
Acceleration-time graph of a freely falling body is:
A.)A straight line with positive slope
B.)A straight line with negative slope
C.)A straight line parallel to the time axis
D.)A straight line parallel to the acceleration axis
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: Think about the influencing forces for a body in a state of free fall. In other words, the only accelerative contribution is that of gravity. And the acceleration due to gravity when not subjected to any external forces remains the same throughout. So, in free fall, if the body is gaining velocity at a constant rate then think of what happens to the acceleration.
Complete answer:
Let us begin by understanding what a freely falling body is.
When a body is falling under the sole influence of gravity wherein it is being acted upon only by the force of gravity is called a freely falling body. There are two important notions that model free falling:
(I)The rate of change of velocity remains the same.
(II)All freely falling bodies on Earth accelerate at a rate of $9.8ms^{-2}$ downwards.
This means that a freely falling body undergoes a uniformly accelerated motion, which has the implication that acceleration remains constant throughout. This means that with time, the velocity increases at a constant rate.
If we were to look at the velocity-time graph, it would look something like:
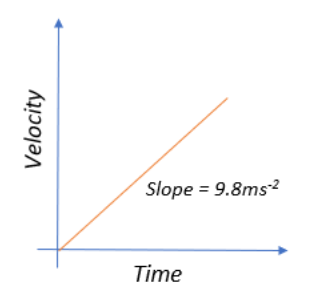
Since the velocity is changing with time, it represents accelerated motion.
We get a diagonal with a constant slope of $9.8ms^{-2}$, which is indicative of constant uniform acceleration, since $acceleration = \dfrac{velocity}{time}$
In this case of constant acceleration where our acceleration does not change with time, we get the following graph:
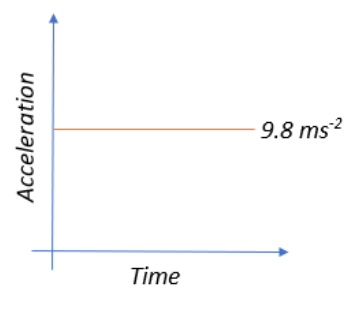
Thus, from the above acceleration-time graph for a freely falling body we can conclude that the right option would be, A straight line parallel to the time axis.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Remember that the acceleration remains constant for a freely falling body because it falls under the influence of only gravity. The velocity changes with time but at a constant rate throughout.
Complete answer:
Let us begin by understanding what a freely falling body is.
When a body is falling under the sole influence of gravity wherein it is being acted upon only by the force of gravity is called a freely falling body. There are two important notions that model free falling:
(I)The rate of change of velocity remains the same.
(II)All freely falling bodies on Earth accelerate at a rate of $9.8ms^{-2}$ downwards.
This means that a freely falling body undergoes a uniformly accelerated motion, which has the implication that acceleration remains constant throughout. This means that with time, the velocity increases at a constant rate.
If we were to look at the velocity-time graph, it would look something like:

Since the velocity is changing with time, it represents accelerated motion.
We get a diagonal with a constant slope of $9.8ms^{-2}$, which is indicative of constant uniform acceleration, since $acceleration = \dfrac{velocity}{time}$
In this case of constant acceleration where our acceleration does not change with time, we get the following graph:

Thus, from the above acceleration-time graph for a freely falling body we can conclude that the right option would be, A straight line parallel to the time axis.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Remember that the acceleration remains constant for a freely falling body because it falls under the influence of only gravity. The velocity changes with time but at a constant rate throughout.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




