
A wire of length $1 \mathrm{~m}$ is moving at a speed of $2 \mathrm{~ms}^{-1}$ perpendicular to its length in a homogeneous magnetic field of $0.5 \mathrm{~T}$. If the ends of the wire are joined to a circuit of resistance the $6 \Omega,$ then the rate at which work is being done to keep the wire moving at constant speed is
A.1 W
B.$\dfrac{1}{3} \mathrm{~W}$
C. $\dfrac{1}{6} \mathrm{~W}$
D. $\dfrac{1}{12} \mathrm{~W}$
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: Power is the rate at which work is done. It is the amount of energy per unit of time that is consumed. The power unit is the Joule per second (J/s), known as the Watt (in honor of the steam engine's eighteenth-century developer, James Watt). Calculate force acting on the wire and then take out the power.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{\mathrm{W}}{\mathrm{t}}=\mathrm{P}$
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
Power is the work performed in a time unit. In other words, power is a measure of how quickly work can be done. Work is the energy needed to apply a force to move a specific distance from an object, where strength is parallel to the displacement. Power is the rate at which that job is performed.
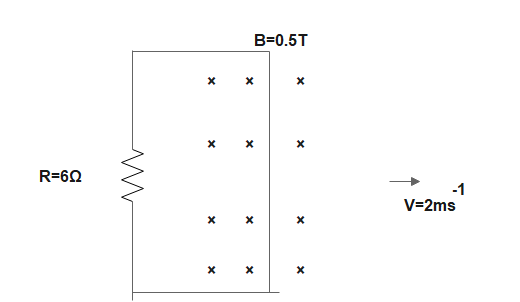
Rate of work $\dfrac{\mathrm{W}}{\mathrm{t}}=\mathrm{P}$
But $P=F v$
Also, $\mathrm{F}=\mathrm{Bil}=\mathrm{B}\left(\dfrac{\mathrm{Bvl}}{\mathrm{R}}\right) \mathrm{l}$
$\left[\because\right.$ induced current $\left.i=\dfrac{B v l}{R}\right]$
$\text{P}=\text{B}\left( \dfrac{\text{Bvl}}{\text{R}} \right)\text{lv}$
$\Rightarrow \text{P}=\dfrac{{{\text{B}}^{2}}{{\text{v}}^{2}}{{\text{l}}^{2}}}{\text{R}}$
$\text{P}=\dfrac{{{(0.5)}^{2}}\times {{(2)}^{2}}\times {{(1)}^{2}}}{6}$
$\therefore \text{P}=\dfrac{1}{6}~\text{W}$
The rate at which work is being done to keep the wire moving at constant speed is $\dfrac{1}{6}~\text{W}$
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
The work is a product of the external force and the distance it moves applied to an object or system. Power is a measure of the amount of work per unit of time that is done. In a Force-Distance curve, the work can be computed as the area under a curve. The net work done on an object is equal to the shift in kinetic energy of the object. The alternating-current power in watts delivered to a load by an amplifier is also called the work-energy principle.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{\mathrm{W}}{\mathrm{t}}=\mathrm{P}$
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
Power is the work performed in a time unit. In other words, power is a measure of how quickly work can be done. Work is the energy needed to apply a force to move a specific distance from an object, where strength is parallel to the displacement. Power is the rate at which that job is performed.

Rate of work $\dfrac{\mathrm{W}}{\mathrm{t}}=\mathrm{P}$
But $P=F v$
Also, $\mathrm{F}=\mathrm{Bil}=\mathrm{B}\left(\dfrac{\mathrm{Bvl}}{\mathrm{R}}\right) \mathrm{l}$
$\left[\because\right.$ induced current $\left.i=\dfrac{B v l}{R}\right]$
$\text{P}=\text{B}\left( \dfrac{\text{Bvl}}{\text{R}} \right)\text{lv}$
$\Rightarrow \text{P}=\dfrac{{{\text{B}}^{2}}{{\text{v}}^{2}}{{\text{l}}^{2}}}{\text{R}}$
$\text{P}=\dfrac{{{(0.5)}^{2}}\times {{(2)}^{2}}\times {{(1)}^{2}}}{6}$
$\therefore \text{P}=\dfrac{1}{6}~\text{W}$
The rate at which work is being done to keep the wire moving at constant speed is $\dfrac{1}{6}~\text{W}$
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
The work is a product of the external force and the distance it moves applied to an object or system. Power is a measure of the amount of work per unit of time that is done. In a Force-Distance curve, the work can be computed as the area under a curve. The net work done on an object is equal to the shift in kinetic energy of the object. The alternating-current power in watts delivered to a load by an amplifier is also called the work-energy principle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




