
a) What are the characteristics of an image formed by a plane mirror?
(b) By giving sign conventions made, derive the mirror formula for a concave mirror.
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: Draw the correct ray diagram for both the problems and determine the nature of the image. Find the relative position, shape, and direction of the image. For finding the concave mirror formula, find the similar triangles and compare the sides. Use the appropriate sign conventions for the sides.
Complete step by step answer:
(A) Let’s look at the ray diagram for the plane mirror:
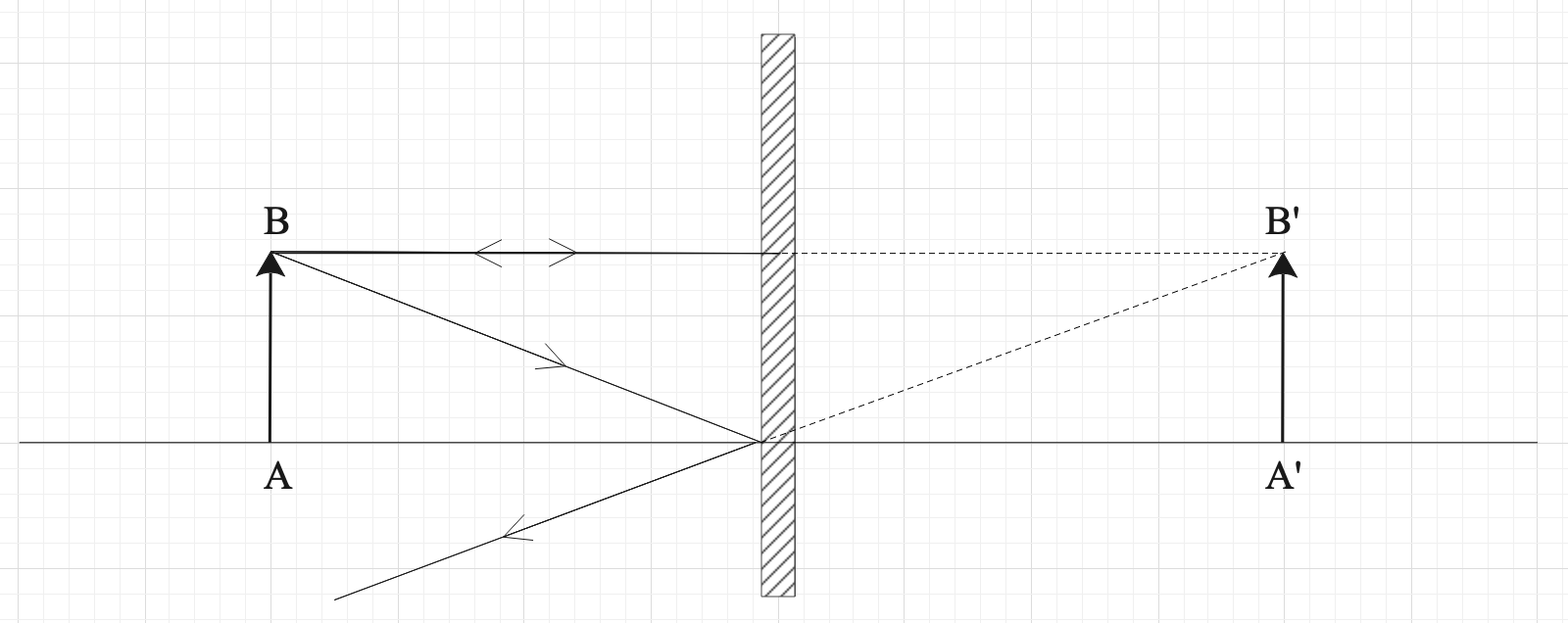
It is quite apparent from the ray diagram that the image produced by a plane mirror is erect, virtual, and has unit magnification.
It also has lateral inversion.
(B) We should start the derivation by drawing a clear ray diagram of the concave mirror.
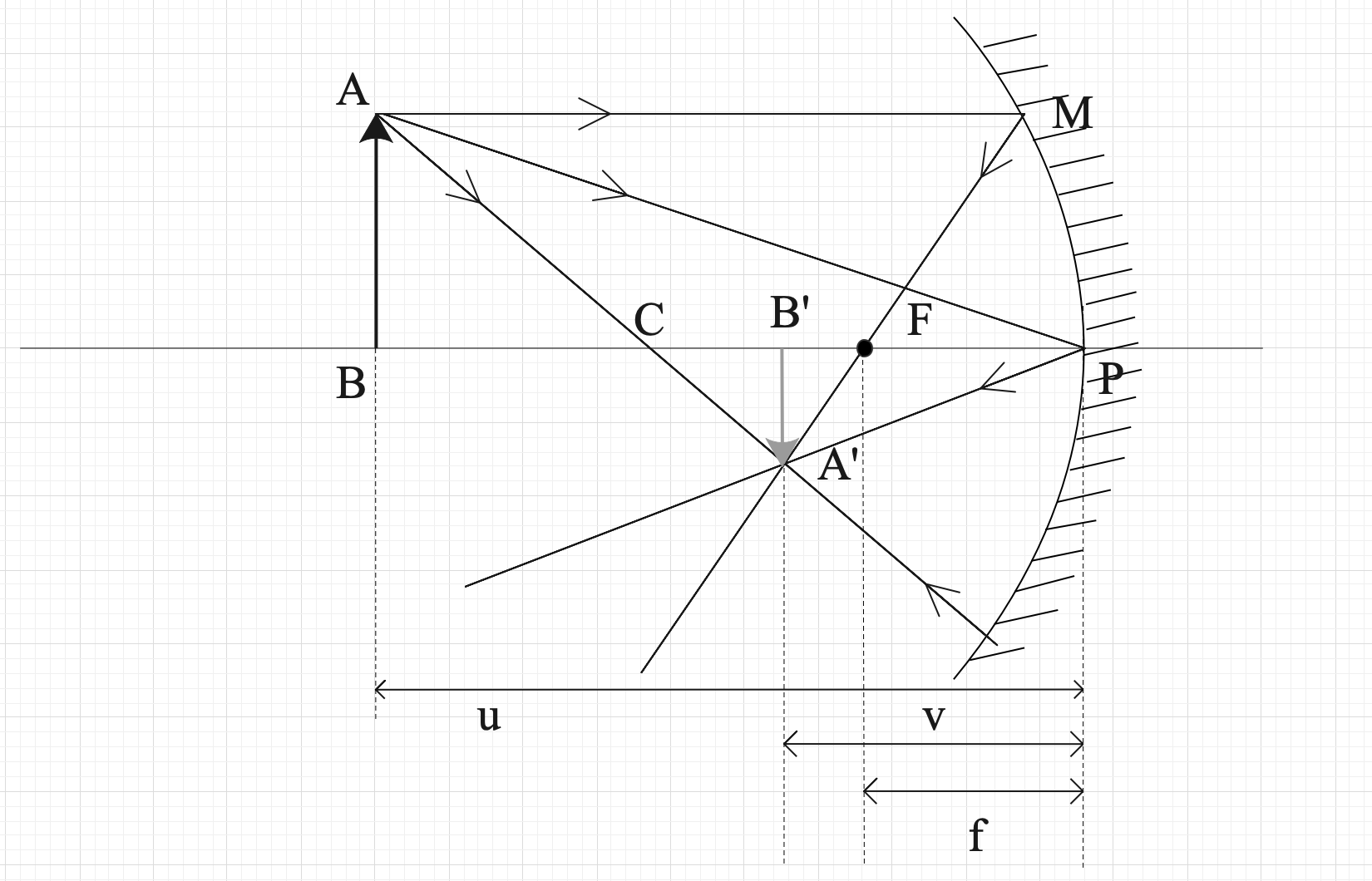
An object AB is kept at a distance of u from the pole of the concave mirror.
The image A’B’ is formed at a distance of v from the pole of the concave mirror.
The focal length of the concave mirror is at a distance of f from the concave mirror.
Sign Convention: Any point which is at the left of the pole of the concave mirror is considered to be negative.
So, we can write the following,
BP = -u, B’P=-v, and FP=-f
Now, we can proceed to the derivation,
For the paraxial ray, we can consider MP to be a straight line, and MPF is forming a right-angled triangle.
Hence, we can consider triangles A’B’F and MPF to be two similar right-angled triangles.
So, we can write,
$\dfrac{B'A'}{PM}=\dfrac{B'F}{FP}$ or, $\dfrac{B'A'}{BA}=\dfrac{B'F}{FP}$.........................(1)
ABP and A’B’P’ are also similar triangles, because,
$\angle APB=\angle A'PB'$
Hence, we can write,
$\dfrac{B'A'}{BA}=\dfrac{B'P}{BP}$.........................(2)
Comparing equation (1) and (2), we get,
$\dfrac{B'F}{FP}=\dfrac{B'P-FP}{FP}=\dfrac{B'P}{BP}$........................(3)
If we put the sign conversion, in the equation (3) we get,
$\dfrac{-v+f}{-f}=\dfrac{-v}{-u}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{v-f}{f}=\dfrac{v}{u}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
So, the mirror formula is,
$\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Note: You need to remember the sign convention that we have mentioned. It is very important that you follow a specific sign convention while solving optics problems. This will make sure that you don’t commit unnecessary mistakes.
