
ABC is any triangle inscribed in the circle $ {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}} $ such that A is a fixed point. If the external and internal bisectors of $ \angle A $ intersect the circle at D and E, respectively, then which of the following statements is true about $ \Delta ADE $?
A. Its centroid is a fixed point.
B. Its circumcentre is a fixed point.
C. Its orthocentre is a fixed point.
D. none of these
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint:
We know that angle between the external and internal bisectors of any angle is always $ \dfrac{\pi }{2} $. We use that theorem to find the inscribed right-angle triangle inside the circle. We form it as a circumcircle for the $ \Delta DAE $. We find the fixed point of centre as the circumcentre.
Complete step by step answer:
ABC is any triangle inscribed in the circle $ {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}} $ such that A is a fixed point.
The external and internal bisectors of $ \angle A $ intersect the circle at D and E.
We know that the angle between the external and internal bisectors of any angle is always $ \dfrac{\pi }{2} $ . Now we try to draw the diagram.
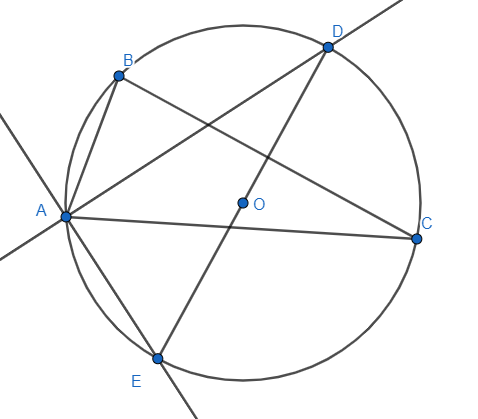
Step: 1
Point A is fixed. The internal and external bisectors of $ \angle BAC $, AD and AE intersect the circle at D and E respectively.
The angle $ \angle DAE $ for the $ \Delta DAE $ is $ \dfrac{\pi }{2} $ . So, $ \Delta DAE $ is a right-angle triangle.
Step: 2
All the three vertices of $ \Delta DAE $ are on the circle and the fixed vertices A creates a right angle. We can say that the circle becomes a circumcircle for the $ \Delta DAE $.
Step: 3
The centre will be the middle point of the hypotenuse as we know that for a right-angle triangle, the circumcentre is the middle point of the hypotenuse.
Step: 4
As the $ \Delta DAE $ is created based on the position of the vertices A and the vertices is fixed, the position of the point O will also be fixed as the circumcentre.
The correct option is B.
Note:
The point A is fixed and even if we change the position of the points B and C, the condition of the centre and the circumcentre being fixed at point O is satisfied. We check the below images to understand the condition better.
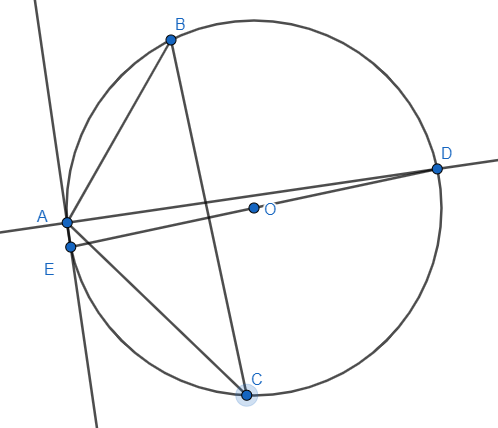
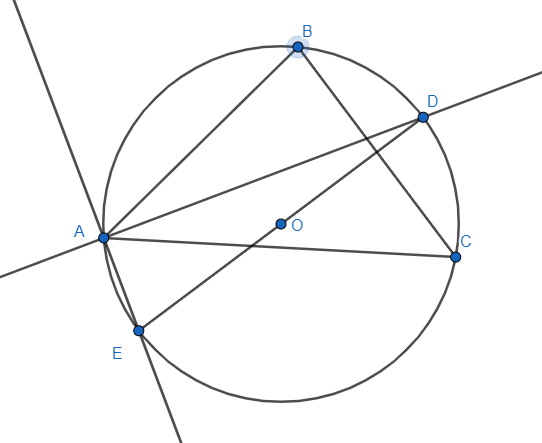
We know that angle between the external and internal bisectors of any angle is always $ \dfrac{\pi }{2} $. We use that theorem to find the inscribed right-angle triangle inside the circle. We form it as a circumcircle for the $ \Delta DAE $. We find the fixed point of centre as the circumcentre.
Complete step by step answer:
ABC is any triangle inscribed in the circle $ {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}} $ such that A is a fixed point.
The external and internal bisectors of $ \angle A $ intersect the circle at D and E.
We know that the angle between the external and internal bisectors of any angle is always $ \dfrac{\pi }{2} $ . Now we try to draw the diagram.

Step: 1
Point A is fixed. The internal and external bisectors of $ \angle BAC $, AD and AE intersect the circle at D and E respectively.
The angle $ \angle DAE $ for the $ \Delta DAE $ is $ \dfrac{\pi }{2} $ . So, $ \Delta DAE $ is a right-angle triangle.
Step: 2
All the three vertices of $ \Delta DAE $ are on the circle and the fixed vertices A creates a right angle. We can say that the circle becomes a circumcircle for the $ \Delta DAE $.
Step: 3
The centre will be the middle point of the hypotenuse as we know that for a right-angle triangle, the circumcentre is the middle point of the hypotenuse.
Step: 4
As the $ \Delta DAE $ is created based on the position of the vertices A and the vertices is fixed, the position of the point O will also be fixed as the circumcentre.
The correct option is B.
Note:
The point A is fixed and even if we change the position of the points B and C, the condition of the centre and the circumcentre being fixed at point O is satisfied. We check the below images to understand the condition better.


Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




