
According to Huckel’s rule, a compound is said to be aromatic, if it contains:
a. - (4n+2) $\pi $ bonds
b. - (4n+2) $\sigma $ bonds
c. - (4n+2) carbon atoms
d.- (4n+2) $\pi $ electrons
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: In organic compounds, Hückel's rule helps in deciding whether a planar ring molecule will have aromatic properties or not.
Complete answer:
Aromatic compounds are more stable than theoretically predicted as for simple alkenes; the additional stability is due to the delocalized cloud of electrons, called resonance energy.
Properties of simple aromatic compound are:
1.-The molecule must have $4n + 2$ electrons in a conjugated system of p orbitals,on \[s{p^2}\]-hybridized atoms ( i.e. huckel’s rule )
2.-The molecule must be (close to) planar (implicit in the requirement for conjugation).
3.-The molecule must be cyclic.
4.-The molecule must have a continuous ring of p atomic orbitals (there cannot be any \[\;s{p^3}\;\] atoms in the ring).
Let’s talk about Huckel’s $4n + 2$ Pi Electron Rule.A ring-shaped cyclic molecule is said to follow the Huckel rule when the total number of pi electrons belonging to the molecule can be equated to the formula ($4n+2$) where n can be any integer with a positive value (including zero).
For example, molecules following Huckel’s rule have only been established for values of ‘n’ ranging from zero to six.
The total number of pi electrons in the benzene molecule depicted below can be found to be 6, obeying the $4n+2$ $\pi $ electron rule where $n=1$.
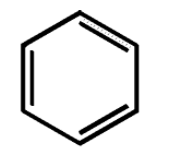
Thus, the benzene molecule is an aromatic compound as it obeys the Huckel rule.
In such way Huckel’s rule is used for identifying aromatic compounds, having ($4n+2$) $\pi $ electrons (values of ‘n’ ranging from zero to six)
Hence the correct option is (d) ($4n+2$) $\pi $ electrons.
Note:
Don’t get confused with ($4n+2$) $\pi $ electrons and ($4n+2$) $\pi $bonds. Both are different things. No. of electrons is always double then the number of bonds.
Complete answer:
Aromatic compounds are more stable than theoretically predicted as for simple alkenes; the additional stability is due to the delocalized cloud of electrons, called resonance energy.
Properties of simple aromatic compound are:
1.-The molecule must have $4n + 2$ electrons in a conjugated system of p orbitals,on \[s{p^2}\]-hybridized atoms ( i.e. huckel’s rule )
2.-The molecule must be (close to) planar (implicit in the requirement for conjugation).
3.-The molecule must be cyclic.
4.-The molecule must have a continuous ring of p atomic orbitals (there cannot be any \[\;s{p^3}\;\] atoms in the ring).
Let’s talk about Huckel’s $4n + 2$ Pi Electron Rule.A ring-shaped cyclic molecule is said to follow the Huckel rule when the total number of pi electrons belonging to the molecule can be equated to the formula ($4n+2$) where n can be any integer with a positive value (including zero).
For example, molecules following Huckel’s rule have only been established for values of ‘n’ ranging from zero to six.
The total number of pi electrons in the benzene molecule depicted below can be found to be 6, obeying the $4n+2$ $\pi $ electron rule where $n=1$.

Thus, the benzene molecule is an aromatic compound as it obeys the Huckel rule.
In such way Huckel’s rule is used for identifying aromatic compounds, having ($4n+2$) $\pi $ electrons (values of ‘n’ ranging from zero to six)
Hence the correct option is (d) ($4n+2$) $\pi $ electrons.
Note:
Don’t get confused with ($4n+2$) $\pi $ electrons and ($4n+2$) $\pi $bonds. Both are different things. No. of electrons is always double then the number of bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




