
What acts as an inducer in lac operon? How does it switch on the operon?
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint:An operon is a unit of linked genes that regulates protein synthesis by other genes. A lac operon or a lactose operon is a unit required for the metabolism and transport of lactose inside bacterial cells. It is extensively studied in E. coli.
Complete answer:A lactose operon is an operon unit present on the genome of many enteric (gut) bacteria and E. coli. It regulates the transport and metabolism of lactose. Lactose is a sugar that is required for energy production when glucose is not present. It is a secondary food for bacterial cells and glucose is the preferred food source. The lac operon utilized the beta-galactosidase activity to digest lactose in place of glucose. The lac operon is the first to represent the genetic regulatory mechanism of prokaryotic gene regulation.
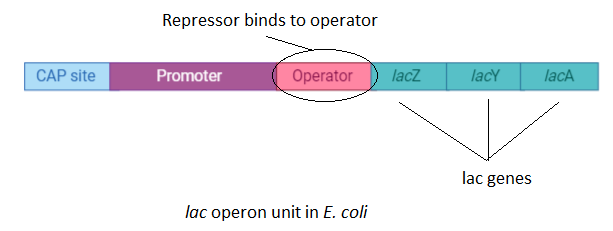
The bacterial operons are polycistronic transcripts. This means that they are capable of producing multiple proteins from one mRNA transcript unit. In the lac operon, lactose is required as a sugar source to stimulate the three genes of the lac operon. These genes are lacZ, lacA, and lacY. These genes produce beta-galactosidase, Transacetylase, and Permease respectively. Thus, lactose acts as an inducer that controls the switching on and off of the lac operon.
Once the lactose molecules enter the E. coli cells they bind to the repressor bind to the operator of the lac operon. The repressor is responsible for the inactivity of the lac operon. So, when it attaches to lactose, the operator of the lac operon becomes free and this is called switching on of lac operon. This is caused by conformational changes in the binding site to the operator. The free operator unit causes RNA polymerase to move over the structural gene. Transcription of the structural gene occurs making a polycistronic mRNA molecule. This mRNA molecule translates to form the three enzymes by genes Z, A, and Y.
Hence, the inducer for lac operon is lactose.
Note:The lac gene and its derivatives are utilized as a reporter gene in selection techniques for bacterial species. The switching on of lac operon releases beta-galactosidase which turns X-gal in the Lactose broth plates of bacterial cultures blue in color from white. Thus it acts as a selection mechanism for specific enteric bacterial colonies growing over plates in a lab.
Complete answer:A lactose operon is an operon unit present on the genome of many enteric (gut) bacteria and E. coli. It regulates the transport and metabolism of lactose. Lactose is a sugar that is required for energy production when glucose is not present. It is a secondary food for bacterial cells and glucose is the preferred food source. The lac operon utilized the beta-galactosidase activity to digest lactose in place of glucose. The lac operon is the first to represent the genetic regulatory mechanism of prokaryotic gene regulation.

The bacterial operons are polycistronic transcripts. This means that they are capable of producing multiple proteins from one mRNA transcript unit. In the lac operon, lactose is required as a sugar source to stimulate the three genes of the lac operon. These genes are lacZ, lacA, and lacY. These genes produce beta-galactosidase, Transacetylase, and Permease respectively. Thus, lactose acts as an inducer that controls the switching on and off of the lac operon.
Once the lactose molecules enter the E. coli cells they bind to the repressor bind to the operator of the lac operon. The repressor is responsible for the inactivity of the lac operon. So, when it attaches to lactose, the operator of the lac operon becomes free and this is called switching on of lac operon. This is caused by conformational changes in the binding site to the operator. The free operator unit causes RNA polymerase to move over the structural gene. Transcription of the structural gene occurs making a polycistronic mRNA molecule. This mRNA molecule translates to form the three enzymes by genes Z, A, and Y.
Hence, the inducer for lac operon is lactose.
Note:The lac gene and its derivatives are utilized as a reporter gene in selection techniques for bacterial species. The switching on of lac operon releases beta-galactosidase which turns X-gal in the Lactose broth plates of bacterial cultures blue in color from white. Thus it acts as a selection mechanism for specific enteric bacterial colonies growing over plates in a lab.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




