
According to Langmuir isotherm, the amount of gas adsorbed at very high pressure:
A. reaches a constant limiting value
B. goes on increasing with pressure
C. goes on decreasing with pressure
D. increases first and decreases later with pressure.
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Adsorption is a phenomenon which involves attracting and retaining the molecules of substance at the surface of liquid or a solid resulting in the higher concentration of molecules at the surface. The substance thus adsorbed on the surface is called adsorbate and the substance on which it is adsorbed is called adsorbent.
Complete step by step answer:
The process of adsorption taking place at a constant temperature but the pressure varies is called adsorption isotherm. It is of two types –
(a) Freundlich’s adsorption isotherm
(b) Langmuir adsorption isotherm.
Langmuir adsorption isotherm:
The Langmuir adsorption isotherm is used to describe the equilibrium between adsorbate and adsorbent system, where the adsorbate adsorption is limited to one molecular layer at or before a relative pressure of unity is reached.
Langmuir’s adsorption isotherm is based on the kinetic theory of gases. Langmuir considered adsorption to consist of the following two opposing processes.
(i) Adsorption of the gas molecules on the surface of the solid.
(ii) Desorption of the adsorbed molecules from the surface of the solid.
In the Langmuir model, the adsorbent surface is considered to possess a number of active interaction sites for adsorption. Langmuir derived a relation between adsorbed material and its equilibrium concentration, i.e.
$\dfrac{x}{m} = K{C_e}^{\frac{1}{n}}$
Where x = mass of solute adsorbed
m = Mass of adsorbent
${C_e} = $Equilibrium concentration of solute
$K,{\text{ n}} = $Equilibrium constant
Thus, the adsorption can be given by the following Langmuir expression,
$\dfrac{x}{m} = \dfrac{{ap}}{{1 + bp}}$
Where x = mass of gas in gm
m = Mass of adsorbent in gm
p = Pressure
a and b = Langmuir parameter
Validity of Langmuir adsorption isotherm:
(a) At moderate pressure$;\dfrac{x}{m} = \dfrac{{ap}}{{1 + bp}}$
(b) At low pressure; bp < < 1
$\therefore \dfrac{x}{m} = ap{\text{ i}}{\text{.e}}{\text{. }}\dfrac{x}{m} \propto p$
(c) At high pressure$;{\text{ bp}} > > 1$
$\therefore \dfrac{x}{m} = \dfrac{{ap}}{{bp}} = \dfrac{a}{b} = $constant
The Langmuir expression can be represented as under
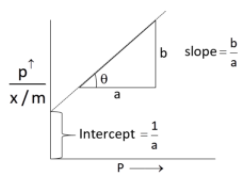
$\dfrac{x}{m} = \dfrac{{ap}}{{1 + bp}}{\text{ or }}\dfrac{{x/m}}{p} = \dfrac{a}{{1 + bp}}$
On taking reciprocal,
\[\dfrac{p}{{x/m}} = \dfrac{{1 + bp}}{a} = \dfrac{1}{a} + \dfrac{{bp}}{a}\]
Since, a and b are constant. Hence, graph between $\dfrac{p}{{x/m}}$ and p should be a straight line and the slope is equal to $\dfrac{b}{a}$, intercept is equal to $\dfrac{1}{a}$.
According to Langmuir adsorption, the amount of gas adsorbed at a very high pressure, reaches a constant limiting value.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: The process of adsorption depends on the nature of gas, temperature, pressure and surface area of adsorbent. The isotherm explains the effect of pressure on the process of adsorption. But the pressure does not play the same role after reaching a saturation value. The process of adsorption stops when the surface area of adsorbent is fully covered but there is a dynamic equilibrium between adsorption and desorption. The adsorbing gas adsorbs into an immobile state. Each site can hold at most one molecule of mono – layer coverage only, no interaction between adsorbate molecules on adjacent sites.
Complete step by step answer:
The process of adsorption taking place at a constant temperature but the pressure varies is called adsorption isotherm. It is of two types –
(a) Freundlich’s adsorption isotherm
(b) Langmuir adsorption isotherm.
Langmuir adsorption isotherm:
The Langmuir adsorption isotherm is used to describe the equilibrium between adsorbate and adsorbent system, where the adsorbate adsorption is limited to one molecular layer at or before a relative pressure of unity is reached.
Langmuir’s adsorption isotherm is based on the kinetic theory of gases. Langmuir considered adsorption to consist of the following two opposing processes.
(i) Adsorption of the gas molecules on the surface of the solid.
(ii) Desorption of the adsorbed molecules from the surface of the solid.
In the Langmuir model, the adsorbent surface is considered to possess a number of active interaction sites for adsorption. Langmuir derived a relation between adsorbed material and its equilibrium concentration, i.e.
$\dfrac{x}{m} = K{C_e}^{\frac{1}{n}}$
Where x = mass of solute adsorbed
m = Mass of adsorbent
${C_e} = $Equilibrium concentration of solute
$K,{\text{ n}} = $Equilibrium constant
Thus, the adsorption can be given by the following Langmuir expression,
$\dfrac{x}{m} = \dfrac{{ap}}{{1 + bp}}$
Where x = mass of gas in gm
m = Mass of adsorbent in gm
p = Pressure
a and b = Langmuir parameter
Validity of Langmuir adsorption isotherm:
(a) At moderate pressure$;\dfrac{x}{m} = \dfrac{{ap}}{{1 + bp}}$
(b) At low pressure; bp < < 1
$\therefore \dfrac{x}{m} = ap{\text{ i}}{\text{.e}}{\text{. }}\dfrac{x}{m} \propto p$
(c) At high pressure$;{\text{ bp}} > > 1$
$\therefore \dfrac{x}{m} = \dfrac{{ap}}{{bp}} = \dfrac{a}{b} = $constant
The Langmuir expression can be represented as under
$\dfrac{x}{m} = \dfrac{{ap}}{{1 + bp}}{\text{ or }}\dfrac{{x/m}}{p} = \dfrac{a}{{1 + bp}}$
On taking reciprocal,
\[\dfrac{p}{{x/m}} = \dfrac{{1 + bp}}{a} = \dfrac{1}{a} + \dfrac{{bp}}{a}\]
Since, a and b are constant. Hence, graph between $\dfrac{p}{{x/m}}$ and p should be a straight line and the slope is equal to $\dfrac{b}{a}$, intercept is equal to $\dfrac{1}{a}$.

According to Langmuir adsorption, the amount of gas adsorbed at a very high pressure, reaches a constant limiting value.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: The process of adsorption depends on the nature of gas, temperature, pressure and surface area of adsorbent. The isotherm explains the effect of pressure on the process of adsorption. But the pressure does not play the same role after reaching a saturation value. The process of adsorption stops when the surface area of adsorbent is fully covered but there is a dynamic equilibrium between adsorption and desorption. The adsorbing gas adsorbs into an immobile state. Each site can hold at most one molecule of mono – layer coverage only, no interaction between adsorbate molecules on adjacent sites.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




