
ABCD is a parallelogram as shown in fig. If AB=2AD and P is mid-point of AB, then $\angle CPD$ is equal to:
$\left( a \right){90^\circ}$
$\left( b \right){60^\circ}$
$\left( c \right){45^\circ}$
$\left( d \right){135^\circ}$
Answer
611.7k+ views
Hint – In this problem use the concept that opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal so AD=BC and that angles opposite to equal sides are equal thus $\angle APD$ = $\angle ADP$ and $\angle BPC$ = $\angle PCB$. These concepts along with the fact that adjacent angles of parallelogram make ${180^\circ}$ will help getting the required angle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
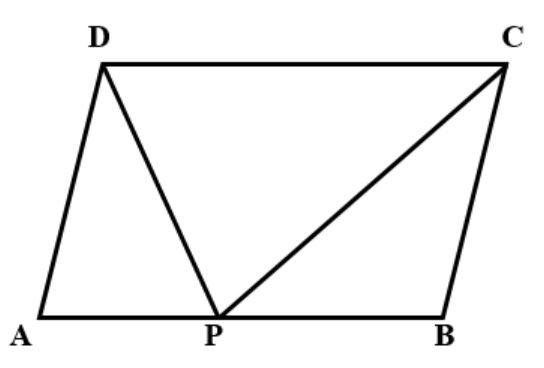
Since P is the midpoint of AB. From this we conclude that
AP = PB=$\dfrac{1}{2}$AB
$\because $AB= 2AD, so from this we get
AP=PB=$\dfrac{1}{2}$AD$ \times $2= AD ………… (i)
Also as we know that in case of parallelogram opposite sides are equal and parallel therefore,
AD = BC
So, from equation (1) $\Delta $APD and $\Delta $BPC are isosceles as AP = AD and PB = BC and with PD and PC as bases respectively
Also, $\angle $APD = $\angle $ADP and $\angle $BPC = $\angle $PCB (as angles opposite to equal sides are also equal)……….. (ii)
Now, $\angle $APD = $\angle $PDC and $\angle $BPC = $\angle $PCD (Alternate Angles between the parallels AB and CD)………… (iii)
So from equations (ii) and (iii)
$\angle $ADP = $\angle $ PDC
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $ ADP + $\angle $PDC = $\angle $ ADC = 2$\angle $PDC…… (iv)
And $\angle $ PCB = $\angle $PCD
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle $PCD + $\angle $PCB =$\angle $BCD = 2$\angle $PCD…….. (v)
Now add equations (iv) and (v) we get
$\angle $ADC +$\angle $BCD = 2($\angle $PDC +$\angle $PCD)……. (vi)
From the property of parallelogram that sum of adjacent angles of parallelogram is 180°.
So from equation (vi)
2($\angle $PDC+$\angle $PCD) =180°
$\therefore $ $\angle $PDC + $\angle $PCD = 90°…………………… (A)
Now in $\Delta $PDC,
By angle sum property of triangle the sum of all interior angles is equal to 180°
$\angle $CPD = 180° - ($\angle $PDC + $\angle $PCD)
$\therefore $$\angle $CPD = 180° - 90° = 90° (from equation A)
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (a) is correct.
Note – A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and equal. A quadrilateral with equal sides is called a rhombus and a parallelogram whose all angles are right angles is called a rectangle. It is advised to have a good understanding of the figures involved in geometry while solving problems of this kind as it helps in figuring out the alternate angels and other angel properties.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Since P is the midpoint of AB. From this we conclude that
AP = PB=$\dfrac{1}{2}$AB
$\because $AB= 2AD, so from this we get
AP=PB=$\dfrac{1}{2}$AD$ \times $2= AD ………… (i)
Also as we know that in case of parallelogram opposite sides are equal and parallel therefore,
AD = BC
So, from equation (1) $\Delta $APD and $\Delta $BPC are isosceles as AP = AD and PB = BC and with PD and PC as bases respectively
Also, $\angle $APD = $\angle $ADP and $\angle $BPC = $\angle $PCB (as angles opposite to equal sides are also equal)……….. (ii)
Now, $\angle $APD = $\angle $PDC and $\angle $BPC = $\angle $PCD (Alternate Angles between the parallels AB and CD)………… (iii)
So from equations (ii) and (iii)
$\angle $ADP = $\angle $ PDC
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $ ADP + $\angle $PDC = $\angle $ ADC = 2$\angle $PDC…… (iv)
And $\angle $ PCB = $\angle $PCD
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle $PCD + $\angle $PCB =$\angle $BCD = 2$\angle $PCD…….. (v)
Now add equations (iv) and (v) we get
$\angle $ADC +$\angle $BCD = 2($\angle $PDC +$\angle $PCD)……. (vi)
From the property of parallelogram that sum of adjacent angles of parallelogram is 180°.
So from equation (vi)
2($\angle $PDC+$\angle $PCD) =180°
$\therefore $ $\angle $PDC + $\angle $PCD = 90°…………………… (A)
Now in $\Delta $PDC,
By angle sum property of triangle the sum of all interior angles is equal to 180°
$\angle $CPD = 180° - ($\angle $PDC + $\angle $PCD)
$\therefore $$\angle $CPD = 180° - 90° = 90° (from equation A)
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (a) is correct.
Note – A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and equal. A quadrilateral with equal sides is called a rhombus and a parallelogram whose all angles are right angles is called a rectangle. It is advised to have a good understanding of the figures involved in geometry while solving problems of this kind as it helps in figuring out the alternate angels and other angel properties.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




