
ABCD is a parallelogram (see figure below). The ratio of DE to EC is 1:3. Height AE has a length of 3. If quadrilateral ABCE has an area of 21, what is the area of ABCD?

Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint:
First, break quadrilateral ABCE into two pieces: A \[3 \times 3x\] rectangle and a right triangle with a base of $x$ and a height of 3.
Formula used:
We know that,
Area of rectangle is \[\left( {base} \right)\; \times \;\left( {height} \right)\]
Area of right angle triangle is \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height\]
Complete step by step answer:
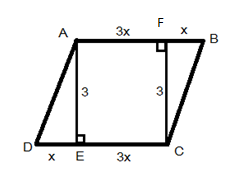
It is given that the ratio of DE to EC is 1:3
Let us consider \[DE{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}x\] and\[EC{\rm{ }} = 3x\],
Also given that area of quadrilateral ABCE 21unit.
Therefore, the area of quadrilateral ABCE is given by the following equation:
We can see the picture, we can come to a conclusion that,
Area of quadrilateral ABCE is combination of Area of rectangle and right angle triangle\[BCF\]
The area of quadrilateral ABCE =area of the rectangle + area of the triangle.
The area of quadrilateral ABCE = \[\left( {3 \times 3x} \right) + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 3x\]
Solve and we get,
\[ = 9x + 1.5x\]
The area of the quadrilateral \[ = 10.5x\]
Now, it is given that ABCE has an area of 21,
Hence by equating the area we get,
\[\Rightarrow 21 = 10.5x\]
Hence by solving the above equation, we get
\[\Rightarrow x = 2\]
Now, we have to find the area of Quadrilateral ABCD.
We know that the Quadrilateral ABCD is a parallelogram,
So we can use the formula of parallelogram,
Here base of the parallelogram is found by adding $DE \text{ and } EC$
$\Rightarrow DE+EC=x+3x=4x$
We know that height is given as 3,
Area of the parallelogram \[ = {\rm{ }}\left( {base} \right)\; \times \;\left( {height} \right)\]
Let us substitute base, height and \[x = 2\] in the area formula, we get
\[\Rightarrow Area = 4\left( 2 \right) \times 3\]
\[\Rightarrow Area = 24{\rm{ }}uni{t^2}\]
$\therefore$ The area of Quadrilateral ABCD is \[24{\rm{ }}uni{t^2}\]
Note:
A parallelogram is a special type of quadrilateral that has equal and parallel opposite sides. The opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length. Diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
First, break quadrilateral ABCE into two pieces: A \[3 \times 3x\] rectangle and a right triangle with a base of $x$ and a height of 3.
Formula used:
We know that,
Area of rectangle is \[\left( {base} \right)\; \times \;\left( {height} \right)\]
Area of right angle triangle is \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height\]
Complete step by step answer:

It is given that the ratio of DE to EC is 1:3
Let us consider \[DE{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}x\] and\[EC{\rm{ }} = 3x\],
Also given that area of quadrilateral ABCE 21unit.
Therefore, the area of quadrilateral ABCE is given by the following equation:
We can see the picture, we can come to a conclusion that,
Area of quadrilateral ABCE is combination of Area of rectangle and right angle triangle\[BCF\]
The area of quadrilateral ABCE =area of the rectangle + area of the triangle.
The area of quadrilateral ABCE = \[\left( {3 \times 3x} \right) + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 3x\]
Solve and we get,
\[ = 9x + 1.5x\]
The area of the quadrilateral \[ = 10.5x\]
Now, it is given that ABCE has an area of 21,
Hence by equating the area we get,
\[\Rightarrow 21 = 10.5x\]
Hence by solving the above equation, we get
\[\Rightarrow x = 2\]
Now, we have to find the area of Quadrilateral ABCD.
We know that the Quadrilateral ABCD is a parallelogram,
So we can use the formula of parallelogram,
Here base of the parallelogram is found by adding $DE \text{ and } EC$
$\Rightarrow DE+EC=x+3x=4x$
We know that height is given as 3,
Area of the parallelogram \[ = {\rm{ }}\left( {base} \right)\; \times \;\left( {height} \right)\]
Let us substitute base, height and \[x = 2\] in the area formula, we get
\[\Rightarrow Area = 4\left( 2 \right) \times 3\]
\[\Rightarrow Area = 24{\rm{ }}uni{t^2}\]
$\therefore$ The area of Quadrilateral ABCD is \[24{\rm{ }}uni{t^2}\]
Note:
A parallelogram is a special type of quadrilateral that has equal and parallel opposite sides. The opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length. Diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




