
When a wheat variety of red kernels (homozygous for two non-allelic and independent dominant gene) is crossed with white kernelled wheat (homozygous for two recessive non-allelic independent genes), the phenotypic ratio is F2 generation would be
(a) 9: 7
(b) 1: 10: 4: 1
(c) 1: 4: 6: 4: 1
(d) 1: 2: 4: 2: 4: 2: 1
Answer
602.4k+ views
Hint:In a cross between a wheat variety of red kernels (homozygous for two non-allelic and independent dominant genes) and white kernelled wheat (homozygous for two recessive non-allelic independent genes), the phenotypic ratio in F2 generation would be 1:4:6:4:1 showing a type of inheritance called as polygenic inheritance.
Polygenic inheritance, also known as quantitative inheritance can be defined as a phenomenon where a single inherited phenotypic trait is controlled by two or more different genes.
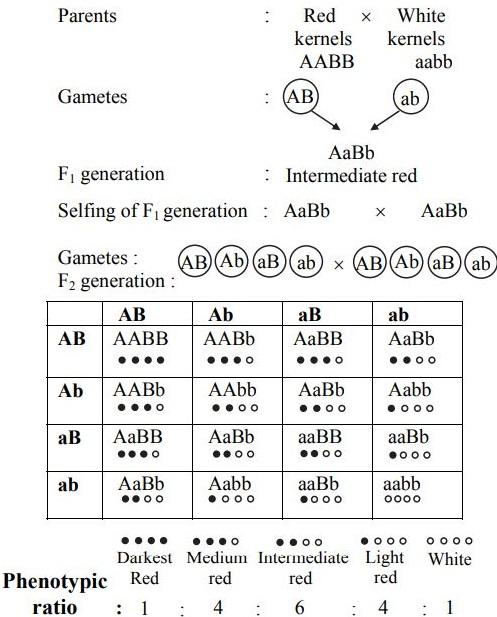
Complete answer:A "polygenic” is a member of a group of non-epistatic genes whose individual effect on a phenotype is too small to be observed but when it acts additively with other genes it can influence that phenotypic trait thus polygenic inheritance, also known as quantitative inheritance. In the above question two varieties of wheat plants are used, one wheat plant showing red kernels and another wheat plant showing white kernels.
As we know Kernel colour of wheat is determined by two pairs of genes i.e AA and BB (dominant) .
The red color of kernel is determined by genes A and B , these same two genes are dominant over their recessive alleles 'a' and 'b' . Each gene pair shows Mendelian segregation. After crossing the two plants it is observed that F1 generation is uniformly red but intermediate between red and white of parental generations. When F1 plants were self-crossed, five different types of phenotypes were obtained in the F2 generation and the ratio is described as 1:4:6:4:1.
As shown in the punnett's table below, the phenotypic ratio for F2 generation is '1 : 4 : 6 : 4 : 1'.
Note:In humans some the physical traits that are controlled by polygenic inheritance, includes hair color, height and skin color, as well as the non-visible traits such as blood pressure, intelligence etc
Polygenic inheritance, also known as quantitative inheritance can be defined as a phenomenon where a single inherited phenotypic trait is controlled by two or more different genes.
Complete answer:A "polygenic” is a member of a group of non-epistatic genes whose individual effect on a phenotype is too small to be observed but when it acts additively with other genes it can influence that phenotypic trait thus polygenic inheritance, also known as quantitative inheritance. In the above question two varieties of wheat plants are used, one wheat plant showing red kernels and another wheat plant showing white kernels.
As we know Kernel colour of wheat is determined by two pairs of genes i.e AA and BB (dominant) .
The red color of kernel is determined by genes A and B , these same two genes are dominant over their recessive alleles 'a' and 'b' . Each gene pair shows Mendelian segregation. After crossing the two plants it is observed that F1 generation is uniformly red but intermediate between red and white of parental generations. When F1 plants were self-crossed, five different types of phenotypes were obtained in the F2 generation and the ratio is described as 1:4:6:4:1.
As shown in the punnett's table below, the phenotypic ratio for F2 generation is '1 : 4 : 6 : 4 : 1'.
Note:In humans some the physical traits that are controlled by polygenic inheritance, includes hair color, height and skin color, as well as the non-visible traits such as blood pressure, intelligence etc

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




