
A) Write two features of carbon which lead to form a huge number of compounds. Write the nature of bonding in organic compounds.
B) Give the formula of two higher homologues of ethane.
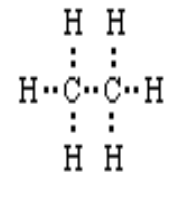
C) Draw the electron dot structure of ethane.
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: In the given question nature of bonding in organic compounds along with electron dot structure is discussed. As we all know that bonding in organic compounds takes place through the covalent bonds mainly. Also the electron dot structure of any compound is based on the covalent bonding.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A) The two features of carbon which lead to form huge numbers of compounds are catenation and tetravalency.
1) Catenation - It is the relation of atoms of the similar element into lengthier chains. Catenation occurs most readily in carbon, which will form covalent bonds with other carbon atoms to form longer chains and structures. The two carbon atoms voluntarily form covalent bonds and this bond formed is more stable than the bonds formed by the other elements.Thus, this is the purpose for the presence of the vast number of organic compounds into nature.
2) Tetravalency -A tetravalence is the state of an atom within the four electrons accessible for covalent chemical bonding in its valence that is outermost electron shell and the Carbon atoms readily form are the covalent bonds with the other atoms.
Therefore, the nature of bonding of organic compounds have covalent bonds in their structure.
B) The two higher homologues of ethane are first propane which have formula $C_3H_8$ (three carbon) and second butane which have formula $C_4H_10$ (four carbon) correspondingly.
C) Electron dot structure as shown in image.
Note: Some other features of carbon are isomerism, bond strength and ability to form multiple bonds. Carbon can form bonds with other carbon atoms to form single, double or triple covalent bonds. Because of this, long chain structures can form and this is known as catenation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A) The two features of carbon which lead to form huge numbers of compounds are catenation and tetravalency.
1) Catenation - It is the relation of atoms of the similar element into lengthier chains. Catenation occurs most readily in carbon, which will form covalent bonds with other carbon atoms to form longer chains and structures. The two carbon atoms voluntarily form covalent bonds and this bond formed is more stable than the bonds formed by the other elements.Thus, this is the purpose for the presence of the vast number of organic compounds into nature.
2) Tetravalency -A tetravalence is the state of an atom within the four electrons accessible for covalent chemical bonding in its valence that is outermost electron shell and the Carbon atoms readily form are the covalent bonds with the other atoms.
Therefore, the nature of bonding of organic compounds have covalent bonds in their structure.
B) The two higher homologues of ethane are first propane which have formula $C_3H_8$ (three carbon) and second butane which have formula $C_4H_10$ (four carbon) correspondingly.
C) Electron dot structure as shown in image.

Note: Some other features of carbon are isomerism, bond strength and ability to form multiple bonds. Carbon can form bonds with other carbon atoms to form single, double or triple covalent bonds. Because of this, long chain structures can form and this is known as catenation.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




