
A wire is getting elongated by $lmm$ when a load $W$ is hanged from it. When the wire goes over a pulley and two weights $W$ each are hung at the two ends, what will be the elongation of the wire in millimetre?
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: At equilibrium, the tension in the wire will be equivalent to the weight of the body or the load hanging on it. The young's modulus can be found by taking the ratio of the weight of the load to the area of cross section which is divided by the ratio of elongated length of the wire to the initial length of the wire. Consider this in both the situations. This will help you in answering this question.
Complete answer:
First of all let us consider the first situation.
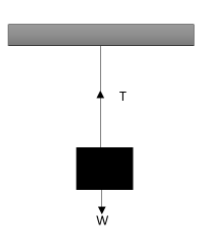
Here at equilibrium, the tension in the wire will be equivalent to the weight of the body or the load hanging on it. Therefore we can write that,
$T=W$
The young's modulus can be found by taking the ratio of the weight of the load to the area of cross section which is divided by the ratio of elongated length of the wire to the initial length of the wire. This can be written as,
$Y=\dfrac{\dfrac{W}{A}}{\dfrac{l}{L}}$
Now in the second situation also, as the load hanging on both the sides are equal, the tension in the wire will be equivalent to the weight of the body hanged.
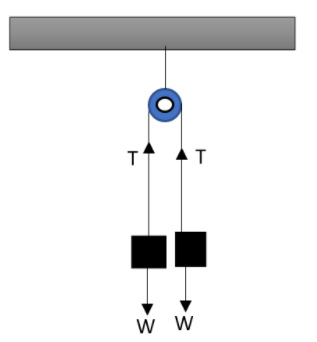
That is,
$T=W$
The young’s modulus for this situation can be written as,
$Y=\dfrac{\dfrac{W}{A}}{\dfrac{l}{L}}$
Therefore the elongation will be the same in both the situations. Hence the elongation of the wire in the second situation will be equivalent to $lmm$.
Note:
The stress in a wire can be found by taking the ratio of the force acting on the wire to the area of the cross section. Strain is another phenomenon occurring which can be found by taking the ratio of the elongated length to the original length. Hence the young’s modulus will be the ratio of the stress to the strain.
Complete answer:
First of all let us consider the first situation.

Here at equilibrium, the tension in the wire will be equivalent to the weight of the body or the load hanging on it. Therefore we can write that,
$T=W$
The young's modulus can be found by taking the ratio of the weight of the load to the area of cross section which is divided by the ratio of elongated length of the wire to the initial length of the wire. This can be written as,
$Y=\dfrac{\dfrac{W}{A}}{\dfrac{l}{L}}$
Now in the second situation also, as the load hanging on both the sides are equal, the tension in the wire will be equivalent to the weight of the body hanged.

That is,
$T=W$
The young’s modulus for this situation can be written as,
$Y=\dfrac{\dfrac{W}{A}}{\dfrac{l}{L}}$
Therefore the elongation will be the same in both the situations. Hence the elongation of the wire in the second situation will be equivalent to $lmm$.
Note:
The stress in a wire can be found by taking the ratio of the force acting on the wire to the area of the cross section. Strain is another phenomenon occurring which can be found by taking the ratio of the elongated length to the original length. Hence the young’s modulus will be the ratio of the stress to the strain.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




