
$ABC$ is a triangle. Locate a point in the interior of $\Delta ABC$ which is equidistant from all the vertices of $\Delta ABC$.
Answer
613.5k+ views
Hint: The given problem is related to various points in a triangle. The circumcentre of a triangle is equidistant from all the vertices and can be located as the point of intersection of the perpendicular bisectors of the sides of the triangle.
Complete step by step answer: -
A point which is equidistant from all the vertices of $\Delta ABC$, is called the triangle’s circumcentre. Let’s call this point $S$, and its distance from the vertices is known as the circumradius of the triangle, and can be denoted by $R$.
Now, let’s imagine the triangle’s figure. It’ll have three points joined to each other, and we need to find a point inside the triangle that is equidistant from each of these points.
We all know that all the points on a circle are equidistant from the centre of the circle, and their distance from the centre is called the circle’s radius or $r$.
Thus, we can apply the same knowledge here, and say that if we construct a circle passing through the three points $A$, $B$ and $C$, and then find the centre of this circle, then we’ll get the point that is equidistant from $A$, $B$ and $C$. Thus, the circumcentre is nothing but the centre of the circle constructed that passes through all the three vertices of the triangle, whose circumcentre needs to be located.
Proceeding from here, we now know that this question is a question that requires us to locate the circumcentre by making some constructions on the triangle$ABC$.
In general, the way to locate the circumcentre of a triangle is to draw perpendicular bisectors to any two of its sides, and then find the point of intersection of those two perpendicular bisectors. This point of intersection will be our required circumcentre.
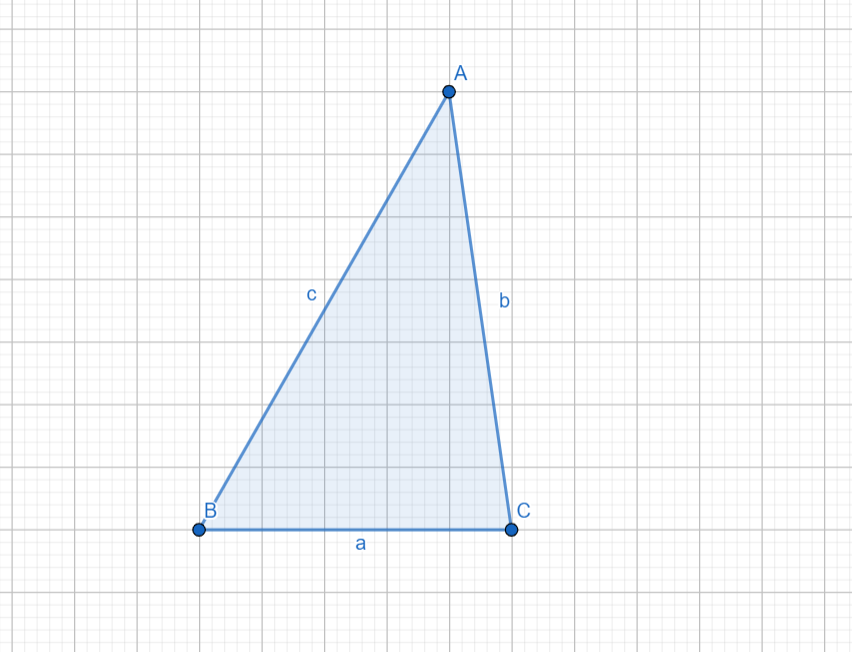
Let this be the triangle $ABC$ mentioned in the question. The triangle can have any measurements, since none are specified in the question.
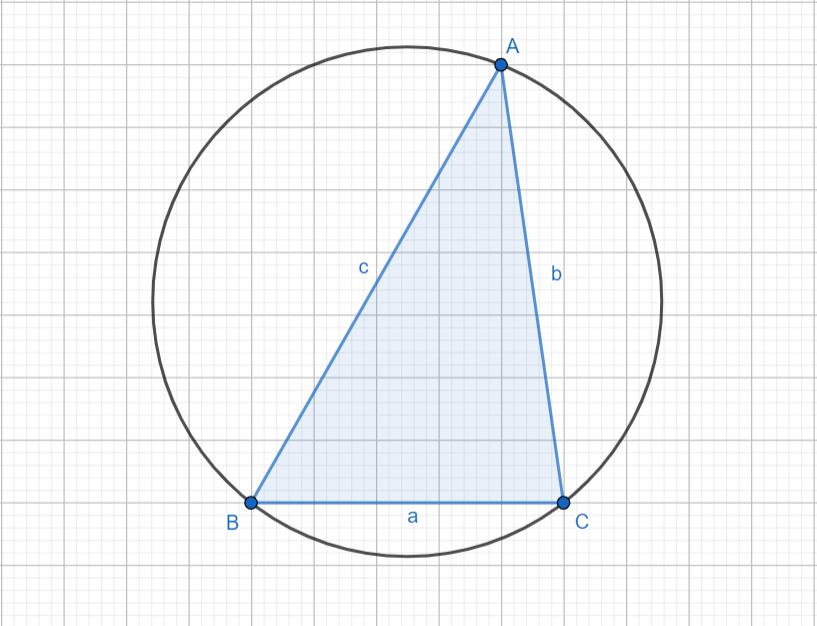
Here, the circle drawn is the triangle’s circumcircle and the centre of this triangle is the circumcentre of triangle$ABC$.
