
Account for the following:
${{p}}{{{K}}_{{a}}}$ value of $4 - $nitrobenzoic acid is lower than that of benzoic acid.
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: Acid dissociation constant, ${{{K}}_{{a}}}$ measures the strength of an acid in solution quantitatively. If the value of ${{p}}{{{K}}_{{a}}}$ value is small, then the acid will be stronger. Acidity of an organic compound depends upon several factors like inductive effect, resonance effect, etc.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider the dissociation of a compound ${{HA}}$.
${{HA}} \rightleftharpoons {{{H}}^ + } + {{{A}}^ - }$
The acid dissociation constant can be expressed as:
${{{K}}_{{a}}} = \dfrac{{\left[ {{{{A}}^ - }} \right]\left[ {{{{H}}^ + }} \right]}}{{\left[ {{{HA}}} \right]}}$
${{p}}{{{K}}_{{a}}}$ is used because using ${{{K}}_{{a}}}$ will be inconvenient practically. ${{p}}{{{K}}_{{a}}}$ is the negative logarithm of ${{{K}}_{{a}}}$. ${{p}}{{{K}}_{{a}}}$ is expressed as negative logarithm of ${{{K}}_{{a}}}$.
The structure of $4 - $nitrobenzoic acid and benzoic acid is given below:
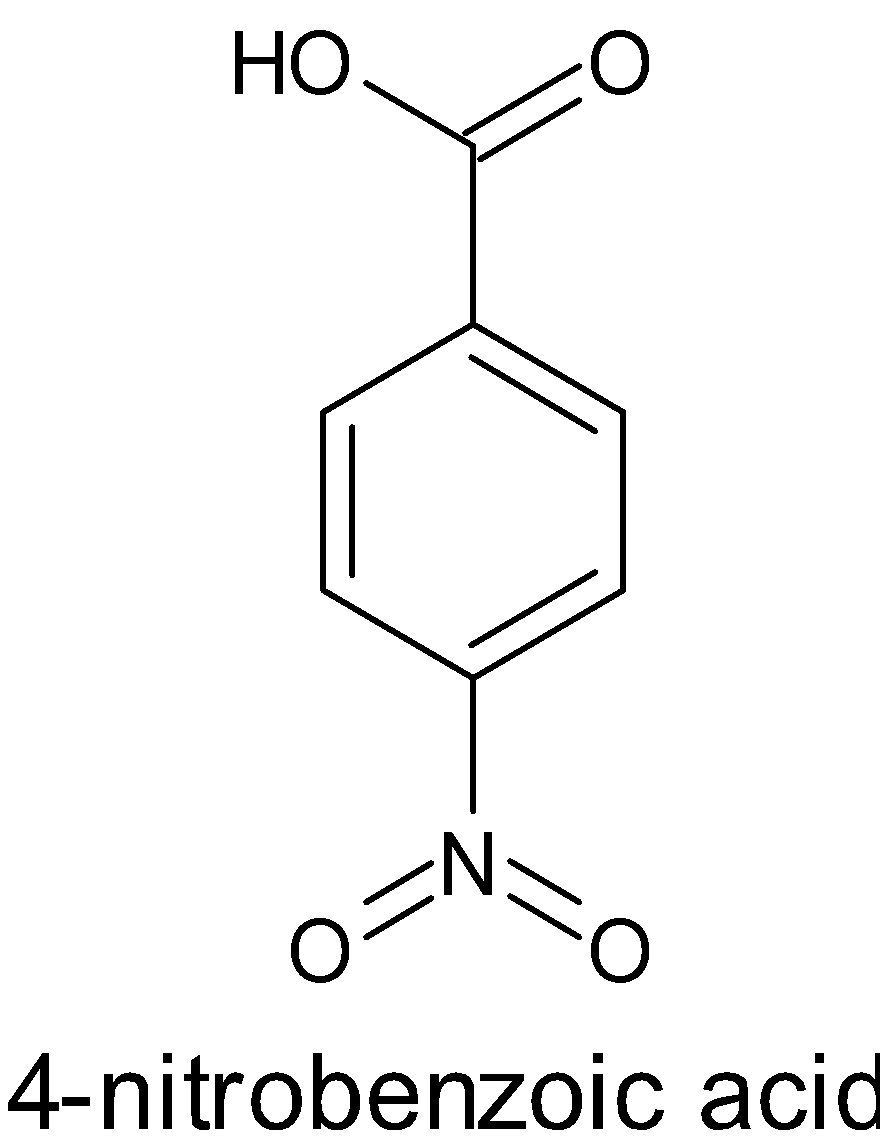
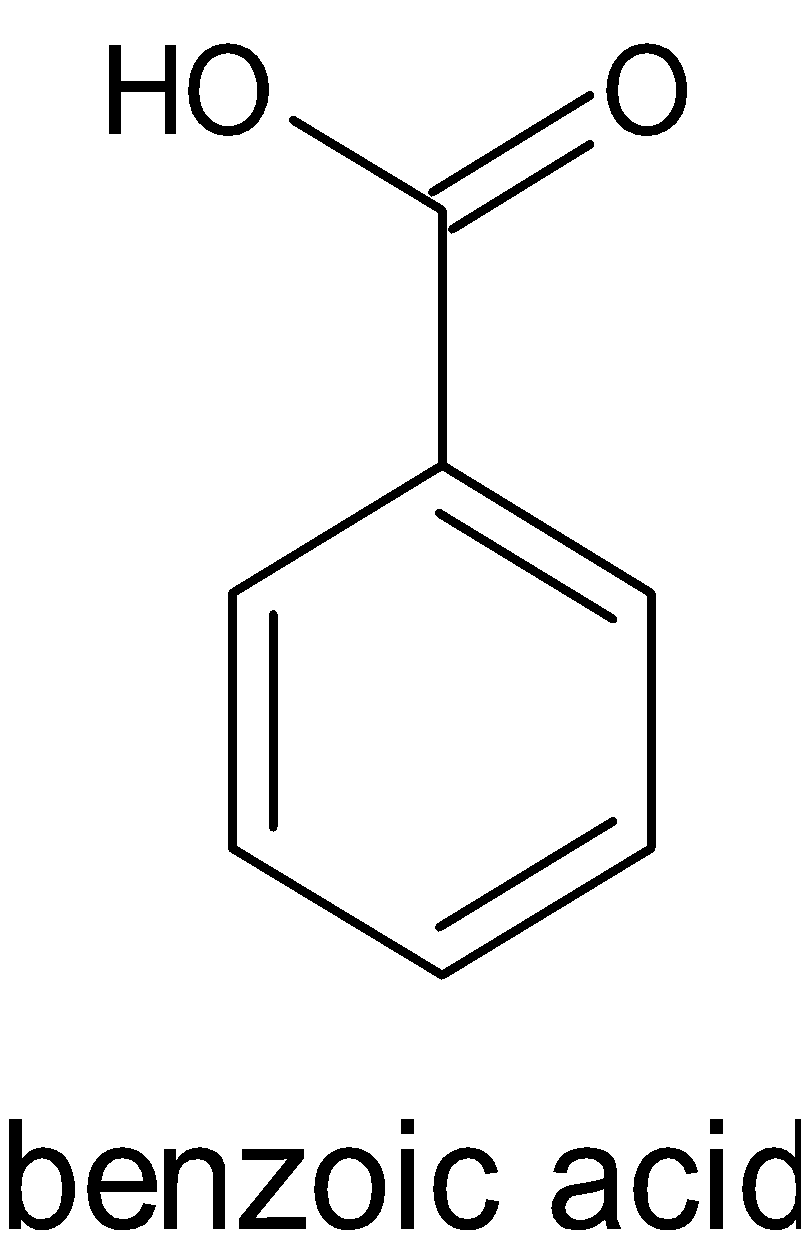
Acids donate protons, \[{{{H}}^ + }\]. Benzoic acid is an acid from the name itself. This gives a base by donating a proton. When this occurs, it forms carboxylate ions. The negative charge in the carboxylate ion is involved in resonance. Resonance structures are the ones in which the position of valence electrons are different. It stabilizes the molecule. Thus it is said to be a strong acid.
When electron withdrawing groups are added to the benzoic acid, it makes the carboxylate ion more stable. Thus the charge of the carboxylate ion will be delocalized.
Some examples of electron withdrawing groups are $ - {{CN}}, - {{N}}{{{O}}_2}, - {{CHO}},$ etc.
When these groups are present, it decreases the electron density of the molecule, thus it is able to accept electrons. This makes the molecule more acidic. This is called $ - {{I}}$ effect or negative inductive effect. When the number of electron withdrawing groups is more, then more stronger will be the acid. $ - {{N}}{{{O}}_2}$ is an electron withdrawing group. Thus it is obvious that the $4 - $nitrobenzoic acid is more acidic than benzoic acid.
Note:
