
Acetic acid is a dimer in benzene due to:
A. condensation reaction
B. hydrogen bonding
C. presence of a carboxylic group
D. presence of hydrogen atom at \[\alpha \] -carbon
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Acetic acid is a carboxylic acid containing \[ - COOH\] a group. It donates protons and shows acidity. It is also called protonic acid. Benzene is a cyclic compound, containing carbon. Benzene is liquid at room temperature, so it can be used as a solvent in many reactions. It can dissolve any organic molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
In the case of acetic acid, due to the presence of \[C - O\] bonds, it is a polar molecule. Due to this polar nature, it can also dissolve into a polar solvent like water. In polar solvents, acetic acid can dissociate and generate protons. Now, benzene is an anion polar molecule. So, dissociation of acetic acid in benzene is not possible.
Therefore, acetic acid molecules form hydrogen bonding in benzene solvent. In this case, the two acetic acid molecules form intermolecular hydrogen bonding and form a dimer. The structure of the dimer is shown below,
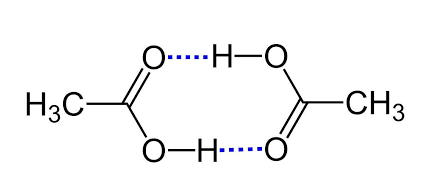
Hence option B is correct.
Additional information:
The acidity of an organic compound is depending upon the electron deficiency of the hydrogen atom. The higher the electron deficiency of the hydrogen higher will be the acidity character of that hydrogen.
Now to be acidic hydrogen that hydrogen should be attached with a high electronegative group or electron-withdrawing group. The higher the electronegativity of the group, the higher will be the electron deficiency of the hydrogen, attached to that group as well as the acidity.
In the case of acetic acid, the hydrogen is attached with the high electronegative oxygen atom, as a result, an electron deficiency is formed on hydrogen, and shows acidity.
The acidity of the carboxylic acid depends upon the electronic nature of the group attached to a carboxylic acid. The higher the electron-withdrawing nature of the group higher will be the acidity and vice-versa.
Note:
Now to be acidic hydrogen that hydrogen should be attached with a high electronegative group or electron-withdrawing group. The higher the electronegativity of the group, the higher will be the electron deficiency of the hydrogen, attached to that group as well as the acidity. Now in the case or carbon, the electronegativity varies with hybridization. With increasing the s character in the hybridization electronegativity of the carbon increases and vice-versa. Now the order of the electronegativity of the different hybridization of carbon Is \[s{p^3} < s{p^2} < sp\] . Therefore, the order of the acidity of the hydrogen attached to these hybridized carbons is \[{C_{s{p^3}}} - H < {C_{s{p^2}}} - H < {C_{sp}} - H\] .
Complete step by step answer:
In the case of acetic acid, due to the presence of \[C - O\] bonds, it is a polar molecule. Due to this polar nature, it can also dissolve into a polar solvent like water. In polar solvents, acetic acid can dissociate and generate protons. Now, benzene is an anion polar molecule. So, dissociation of acetic acid in benzene is not possible.
Therefore, acetic acid molecules form hydrogen bonding in benzene solvent. In this case, the two acetic acid molecules form intermolecular hydrogen bonding and form a dimer. The structure of the dimer is shown below,

Hence option B is correct.
Additional information:
The acidity of an organic compound is depending upon the electron deficiency of the hydrogen atom. The higher the electron deficiency of the hydrogen higher will be the acidity character of that hydrogen.
Now to be acidic hydrogen that hydrogen should be attached with a high electronegative group or electron-withdrawing group. The higher the electronegativity of the group, the higher will be the electron deficiency of the hydrogen, attached to that group as well as the acidity.
In the case of acetic acid, the hydrogen is attached with the high electronegative oxygen atom, as a result, an electron deficiency is formed on hydrogen, and shows acidity.
The acidity of the carboxylic acid depends upon the electronic nature of the group attached to a carboxylic acid. The higher the electron-withdrawing nature of the group higher will be the acidity and vice-versa.
Note:
Now to be acidic hydrogen that hydrogen should be attached with a high electronegative group or electron-withdrawing group. The higher the electronegativity of the group, the higher will be the electron deficiency of the hydrogen, attached to that group as well as the acidity. Now in the case or carbon, the electronegativity varies with hybridization. With increasing the s character in the hybridization electronegativity of the carbon increases and vice-versa. Now the order of the electronegativity of the different hybridization of carbon Is \[s{p^3} < s{p^2} < sp\] . Therefore, the order of the acidity of the hydrogen attached to these hybridized carbons is \[{C_{s{p^3}}} - H < {C_{s{p^2}}} - H < {C_{sp}} - H\] .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