The first step to finding out the circumcentre is to construct the perpendicular bisectors to any two of the three triangle sides. First, let’s draw a perpendicular bisector to $AB$. This is done by putting the pin of the compass at $A$ first, widening it to a length which is more than half the length of $AB$, and cutting an arc at the top and bottom of $AB$, with the same length on the compass. Now, keeping the widening of the compass unchanged, the same is to be done by putting the pin of the compass at $B$.
The next step is to join the intersection points of the two circular arcs drawn from $A$ and $B$, above and below the line $AB$. This joining gives us the perpendicular bisector of $AB$.
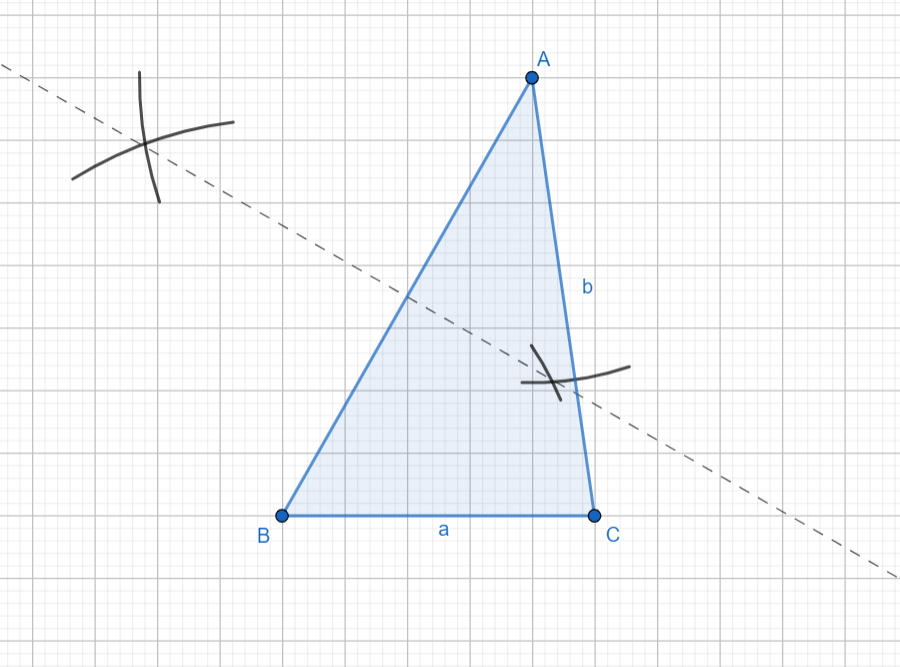
Repeat the same process for the line $AC$ now. Again put the compass at $A$ first, measure more than half the length of $AC$, and cut circular arcs above and below $AC$. Then, without changing the measurement of the compass, keep the pin at $C$ and draw similar arcs above and below $AC$, cutting the earlier arcs made from $A$. The line joining these two points of intersection, gives us the perpendicular bisector of side $AC$.
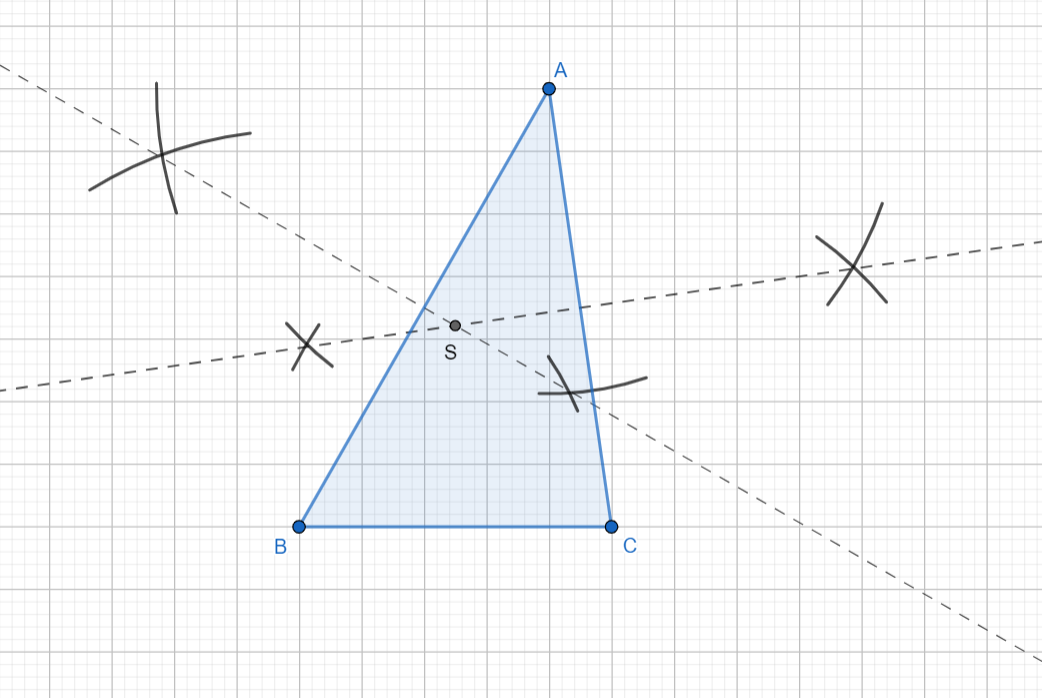
Thus, we have the perpendicular bisectors of two sides, $AB$ and $AC$. The intersection point of these two perpendicular bisectors is the circumcentre, labelled $S$, and this is also equidistant from all the three vertices of the triangle.