Similarly, when electron donating groups are present, it increases the electron density of the molecule, thus it is able to donate electrons. This makes it more basic. This is called ${{ + I}}$ effect. ${{p}}{{{K}}_{{a}}}$ of $4 - $nitrobenzoic acid is $3.41$ and benzoic acid is $4.19$.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider the dissociation of a compound ${{HA}}$.
${{HA}} \rightleftharpoons {{{H}}^ + } + {{{A}}^ - }$
The acid dissociation constant can be expressed as:
${{{K}}_{{a}}} = \dfrac{{\left[ {{{{A}}^ - }} \right]\left[ {{{{H}}^ + }} \right]}}{{\left[ {{{HA}}} \right]}}$
${{p}}{{{K}}_{{a}}}$ is used because using ${{{K}}_{{a}}}$ will be inconvenient practically. ${{p}}{{{K}}_{{a}}}$ is the negative logarithm of ${{{K}}_{{a}}}$. ${{p}}{{{K}}_{{a}}}$ is expressed as negative logarithm of ${{{K}}_{{a}}}$.
The structure of $4 - $nitrobenzoic acid and benzoic acid is given below:


Acids donate protons, \[{{{H}}^ + }\]. Benzoic acid is an acid from the name itself. This gives a base by donating a proton. When this occurs, it forms carboxylate ions. The negative charge in the carboxylate ion is involved in resonance. Resonance structures are the ones in which the position of valence electrons are different. It stabilizes the molecule. Thus it is said to be a strong acid.
When electron withdrawing groups are added to the benzoic acid, it makes the carboxylate ion more stable. Thus the charge of the carboxylate ion will be delocalized.
Some examples of electron withdrawing groups are $ - {{CN}}, - {{N}}{{{O}}_2}, - {{CHO}},$ etc.
When these groups are present, it decreases the electron density of the molecule, thus it is able to accept electrons. This makes the molecule more acidic. This is called $ - {{I}}$ effect or negative inductive effect. When the number of electron withdrawing groups is more, then more stronger will be the acid. $ - {{N}}{{{O}}_2}$ is an electron withdrawing group. Thus it is obvious that the $4 - $nitrobenzoic acid is more acidic than benzoic acid.
Note:
Similarly, when electron donating groups are present, it increases the electron density of the molecule, thus it is able to donate electrons. This makes it more basic. This is called ${{ + I}}$ effect. ${{p}}{{{K}}_{{a}}}$ of $4 - $nitrobenzoic acid is $3.41$ and benzoic acid is $4.19$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




