
ABCD is cyclic quadrilateral with $\angle ADC=135{}^\circ $, sides BA and CD produced meet at point P, sides AD and BC produced meet at point Q. If $\angle P:\angle Q=2:1$, find angles P and Q.
Answer
611.4k+ views
Hint: In a cyclic quadrilateral the sum of opposite angles of the quadrilateral is always equal to $180{}^\circ $. Also, in any triangle the sum of its three angles is always equal to $180{}^\circ $.
Complete step-by-step answer:
An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the opposite interior angles.
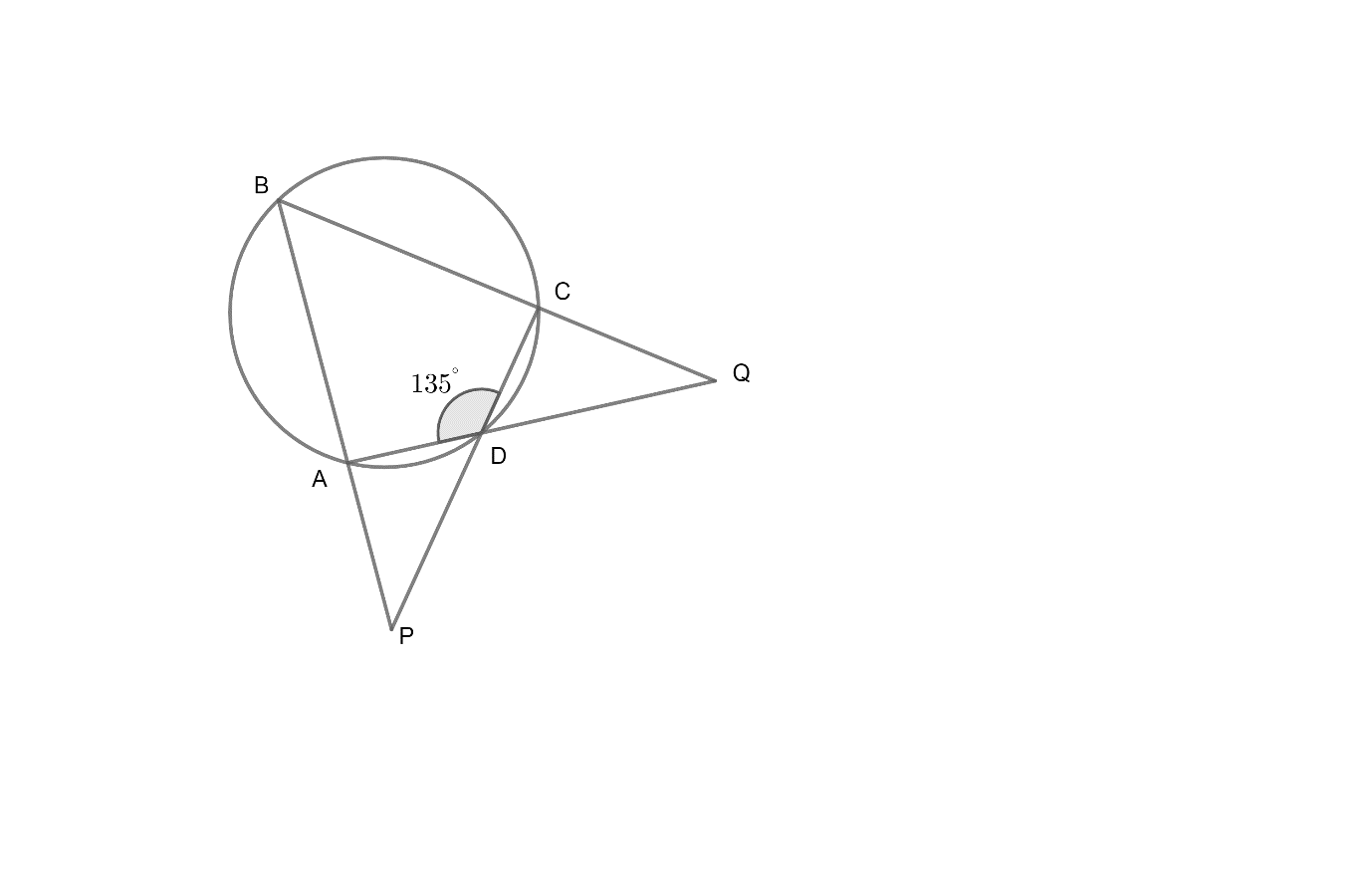
Given:
$P:Q=2:1$
Let the ratio constant be x
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{P}{Q}=\dfrac{2x}{1x}$
$\Rightarrow $ Hence, $\angle P=2x$, then $\angle Q=x$
Now, in cyclic quadrilateral ABCD,
Given, $\angle ADC=135{}^\circ $
From the property of cyclic quadrilateral (given in hint)
$\begin{align}
& \angle B=180{}^\circ -\angle ADC \\
& \Rightarrow \angle B=180{}^\circ -135{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle B=45{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
We know the sum of angles of a linear pair is equal to $180{}^\circ $.
