
(a) Why is nitrogen important to all living beings?
(b) What is nitrogen fixation?
Answer
522.9k+ views
Hint: The chemical element nitrogen has the symbol N and the atomic number 7. Daniel Rutherford, a Scottish physician, was the first to discover and isolate it in 1772. Despite the fact that Carl Wilhelm Scheele and Henry Cavendish had separately done so about the same time, Rutherford is often given credit for his work since it was first published.
Complete answer: Because nitrogen is a key component of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins, and nucleic acids, such as DNA, which transmits genetic information to successive generations of organisms, nitrogen is vital for all living things. Nitrogen makes up around 78 percent of the atmosphere, but plants and animals can't get it straight from the air. This is accomplished by a mechanism known as the nitrogen cycle. Protein is found in all human tissue, including muscles, skin, hair, nails, and blood. Nitrogen is required for normal development, cell renewal, and tissue repair, and proteins in the form of enzymes are required for your body's metabolic functions. Nitrogen is required for plant growth and survival. Plants perish without proteins — some as structural components, others as enzymes. Nitrogen makes up a substantial portion of chlorophyll, which plants require for photosynthesis, the process of converting water and carbon dioxide into sugars using the sun's energy. Nitrogen is found in energy-transfer molecules like ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which allows cells to preserve and utilise the energy created during metabolism. Nucleic acids, such as DNA, are also required for plant growth and reproduction. Plants absorb nitrogen in a different method than mammals, receiving it in the form of nitrates and ammonium from the water and soil.
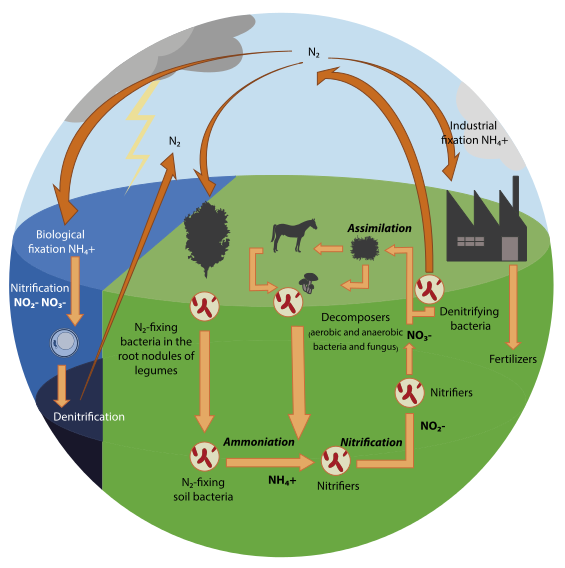
B.Nitrogen fixation is a chemical reaction that converts molecular nitrogen from the air into ammonia or other nitrogenous compounds in soil or aquatic environments. Except for a few microbes, atmospheric nitrogen is molecular dinitrogen, a generally non reactive molecule that is biologically worthless. Biological nitrogen fixation, also known as diazotrophs, is a microbially driven process that uses the nitrogenase protein complex to convert nitrogen gas to ammonia. Because all nitrogen-containing organic substances, including as amino acids and proteins, nucleoside triphosphates, and nucleic acids, require the production of fixed inorganic nitrogen molecules, nitrogen fixation is vital to life. It is necessary for agriculture and fertiliser production as part of the nitrogen cycle. It also has an indirect impact on the production of all nitrogen chemical compounds, including certain explosives, medicines, and colours.
Note:
Microorganisms known as diazotrophs, which include bacteria like Azotobacter and archaea, fix nitrogen naturally in soil. Plants, particularly legumes, have symbiotic interactions with some nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Associative interactions between diazotrophs and plants are generally referred to as looser non-symbiotic connections, such as nitrogen fixation on rice roots. Some termites and fungus work together to fix nitrogen. It occurs naturally in the air as a result of lightning-caused $N{O_x}$ generation.
Complete answer: Because nitrogen is a key component of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins, and nucleic acids, such as DNA, which transmits genetic information to successive generations of organisms, nitrogen is vital for all living things. Nitrogen makes up around 78 percent of the atmosphere, but plants and animals can't get it straight from the air. This is accomplished by a mechanism known as the nitrogen cycle. Protein is found in all human tissue, including muscles, skin, hair, nails, and blood. Nitrogen is required for normal development, cell renewal, and tissue repair, and proteins in the form of enzymes are required for your body's metabolic functions. Nitrogen is required for plant growth and survival. Plants perish without proteins — some as structural components, others as enzymes. Nitrogen makes up a substantial portion of chlorophyll, which plants require for photosynthesis, the process of converting water and carbon dioxide into sugars using the sun's energy. Nitrogen is found in energy-transfer molecules like ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which allows cells to preserve and utilise the energy created during metabolism. Nucleic acids, such as DNA, are also required for plant growth and reproduction. Plants absorb nitrogen in a different method than mammals, receiving it in the form of nitrates and ammonium from the water and soil.

B.Nitrogen fixation is a chemical reaction that converts molecular nitrogen from the air into ammonia or other nitrogenous compounds in soil or aquatic environments. Except for a few microbes, atmospheric nitrogen is molecular dinitrogen, a generally non reactive molecule that is biologically worthless. Biological nitrogen fixation, also known as diazotrophs, is a microbially driven process that uses the nitrogenase protein complex to convert nitrogen gas to ammonia. Because all nitrogen-containing organic substances, including as amino acids and proteins, nucleoside triphosphates, and nucleic acids, require the production of fixed inorganic nitrogen molecules, nitrogen fixation is vital to life. It is necessary for agriculture and fertiliser production as part of the nitrogen cycle. It also has an indirect impact on the production of all nitrogen chemical compounds, including certain explosives, medicines, and colours.
Note:
Microorganisms known as diazotrophs, which include bacteria like Azotobacter and archaea, fix nitrogen naturally in soil. Plants, particularly legumes, have symbiotic interactions with some nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Associative interactions between diazotrophs and plants are generally referred to as looser non-symbiotic connections, such as nitrogen fixation on rice roots. Some termites and fungus work together to fix nitrogen. It occurs naturally in the air as a result of lightning-caused $N{O_x}$ generation.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Find the sum of series 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + + 100 class 9 maths CBSE

Distinguish between Conventional and nonconventional class 9 social science CBSE

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

Describe the 4 stages of the Unification of German class 9 social science CBSE

What is the role of Mahatma Gandhi in national movement

What was the Treaty of Constantinople of 1832 class 9 social science CBSE




