
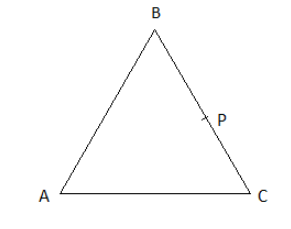
ABC is a triangle and P is any point on BC. If \[\overline {PQ} \] is the resultant of the vectors \[\overline {AP} ,\overline {PB} \] and \[\overline {PC} \]then ACQB is
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint:
A vector has magnitude and direction.
the vector p=\[\overline {PQ} \]
The resultant vector is the vector sum of two or more vectors. It is the result of adding two or more vectors together. If displacement vectors A, B, and C are added together, the result will be vector R.
R=A+B+C.
Here it is given that \[\overline {PQ} \] is the resultant of the vectors \[\overline {AP} ,\overline {PB} \] and \[\overline {PC} \] using this we will find the value of\[\overline {CQ} \] and then relate it with\[\overline {AB} \]which helps in giving information about the required ACQB.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that ABC is a triangle and P is any point on BC.
Also given that, \[\overline {PQ} \] is the resultant of the vectors \[\overline {AP} ,\overline {PB} \] and\[\overline {PC} \].
As we know that we can all the vectors to find the resultant we get,
\[\overline {PQ} = \overline {AP} + \overline {PB} + \overline {PC} \]
Let us take \[\overline {PC} \]to the left hand side,
\[\overline {PQ} - \overline {PC} = \overline {AP} + \overline {PB} \]…(1)
If the direction of the vector \[\overline {PC} \]is changed then we have,\[\overline {PC} = - \overline {CP} \]
Let us substitute the \[\overline {PC} \] in equation (1) we get,
\[\overline {PQ} + \overline {CP} = \overline {AP} + \overline {PB} \]…(2)
Here we have added the vectors hence it will lead to the following resultant vectors,
\[\overline {CQ} = \overline {AB} \]
In the above equation the resultant vector of \[\overline {PQ} \]and \[\overline {CP} \] is\[\overline {CQ} \], the resultant vector of \[\overline {AP} \]and \[\overline {PB} \]is \[\overline {AB} \]
Now, we know if \[\overline {CQ} = \overline {AB} \]then
CQ= AB & CQ||AB which is nothing but the condition of a parallelogram.
So, ACQB is a parallelogram.
Note:
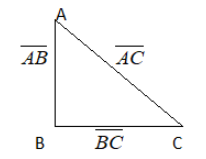
If ABC is a triangle
\[\overline {AB} \] & \[\overline {BC} \]are two vectors then the resultant vector is
\[\overline {AC} = \overline {AB} + \overline {BC} \]. We have used it in equation 2.
And the condition of a shape to be parallelogram is AB=CD and AB||CD.

A vector has magnitude and direction.

the vector p=\[\overline {PQ} \]
The resultant vector is the vector sum of two or more vectors. It is the result of adding two or more vectors together. If displacement vectors A, B, and C are added together, the result will be vector R.
R=A+B+C.
Here it is given that \[\overline {PQ} \] is the resultant of the vectors \[\overline {AP} ,\overline {PB} \] and \[\overline {PC} \] using this we will find the value of\[\overline {CQ} \] and then relate it with\[\overline {AB} \]which helps in giving information about the required ACQB.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that ABC is a triangle and P is any point on BC.
Also given that, \[\overline {PQ} \] is the resultant of the vectors \[\overline {AP} ,\overline {PB} \] and\[\overline {PC} \].
As we know that we can all the vectors to find the resultant we get,
\[\overline {PQ} = \overline {AP} + \overline {PB} + \overline {PC} \]
Let us take \[\overline {PC} \]to the left hand side,
\[\overline {PQ} - \overline {PC} = \overline {AP} + \overline {PB} \]…(1)
If the direction of the vector \[\overline {PC} \]is changed then we have,\[\overline {PC} = - \overline {CP} \]
Let us substitute the \[\overline {PC} \] in equation (1) we get,
\[\overline {PQ} + \overline {CP} = \overline {AP} + \overline {PB} \]…(2)
Here we have added the vectors hence it will lead to the following resultant vectors,
\[\overline {CQ} = \overline {AB} \]
In the above equation the resultant vector of \[\overline {PQ} \]and \[\overline {CP} \] is\[\overline {CQ} \], the resultant vector of \[\overline {AP} \]and \[\overline {PB} \]is \[\overline {AB} \]
Now, we know if \[\overline {CQ} = \overline {AB} \]then
CQ= AB & CQ||AB which is nothing but the condition of a parallelogram.
So, ACQB is a parallelogram.
Note:

If ABC is a triangle
\[\overline {AB} \] & \[\overline {BC} \]are two vectors then the resultant vector is
\[\overline {AC} = \overline {AB} + \overline {BC} \]. We have used it in equation 2.
And the condition of a shape to be parallelogram is AB=CD and AB||CD.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