If we follow the same procedure, we can find the same mirror formula for the convex mirror as well. However, we need to follow the sign conversion according to the convex mirror.
Complete step by step answer:
(A) Let’s look at the ray diagram for the plane mirror:

It is quite apparent from the ray diagram that the image produced by a plane mirror is erect, virtual, and has unit magnification.
It also has lateral inversion.
(B) We should start the derivation by drawing a clear ray diagram of the concave mirror.

An object AB is kept at a distance of u from the pole of the concave mirror.
The image A’B’ is formed at a distance of v from the pole of the concave mirror.
The focal length of the concave mirror is at a distance of f from the concave mirror.
Sign Convention: Any point which is at the left of the pole of the concave mirror is considered to be negative.
So, we can write the following,
BP = -u, B’P=-v, and FP=-f
Now, we can proceed to the derivation,
For the paraxial ray, we can consider MP to be a straight line, and MPF is forming a right-angled triangle.
Hence, we can consider triangles A’B’F and MPF to be two similar right-angled triangles.
So, we can write,
$\dfrac{B'A'}{PM}=\dfrac{B'F}{FP}$ or, $\dfrac{B'A'}{BA}=\dfrac{B'F}{FP}$.........................(1)
ABP and A’B’P’ are also similar triangles, because,
$\angle APB=\angle A'PB'$
Hence, we can write,
$\dfrac{B'A'}{BA}=\dfrac{B'P}{BP}$.........................(2)
Comparing equation (1) and (2), we get,
$\dfrac{B'F}{FP}=\dfrac{B'P-FP}{FP}=\dfrac{B'P}{BP}$........................(3)
If we put the sign conversion, in the equation (3) we get,
$\dfrac{-v+f}{-f}=\dfrac{-v}{-u}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{v-f}{f}=\dfrac{v}{u}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
So, the mirror formula is,
$\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Note: You need to remember the sign convention that we have mentioned. It is very important that you follow a specific sign convention while solving optics problems. This will make sure that you don’t commit unnecessary mistakes.
If we follow the same procedure, we can find the same mirror formula for the convex mirror as well. However, we need to follow the sign conversion according to the convex mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




