
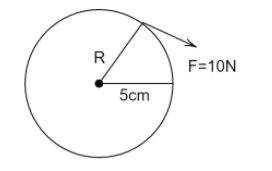
A.Calculate the torque with which the wheel is turning .
B. Which wheel will have more turning effect and why?
i.
ii.
iii.




Answer
484.8k+ views
Hint: The amount of force required to twist an object is measured by torque. For part (A) torque can be found out by the relation between force, radius, and angle between force and lever arm. For part (B) find the individual torque for all three wheels then compare which will have more turning effect.
Complete answer:
Solution of the part (A) -
We have been given the radius of the wheel \[R = 5cm = 0.05m\] and force acting on the wheel is $F = 10N$
The amount of force required to twist an object is measured as torque which is given as
$\tau = RF\sin \theta $
Where $\theta $ is the angle between force and lever arm.
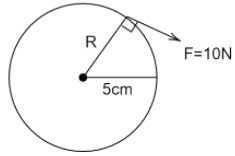
$ \Rightarrow \tau = 0.05 \times 10 \times \sin {90^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow \tau = 0.5Nm$
Hence the torque with which the wheel is turning is $\tau = 0.5Nm$
Solution for part (B)- turning effect depends upon, force, the shortest distance between the force line and axis of rotation.
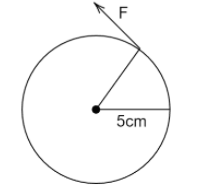
i.
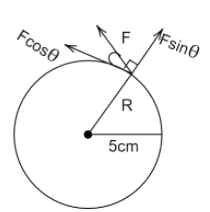
Dividing the given force into its components. Taking the $\cos \theta $ component of force which is making the tangent with the wheel. Torque for the given wheel will be
$ \Rightarrow \tau = RF\cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \tau = 0.05F\cos \theta $
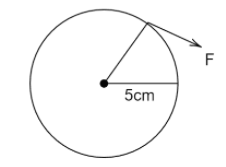
ii.
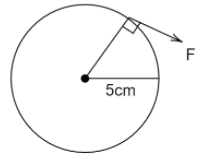
torque for the given wheel is
$\tau = 0.05F$
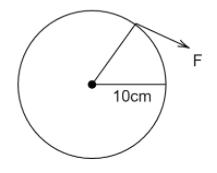
iii.
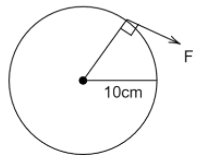
Here radius $R = 10cm = 0.10m$ therefore, torque for the given wheel is
$\tau = 0.10F$
So, the turning effect on the wheel will be like (iii) $ > $ (ii) $ > $(i)
Hence, torque is found to be maximum in wheel given in (iii) therefore, wheel in the (iii) option will have more turning effect.
Note:
A straight line that only touches the circle once is a tangent to a circle. It is called the point of tangency. At this point, the tangent to a circle is always perpendicular to the radius that is why we took $\theta = {90^ \circ }$ here.
Complete answer:
Solution of the part (A) -
We have been given the radius of the wheel \[R = 5cm = 0.05m\] and force acting on the wheel is $F = 10N$
The amount of force required to twist an object is measured as torque which is given as
$\tau = RF\sin \theta $
Where $\theta $ is the angle between force and lever arm.

$ \Rightarrow \tau = 0.05 \times 10 \times \sin {90^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow \tau = 0.5Nm$
Hence the torque with which the wheel is turning is $\tau = 0.5Nm$
Solution for part (B)- turning effect depends upon, force, the shortest distance between the force line and axis of rotation.
i.

Dividing the given force into its components. Taking the $\cos \theta $ component of force which is making the tangent with the wheel. Torque for the given wheel will be
$ \Rightarrow \tau = RF\cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \tau = 0.05F\cos \theta $
ii.

torque for the given wheel is
$\tau = 0.05F$
iii.

Here radius $R = 10cm = 0.10m$ therefore, torque for the given wheel is
$\tau = 0.10F$
So, the turning effect on the wheel will be like (iii) $ > $ (ii) $ > $(i)
Hence, torque is found to be maximum in wheel given in (iii) therefore, wheel in the (iii) option will have more turning effect.
Note:
A straight line that only touches the circle once is a tangent to a circle. It is called the point of tangency. At this point, the tangent to a circle is always perpendicular to the radius that is why we took $\theta = {90^ \circ }$ here.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




