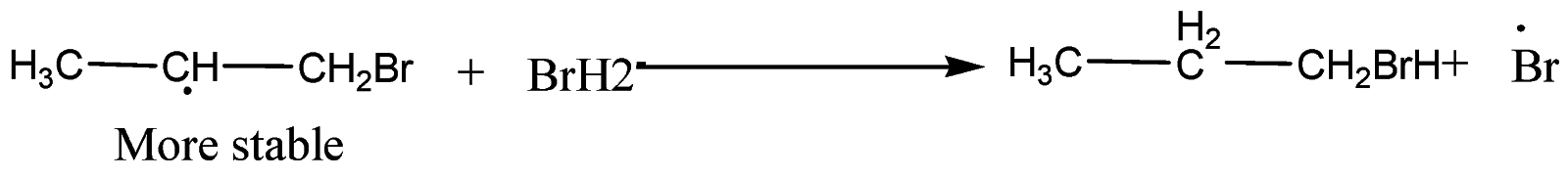
Step-1: Formation of radical
Step-2: Formation of Br radical
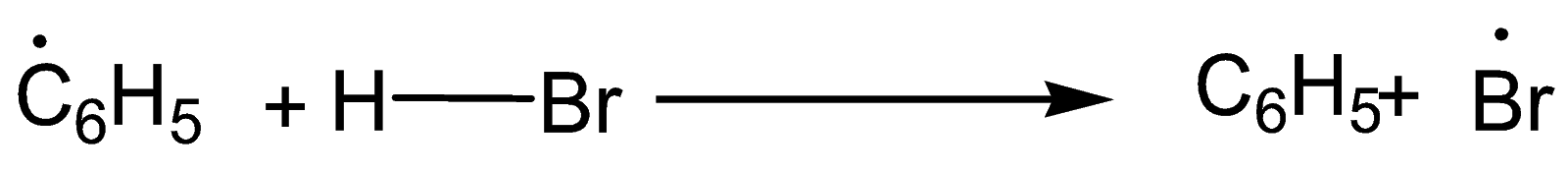
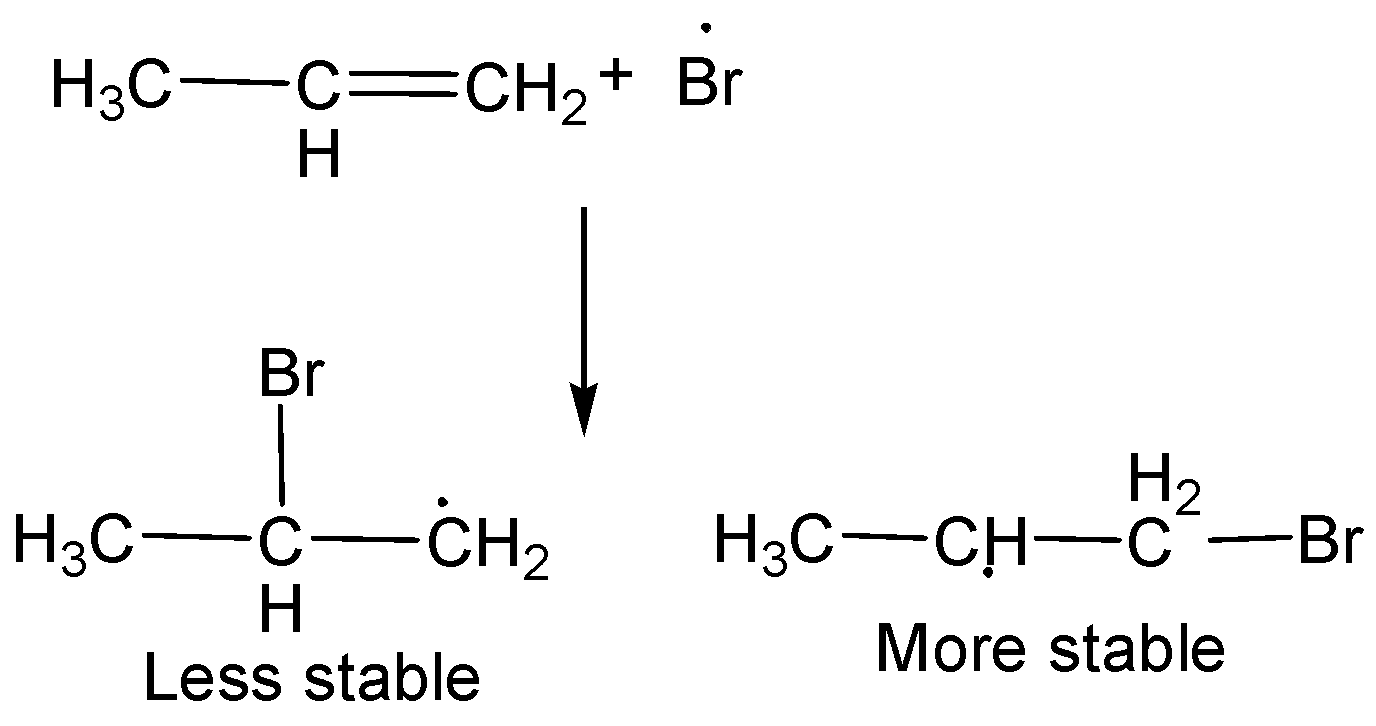
Step-3: Formation of mixture of 1-Bromopropane and 2-Bromopropane
We know that,
Secondary free radicals are more stable than primary radicals and thus, $1 -bromopropane$ is obtained as the major product.
Note: We must remember that in the presence of peroxide,$Br$ free radical acts as an electrophile. Hence, two different products are obtained in addition to \[HBr\] to propene in the absence and presence of peroxide.
Complete step by step answer: Let we see details about the formation of 1-bromopropane and 2-bromopropane.
Formation of 2-Bromopropane:
Addition to HBr to propene (unsymmetrical alkene) follows Markovnikov Rule according to which the negative part of the addition gets attached to that C atom which possesses a lesser number of hydrogen atoms. The reaction proceeds via an ionic mechanism and forms carbocation as intermediate. Secondary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation.