Hence, $\angle ADC+\angle ADP=180{}^\circ $
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle ADP=180{}^\circ -\angle ADC \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ADP=180{}^\circ -135{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ADP=45{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Now, in $\Delta AQB$,
From the property of sum of angles of a triangle (given in hint)
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle A+\angle Q+\angle B=180{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A+x+45{}^\circ =180{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A=180{}^\circ -\left( x+45{}^\circ \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A=\left( 135{}^\circ -x \right)...........\left( i \right) \\
\end{align}$
In $\Delta ADP$,
From exterior angle property of triangle (given in hint)
Exterior angle $A=\angle ADP+\angle P$
$\angle A=45{}^\circ +2x.........\left( ii \right)$
Equating (i) and (ii), we get,
$\Rightarrow 45{}^\circ +2x=135{}^\circ -x$ (Taking terms of x to one side)
$\Rightarrow 3x=135{}^\circ -45{}^\circ $
$\Rightarrow 3x=90{}^\circ $ (Dividing both sides of equation by 3)
$\Rightarrow x=30{}^\circ $
Hence, $\angle Q=30{}^\circ $
$\angle P=2x=60{}^\circ $
Note: In this question, it is very important to draw a rough diagram before solving. In this question the relation between $\angle P$ and $\angle Q$ is given. We need to be careful while choosing the triangles. Therefore, we will choose $\Delta ABQ$ and $\Delta APD$ to apply Angle Sum Property and Exterior Angle Property in these triangles respectively to establish an equation to get the ratio constant.
Complete step-by-step answer:
An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the opposite interior angles.

Given:
$P:Q=2:1$
Let the ratio constant be x
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{P}{Q}=\dfrac{2x}{1x}$
$\Rightarrow $ Hence, $\angle P=2x$, then $\angle Q=x$
Now, in cyclic quadrilateral ABCD,
Given, $\angle ADC=135{}^\circ $
From the property of cyclic quadrilateral (given in hint)
$\begin{align}
& \angle B=180{}^\circ -\angle ADC \\
& \Rightarrow \angle B=180{}^\circ -135{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle B=45{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
We know the sum of angles of a linear pair is equal to $180{}^\circ $.
Hence, $\angle ADC+\angle ADP=180{}^\circ $
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle ADP=180{}^\circ -\angle ADC \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ADP=180{}^\circ -135{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ADP=45{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Now, in $\Delta AQB$,
From the property of sum of angles of a triangle (given in hint)
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle A+\angle Q+\angle B=180{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A+x+45{}^\circ =180{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A=180{}^\circ -\left( x+45{}^\circ \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A=\left( 135{}^\circ -x \right)...........\left( i \right) \\
\end{align}$
In $\Delta ADP$,
From exterior angle property of triangle (given in hint)
Exterior angle $A=\angle ADP+\angle P$
$\angle A=45{}^\circ +2x.........\left( ii \right)$
Equating (i) and (ii), we get,
$\Rightarrow 45{}^\circ +2x=135{}^\circ -x$ (Taking terms of x to one side)
$\Rightarrow 3x=135{}^\circ -45{}^\circ $
$\Rightarrow 3x=90{}^\circ $ (Dividing both sides of equation by 3)
$\Rightarrow x=30{}^\circ $
Hence, $\angle Q=30{}^\circ $
$\angle P=2x=60{}^\circ $
Note: In this question, it is very important to draw a rough diagram before solving. In this question the relation between $\angle P$ and $\angle Q$ is given. We need to be careful while choosing the triangles. Therefore, we will choose $\Delta ABQ$ and $\Delta APD$ to apply Angle Sum Property and Exterior Angle Property in these triangles respectively to establish an equation to get the ratio constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




