
What is the action of following compounds on cyclohexanone in presence of dry hydrogen chloride?
Ethylene Glycol
Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint: Glycol is a class of organic compounds belonging to the alcohol family. The most important feature of these molecules are the two hydroxyl groups attached to different carbon atoms in the molecule.
The simplest of these is ethylene glycol.
Cyclohexanone is an organic compound with the formula \[{(C{H_2})_5}CO\] . The molecule is a cyclic molecule of 6 carbon atoms with a ketone functional group.
Complete answer:
Ethylene glycol has the following structure:
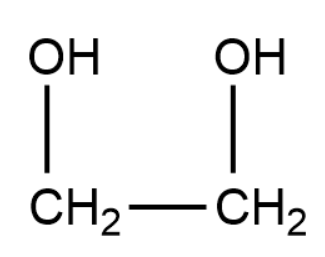
Cyclohexanone has the following structure:
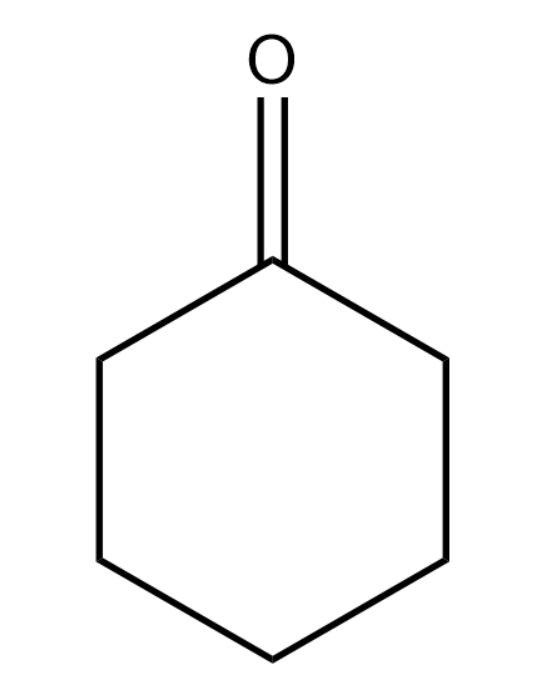
We know that ketones will react with ethylene glycol in the presence of dry hydrogen chloride to form cyclic products known as ethylene glycol ketals. Dry hydrogen chloride will protonate the oxygen of the carbonyl compounds and therefore, increase the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon. This will facilitate the nucleophilic attack of ethylene glycol. Acetals (alkoxyalcohol intermediate formed from aldehydes) and ketals are hydrolysed with aqueous mineral acids to yield corresponding aldehydes and ketones respectively.
This is one of the most important nucleophilic reactions that ketones and aldehydes undergo.
The product obtained in the above reaction is a ketal and is given by the following equation:
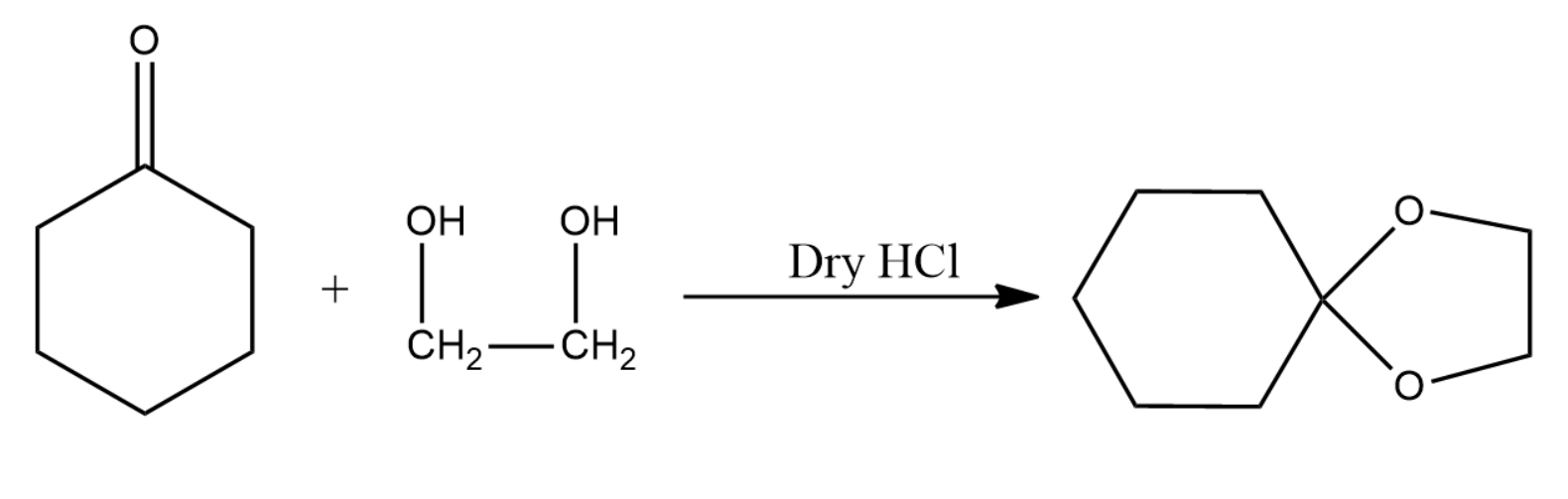
Note:
When aldehydes are treated with alcohols in the presence of any mineral acid, they will for hemiacetals which is an intermediate. Further reaction with one more molecule of alcohol will lead to the formation of a germinal dialkoxy compound known as acetal. Ketals are usually cyclic products whereas acetals may or may not be cyclic.
The simplest of these is ethylene glycol.
Cyclohexanone is an organic compound with the formula \[{(C{H_2})_5}CO\] . The molecule is a cyclic molecule of 6 carbon atoms with a ketone functional group.
Complete answer:
Ethylene glycol has the following structure:

Cyclohexanone has the following structure:

We know that ketones will react with ethylene glycol in the presence of dry hydrogen chloride to form cyclic products known as ethylene glycol ketals. Dry hydrogen chloride will protonate the oxygen of the carbonyl compounds and therefore, increase the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon. This will facilitate the nucleophilic attack of ethylene glycol. Acetals (alkoxyalcohol intermediate formed from aldehydes) and ketals are hydrolysed with aqueous mineral acids to yield corresponding aldehydes and ketones respectively.
This is one of the most important nucleophilic reactions that ketones and aldehydes undergo.
The product obtained in the above reaction is a ketal and is given by the following equation:

Note:
When aldehydes are treated with alcohols in the presence of any mineral acid, they will for hemiacetals which is an intermediate. Further reaction with one more molecule of alcohol will lead to the formation of a germinal dialkoxy compound known as acetal. Ketals are usually cyclic products whereas acetals may or may not be cyclic.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE




