
ABCD is a parallelogram. In which side AB is produced to E so that BE = AB. Prove that ED bisects BC.
Answer
625.5k+ views
Hint: To solve the question, we have to apply the properties of parallelogram to the given parallelogram ABCD to understand that AB, CD are the parallel sides and BC, AD are parallel to each other. Thus, we can apply basic proportionality theorem, SAS symmetry, using this information to arrive at the answer to the given question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that a parallelogram has a pair of equal-parallel sides.
Thus, AB is parallel and equal to CD and BC is parallel and equal to side AD.
AB = CD, BC = AD
Let ED interest the side BC at point F.
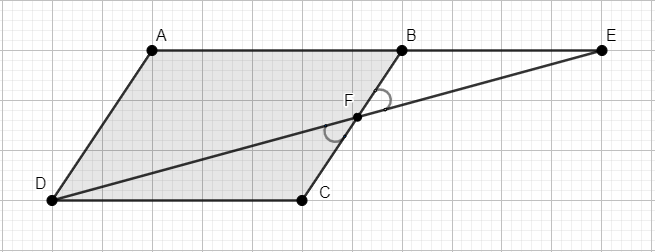
Consider the triangle AED,
Given that B is middle point of AE which implies AB = BE
Thus, BE = CD since AB = CD
BF is parallel to AD since BC is parallel to AD.
We know that, the basic proportionality theorem states that if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
By applying this theorem to the triangle AED, we get
\[\dfrac{AB}{BE}=\dfrac{DF}{FE}\]
Thus, DF = FE
We know that for a pair of intersecting lines vertically opposite angles are equal.
Thus, we get
\[\angle BFE=\angle DFC\]
We know that by SAS (Side-Angle-Side) symmetry which states two triangles are congruent if two corresponding sides and one corresponding angle are equal.
Thus, we get \[\Delta BEF,\Delta DFC\] are congruent
Since DF = FE, BE = CD and \[\angle BFE=\angle DFC\]
We know that for congruent triangles corresponding sides are equal.
Thus, we get BF = FC = half of BC
Thus, F bisects the side BC.
Hence, ED bisects BC.
Note: The possibility of mistake can be not analysing the given information of the parallelogram and apply the properties of parallelogram. The other possibility of mistake can be not applying the basic proportionality theorem, SAS symmetry which eases the procedure of solving.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that a parallelogram has a pair of equal-parallel sides.
Thus, AB is parallel and equal to CD and BC is parallel and equal to side AD.
AB = CD, BC = AD
Let ED interest the side BC at point F.

Consider the triangle AED,
Given that B is middle point of AE which implies AB = BE
Thus, BE = CD since AB = CD
BF is parallel to AD since BC is parallel to AD.
We know that, the basic proportionality theorem states that if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
By applying this theorem to the triangle AED, we get
\[\dfrac{AB}{BE}=\dfrac{DF}{FE}\]
Thus, DF = FE
We know that for a pair of intersecting lines vertically opposite angles are equal.
Thus, we get
\[\angle BFE=\angle DFC\]
We know that by SAS (Side-Angle-Side) symmetry which states two triangles are congruent if two corresponding sides and one corresponding angle are equal.
Thus, we get \[\Delta BEF,\Delta DFC\] are congruent
Since DF = FE, BE = CD and \[\angle BFE=\angle DFC\]
We know that for congruent triangles corresponding sides are equal.
Thus, we get BF = FC = half of BC
Thus, F bisects the side BC.
Hence, ED bisects BC.
Note: The possibility of mistake can be not analysing the given information of the parallelogram and apply the properties of parallelogram. The other possibility of mistake can be not applying the basic proportionality theorem, SAS symmetry which eases the procedure of solving.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