We know that the secondary carbocations are more stable than primary carbocation. Hence, in the next step, bromine attacks the secondary carbocation to form $2 - bromopropane$as the major product.

Formation of 1-Bromopropane:
In the presence of benzoyl peroxide, addition to\[\;HBr\] to propene gives\[1{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}bromopropane\] via anti Markovnikov’s rule. This happens in the presence of peroxide and with \[\;HBr\] only. The reaction proceeds through a free radical mechanism.
Step-1: Formation of radical

Step-2: Formation of Br radical
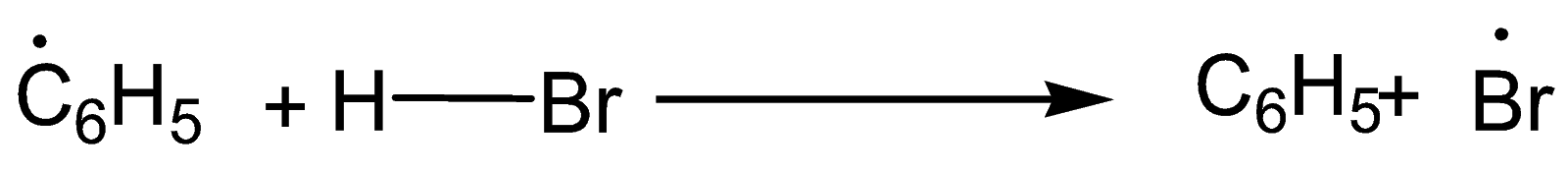
Step-3: Formation of mixture of 1-Bromopropane and 2-Bromopropane

We know that,
Secondary free radicals are more stable than primary radicals and thus, $1 -bromopropane$ is obtained as the major product.

Note: We must remember that in the presence of peroxide,$Br$ free radical acts as an electrophile. Hence, two different products are obtained in addition to \[HBr\] to propene in the absence and presence of peroxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




