
When acetaldehyde reacts with \[PC{l_5}\], the resulting compound is:
A. Ethyl chloride
B. Ethylene chloride
C. Ethylidene chloride
D. Trichloroacetaldehyde
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: Aldehyde functional groups consist of carbonyl groups attached to a carbon atom along with hydrogen. Acetaldehyde is the common name for ethanal and the reaction intermediate involved in the given reaction conditions is carbocation.
Complete answer:
When acetaldehyde or ethanal reacts with \[PC{l_5}\], the resulting compound is Ethylidene chloride. The reaction mechanism involved in the formation of product, is as follows:
Step-1: Formation of carbocation:
The lone pairs of oxygen atoms of acetaldehyde attack phosphorus atoms and the double bond of carbonyl group breaks due to which formation of carbocation takes place. The reaction is as follows:
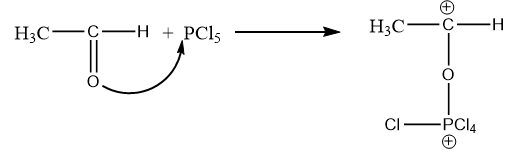
Step-2: Intramolecular attack of chlorine on carbocation:
As chlorine is an electron rich species which results in getting attracted towards the atoms having a positive charge. So, chlorine acts as a nucleophile and intramolecular attack on the carbocation takes place. The reaction is as follows:
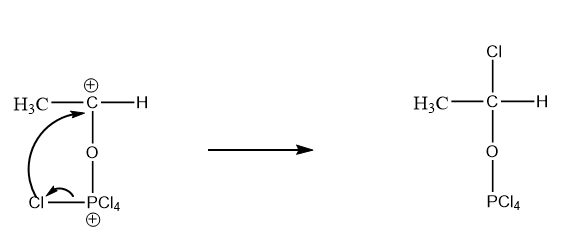
Step-3: Attack of \[{H^ + }\] ion on the oxygen atom of the compound formed.
As the reaction is taking place in an acidic medium, the \[{H^ + }\] ion will attack on the lone pairs of oxygen atoms due to which a positive charge will appear on the oxygen atom. The reaction is as follows:
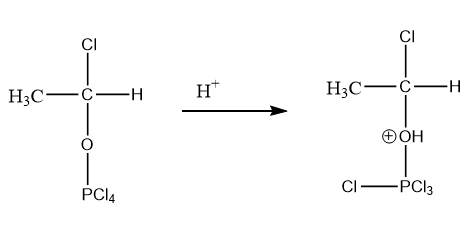
Step-4: Removal of \[POC{l_3}\] takes place:
As we know that when there is a positive charge on the oxygen atom, the compound becomes very unstable. So, by the intramolecular attack of chlorine atoms along with the removal of \[POC{l_3}\] , the formation of gem dichloride or ethylidene chloride takes place. The reaction is as follows:
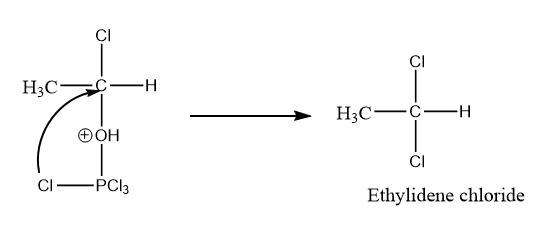
Hence, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
Aldehydes and ketones perform many reactions because of the presence of a carbonyl center in the compound. Due to the presence of carbon-oxygen double bonds, the compounds usually undergo nucleophilic addition reactions. The reaction given in the question was a type of intramolecular nucleophilic addition reaction.
Complete answer:
When acetaldehyde or ethanal reacts with \[PC{l_5}\], the resulting compound is Ethylidene chloride. The reaction mechanism involved in the formation of product, is as follows:
Step-1: Formation of carbocation:
The lone pairs of oxygen atoms of acetaldehyde attack phosphorus atoms and the double bond of carbonyl group breaks due to which formation of carbocation takes place. The reaction is as follows:

Step-2: Intramolecular attack of chlorine on carbocation:
As chlorine is an electron rich species which results in getting attracted towards the atoms having a positive charge. So, chlorine acts as a nucleophile and intramolecular attack on the carbocation takes place. The reaction is as follows:

Step-3: Attack of \[{H^ + }\] ion on the oxygen atom of the compound formed.
As the reaction is taking place in an acidic medium, the \[{H^ + }\] ion will attack on the lone pairs of oxygen atoms due to which a positive charge will appear on the oxygen atom. The reaction is as follows:

Step-4: Removal of \[POC{l_3}\] takes place:
As we know that when there is a positive charge on the oxygen atom, the compound becomes very unstable. So, by the intramolecular attack of chlorine atoms along with the removal of \[POC{l_3}\] , the formation of gem dichloride or ethylidene chloride takes place. The reaction is as follows:

Hence, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
Aldehydes and ketones perform many reactions because of the presence of a carbonyl center in the compound. Due to the presence of carbon-oxygen double bonds, the compounds usually undergo nucleophilic addition reactions. The reaction given in the question was a type of intramolecular nucleophilic addition reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