Hence, point $S$ has been located as the point equidistant from all the three vertices.
Note: It is very important that the compass’s measurement doesn’t change when we move from one end of a side of the triangle to the other end. For example, if the measurement of the compass changes even a bit when we move the pin to vertex $B$ while perpendicularly bisecting side $AB$, then the arc we get will be wrong, and the line we get from joining the intersection points will not be the perpendicular bisector, or it might not even be straight. Thus, the arcs have to be drawn very carefully.
Complete step by step answer: -
A point which is equidistant from all the vertices of $\Delta ABC$, is called the triangle’s circumcentre. Let’s call this point $S$, and its distance from the vertices is known as the circumradius of the triangle, and can be denoted by $R$.
Now, let’s imagine the triangle’s figure. It’ll have three points joined to each other, and we need to find a point inside the triangle that is equidistant from each of these points.
We all know that all the points on a circle are equidistant from the centre of the circle, and their distance from the centre is called the circle’s radius or $r$.
Thus, we can apply the same knowledge here, and say that if we construct a circle passing through the three points $A$, $B$ and $C$, and then find the centre of this circle, then we’ll get the point that is equidistant from $A$, $B$ and $C$. Thus, the circumcentre is nothing but the centre of the circle constructed that passes through all the three vertices of the triangle, whose circumcentre needs to be located.
Proceeding from here, we now know that this question is a question that requires us to locate the circumcentre by making some constructions on the triangle$ABC$.
In general, the way to locate the circumcentre of a triangle is to draw perpendicular bisectors to any two of its sides, and then find the point of intersection of those two perpendicular bisectors. This point of intersection will be our required circumcentre.

Let this be the triangle $ABC$ mentioned in the question. The triangle can have any measurements, since none are specified in the question.

Here, the circle drawn is the triangle’s circumcircle and the centre of this triangle is the circumcentre of triangle$ABC$.
The first step to finding out the circumcentre is to construct the perpendicular bisectors to any two of the three triangle sides. First, let’s draw a perpendicular bisector to $AB$. This is done by putting the pin of the compass at $A$ first, widening it to a length which is more than half the length of $AB$, and cutting an arc at the top and bottom of $AB$, with the same length on the compass. Now, keeping the widening of the compass unchanged, the same is to be done by putting the pin of the compass at $B$.
The next step is to join the intersection points of the two circular arcs drawn from $A$ and $B$, above and below the line $AB$. This joining gives us the perpendicular bisector of $AB$.

Repeat the same process for the line $AC$ now. Again put the compass at $A$ first, measure more than half the length of $AC$, and cut circular arcs above and below $AC$. Then, without changing the measurement of the compass, keep the pin at $C$ and draw similar arcs above and below $AC$, cutting the earlier arcs made from $A$. The line joining these two points of intersection, gives us the perpendicular bisector of side $AC$.

Thus, we have the perpendicular bisectors of two sides, $AB$ and $AC$. The intersection point of these two perpendicular bisectors is the circumcentre, labelled $S$, and this is also equidistant from all the three vertices of the triangle.
Hence, point $S$ has been located as the point equidistant from all the three vertices.
Note: It is very important that the compass’s measurement doesn’t change when we move from one end of a side of the triangle to the other end. For example, if the measurement of the compass changes even a bit when we move the pin to vertex $B$ while perpendicularly bisecting side $AB$, then the arc we get will be wrong, and the line we get from joining the intersection points will not be the perpendicular bisector, or it might not even be straight. Thus, the arcs have to be drawn very carefully.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




